For superior esthetics, you should choose a high-translucency zirconia, often categorized as 4Y or 5Y zirconia. These modern formulations, sometimes called "anterior" or "esthetic" zirconia, contain a higher percentage of cubic-phase crystals, which allows for significantly more light transmission. This results in a restoration that more closely mimics the natural translucency of enamel, but it comes at the direct cost of reduced flexural strength compared to traditional, more opaque zirconia.
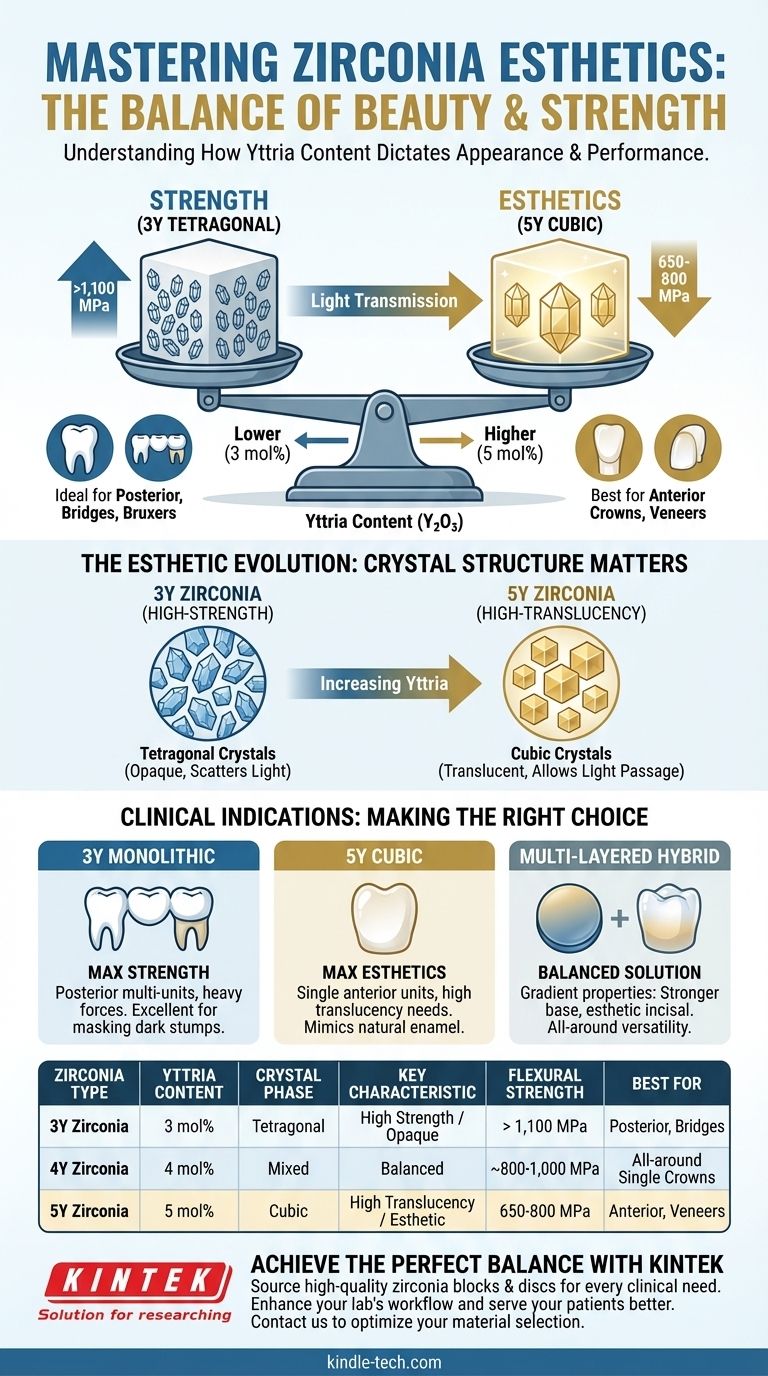
The core principle is a direct trade-off between strength and beauty. The chemical changes that make zirconia more translucent and esthetic also inherently reduce its mechanical strength. Your choice of material must therefore be dictated by the specific clinical demands of the restoration's location and function.
The Core Principle: How Yttria Content Dictates Appearance
Not all zirconia is created equal. The material's properties are fundamentally determined by the concentration of yttrium oxide (yttria), a stabilizing agent added during its manufacturing. This simple chemical difference creates two primary categories with vastly different visual and physical characteristics.
The Original: 3Y Zirconia (High-Strength Tetragonal)
The first generation of zirconia used in dentistry is 3Y-TZP (3 mol% yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal).
This material is primarily composed of very small, tightly packed tetragonal crystals. This dense crystal structure is exceptional at blocking crack propagation, giving 3Y zirconia its signature high flexural strength, often exceeding 1,100 MPa.
However, the numerous boundaries between these small crystals scatter light extensively, making the material highly opaque. While excellent for masking dark underlying tooth structure, this opacity can lead to a less-than-natural, "chalky" appearance.
The Esthetic Evolution: 4Y & 5Y Zirconia (High-Translucency Cubic)
To solve the esthetic problem, manufacturers increased the yttria content to create 4Y and 5Y zirconia (containing 4 and 5 mol% yttria, respectively).
Increasing the yttria content forces a significant portion of the crystals to form in the cubic phase. Cubic crystals are larger and more symmetrical than tetragonal crystals.
This structure allows light to pass through the material with far less scattering. The result is a much higher translucency, which is the key to achieving a lifelike restoration that blends seamlessly with adjacent natural teeth.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Strength vs. Esthetics
Choosing between zirconia types is not about finding the "best" one, but the "right" one for the job. The decision hinges on understanding the non-negotiable compromise between optical properties and mechanical durability.
Flexural Strength: The Critical Compromise
The same cubic crystal phase that makes 5Y zirconia beautiful also makes it weaker. The cubic structure is not as effective at resisting cracks as the tightly packed tetragonal structure.
A typical 5Y cubic zirconia has a flexural strength in the range of 650-800 MPa. While this is still significantly stronger than lithium disilicate, it is a substantial reduction from the 1,100+ MPa strength of traditional 3Y zirconia.
Clinical Indications: Where Each Type Shines
This strength difference directly informs clinical application.
- 3Y Zirconia (High Strength): The ideal choice for posterior crowns and long-span bridges, especially for patients with grinding habits (bruxism). Its opacity is also an advantage for masking dark prepared teeth or metal posts.
- 5Y Zirconia (High Translucency): Best suited for single anterior crowns and veneers where esthetic demands are paramount and biting forces are lower. It allows for beautiful, vital-looking restorations without the need for a porcelain overlay.
The Modern Hybrid: Multi-Layered Zirconia
To bridge this gap, manufacturers developed multi-layered zirconia discs. These discs are engineered with a gradient of properties.
The cervical (gumline) portion of the disc is composed of a stronger, more opaque zirconia (like 4Y), while the body and incisal portions are made from a more translucent, esthetic zirconia (like 5Y). This provides strength where it's needed most while delivering optimal esthetics where it's most visible.
Making the Right Choice for Your Patient
Your material selection should be a deliberate decision based on the restoration's specific requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and durability: Choose a monolithic 3Y (tetragonal) zirconia, especially for posterior multi-unit bridges or patients with heavy occlusal forces.
- If your primary focus is the highest level of esthetics: Choose a 5Y (cubic) zirconia for single anterior units where achieving natural translucency is the top priority.
- If you need a balanced "all-around" solution: Consider a multi-layered zirconia disc, which intelligently combines strength at the base with esthetics at the visible surface.
By understanding the material science, you can confidently select the ideal zirconia to meet the specific functional and esthetic demands of every case.
Summary Table:
| Zirconia Type | Yttria Content | Crystal Phase | Key Characteristic | Flexural Strength | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3Y Zirconia | 3 mol% | Tetragonal | High Strength / Opaque | > 1,100 MPa | Posterior crowns, bridges, bruxers |
| 4Y Zirconia | 4 mol% | Mixed (Tetragonal/Cubic) | Balanced Strength & Esthetics | ~800-1,000 MPa | All-around single crowns |
| 5Y Zirconia | 5 mol% | Cubic | High Translucency / Esthetic | 650-800 MPa | Anterior crowns, veneers |
Achieve the perfect balance of strength and esthetics for your dental restorations.
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality dental lab equipment and materials, including the full range of zirconia blocks and discs. Whether you're crafting ultra-strong posterior bridges or highly translucent anterior crowns, having the right materials is crucial for success.
Let KINTEK support your lab's needs:
- Source the ideal zirconia for every clinical case, from 3Y to multi-layered discs.
- Enhance your workflow with reliable equipment designed for precision and efficiency.
- Serve your patients better with restorations that meet the highest standards of both function and beauty.
Ready to optimize your material selection? Contact our dental lab specialists today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK can be your trusted partner in dental ceramics.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- KF ISO Stainless Steel Vacuum Flange Blind Plate for High Vacuum Systems
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the effect of zirconia sintering temperature? Master the Key to Strength and Stability
- What are the white spots on zirconia after sintering? A Guide to Diagnosing and Preventing Defects
- What is the price of zirconia sintering furnace? Invest in Precision, Not Just a Price Tag
- What is the sintering temperature of zirconium? A Guide to the 1400°C-1600°C Range for Dental Labs
- What is the temperature of sintering zirconia? Mastering the Protocol for Perfect Dental Restorations



