X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) is a cornerstone of elemental analysis, utilized wherever a rapid, accurate, and non-destructive understanding of a material's composition is required. It's a foundational technology in industries ranging from manufacturing and environmental safety to mining and art conservation, providing on-the-spot answers about the elemental makeup of a substance.
The core value of XRF is its unique ability to provide immediate, on-site elemental data without harming the sample. This combination of speed and non-destructive analysis makes it the essential tool for quality control, safety screening, and field research where quick, informed decisions are paramount.

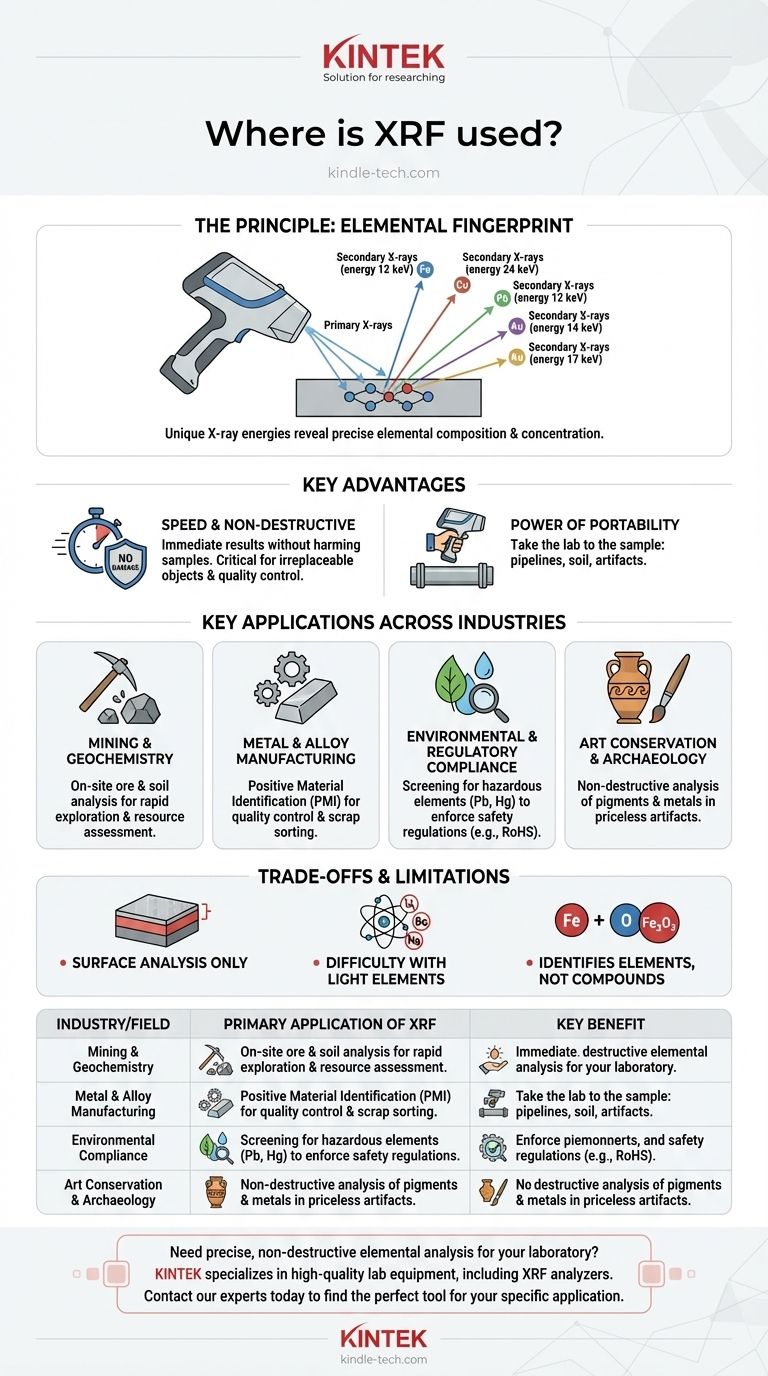
The Principle That Drives Its Wide Adoption
XRF's versatility stems from a simple and powerful working principle. This principle grants it key advantages that are critical for countless real-world applications.
How It Works: An Elemental Fingerprint
An XRF analyzer bombards a material with a primary X-ray beam. This energy causes atoms within the sample to emit secondary, "fluorescent" X-rays.
Each element emits these secondary X-rays at a unique and predictable energy level. The analyzer measures these energies to identify precisely which elements are present and in what concentration.
The Key Advantage: Speed and Non-Destructive Analysis
The most significant benefit of XRF is that it does not damage or alter the sample being tested. This is absolutely critical when analyzing irreplaceable artifacts, critical components, or consumer goods.
Furthermore, the analysis is exceptionally fast, often providing a detailed elemental breakdown in just a few seconds.
The Power of Portability
Modern XRF analyzers are often handheld, resembling a "ray gun" tool. This portability allows operators to take the lab directly to the sample, whether it's a pipeline in a refinery, a patch of soil in a field, or a toy on a store shelf.
Key Applications Across Industries
The combination of speed, safety, and portability has made XRF an indispensable tool for verification, inspection, and research across many sectors.
Mining and Geochemistry
In mineral exploration, portable XRF analyzers are used directly in the field to assess the composition of rocks, ores, and soil. This allows for immediate decisions on where to focus drilling and excavation efforts, saving immense time and resources.
Metal and Alloy Manufacturing
XRF is the backbone of Positive Material Identification (PMI). Fabricators and manufacturers use it to verify the grade of incoming metal alloys and to confirm that finished components meet precise engineering specifications. It's also used to rapidly sort scrap metal for recycling.
Environmental and Regulatory Compliance
Authorities use XRF to screen for hazardous heavy metals like lead, mercury, and arsenic in soil, water filters, and consumer products. It is a primary tool for enforcing regulations like the Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) directive in electronics.
Art Conservation and Archaeology
Because it is non-destructive, XRF is perfect for analyzing priceless cultural artifacts. It can identify the elemental composition of pigments in a painting or the exact metal makeup of an ancient coin without leaving a single mark.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, XRF is not the right tool for every analytical task. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Primarily a Surface Analysis Technique
XRF can only analyze the top layer of a material. If a component is plated, coated, or corroded, the analysis will only reflect the surface and not the bulk material underneath.
Difficulty with Light Elements
Standard XRF analyzers struggle to detect very light elements (those with low atomic numbers). Elements like lithium, beryllium, and sodium are typically invisible to most portable XRF devices.
It Identifies Elements, Not Compounds
XRF tells you what elements are present, but not how they are chemically bonded. For example, it can identify the presence of iron (Fe) and oxygen (O) but cannot distinguish between different iron oxides like rust.
Is XRF the Right Tool for Your Goal?
Choosing the right analytical method depends entirely on the question you need to answer.
- If your primary focus is rapid quality control or sorting: XRF is ideal for verifying alloy grades, screening materials on a production line, or sorting scrap.
- If your primary focus is field-based environmental or geological assessment: A portable XRF analyzer provides immediate, actionable data without needing to send samples to a lab.
- If your primary focus is analyzing precious or unique objects: The non-destructive nature of XRF makes it the perfect choice for art, archaeology, and forensics.
- If your primary focus is detecting very light elements or determining molecular structures: You will need to consider alternative analytical methods beyond XRF.
Ultimately, XRF excels wherever fast, non-destructive elemental identification is the critical requirement for making an informed decision.
Summary Table:
| Industry/Field | Primary Application of XRF | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Mining & Geochemistry | On-site analysis of ores and soil | Rapid exploration & resource assessment |
| Metal & Alloy Manufacturing | Positive Material Identification (PMI) | Quality control & scrap sorting |
| Environmental Compliance | Screening for hazardous elements (e.g., lead, mercury) | Enforce safety regulations (e.g., RoHS) |
| Art Conservation & Archaeology | Analyzing pigments and metals in artifacts | Non-destructive analysis of priceless objects |
Need precise, non-destructive elemental analysis for your laboratory?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment, including XRF analyzers, to meet the diverse needs of laboratories in manufacturing, research, and quality control. Our solutions deliver the speed and accuracy you need for critical decisions in material verification, environmental screening, and more.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect analytical tool for your specific application and enhance your lab's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Tweezers
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Customizable PTFE Wafer Carriers for Semiconductor and Lab Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the specifications for test sieves? A Guide to ASTM & ISO Standards for Accurate Particle Analysis
- What is the function of sieving equipment in CuAlMn alloys? Master Pore Size Precision
- How is a vibratory sieve shaker used in the particle size analysis of mechanically alloyed powders? Expert Guide
- Why is sieve analysis important? Ensure Consistent Quality and Performance of Your Materials
- What is the primary function of a mechanical sieve shaker for biomass analysis? Optimize Particle Size Distribution


















