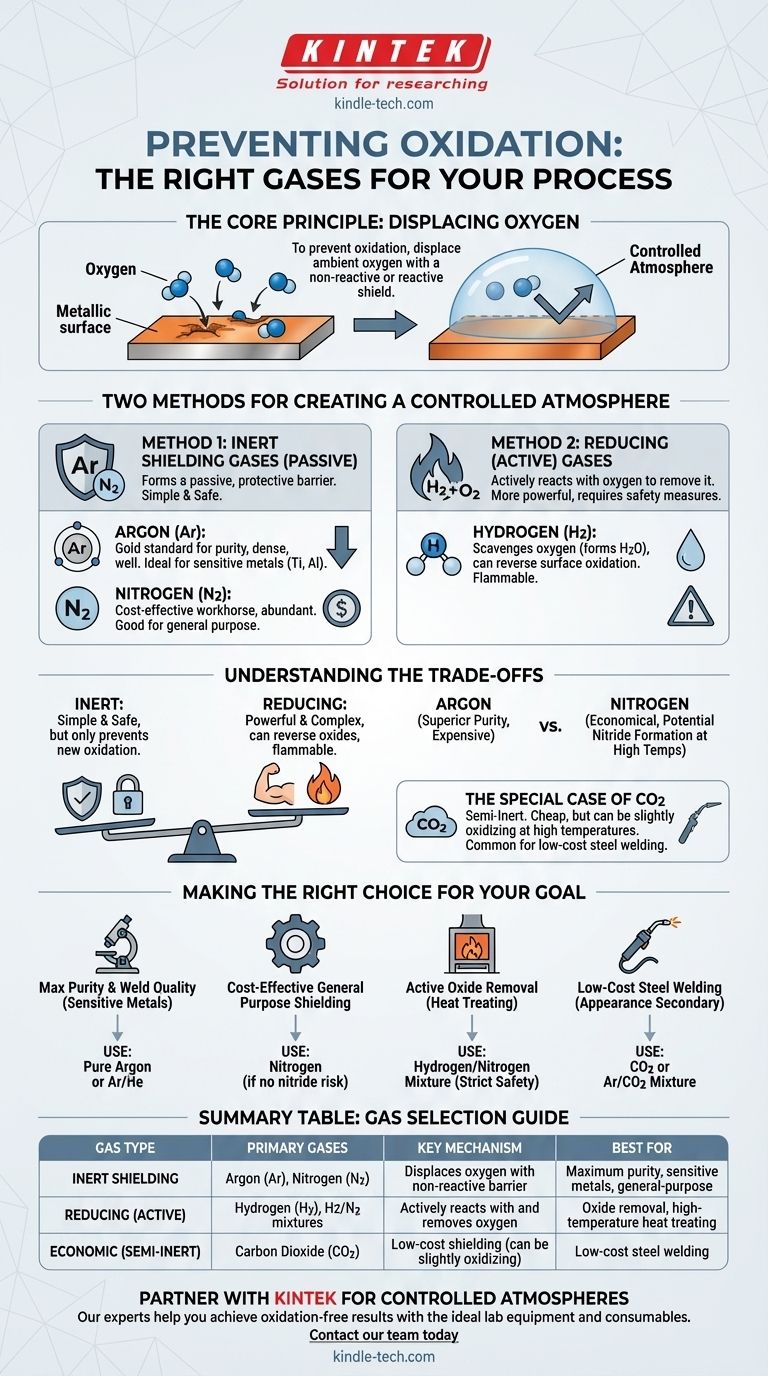
To prevent oxidation, you must use a gas that displaces ambient oxygen from the work area. The most common choices are inert gases like Argon (Ar) and Nitrogen (N2), which create a non-reactive shield. In some high-temperature industrial processes, reducing gases like Hydrogen (H2) or hydrogen-based mixtures are also used to actively remove oxygen.
The core principle is not merely to find a single "anti-oxidation gas," but to control the atmosphere around your material. This is achieved either by passively shielding the part with an inert gas or by actively scrubbing the environment with a reactive, reducing gas.
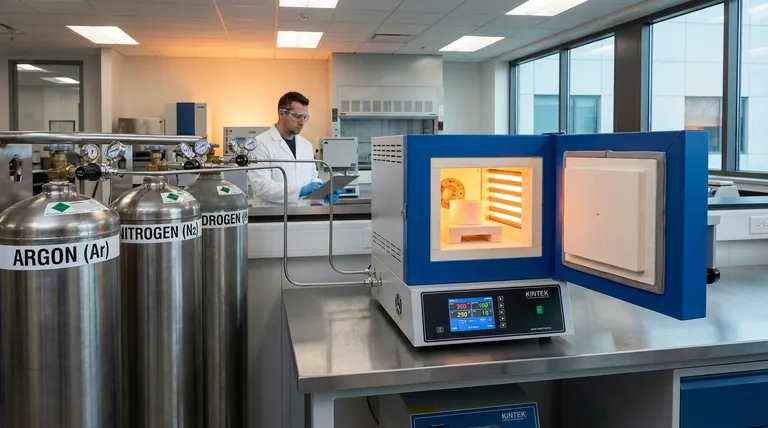

The Core Principle: Displacing Oxygen
Oxidation is a chemical reaction between a material and oxygen, often accelerated by heat. This process can degrade the material's properties, appearance, and structural integrity.
To stop this reaction, you must remove one of the key ingredients: oxygen. Shielding or purging gases accomplish this by physically pushing the ambient air (which is ~21% oxygen) away from the material's surface, creating a controlled atmosphere.
Two Methods for Creating a Controlled Atmosphere
There are two primary strategies for preventing oxidation, each using different types of gases that work on distinct principles.
Method 1: Inert Shielding Gases
Inert gases are chemically stable and do not readily react with other elements, even at high temperatures. They work by forming a passive, protective barrier.
The two most common inert shielding gases are:
- Argon (Ar): This is the gold standard for high-purity applications. Because it is denser than air, it effectively blankets a work area, providing excellent coverage. It is completely inert and will not react with any material, making it ideal for sensitive metals like titanium, aluminum, and stainless steel.
- Nitrogen (N2): Nitrogen is the cost-effective workhorse. It makes up 78% of the air we breathe and is much cheaper to produce than argon. It works well for many general-purpose applications.
Method 2: Reducing (or Active) Gases
Reducing gases work more actively. Instead of just blocking oxygen, they react with any oxygen present (and even with existing oxides on the material's surface) to remove it.
The primary reducing gas is:
- Hydrogen (H2): Hydrogen is extremely effective at scavenging oxygen, reacting with it to form water vapor (H₂O). This "reducing" atmosphere can not only prevent oxidation but can also clean a part by reversing light surface oxidation. It is often used in mixtures, such as with nitrogen in the form of dissociated ammonia, for furnace brazing and heat treating.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right gas requires balancing performance, cost, and safety.
Inert vs. Reducing
The main trade-off here is simplicity versus power. Inert gases are simple and safe (non-flammable), but they only prevent new oxidation from forming.
Reducing gases like hydrogen are more powerful and can reverse existing oxides, but they are flammable and require more complex handling and safety systems.
Argon vs. Nitrogen
Argon provides superior protection due to its density and complete inertness, but it is significantly more expensive.
Nitrogen is highly economical but has one key limitation: at very high temperatures, it can react with certain metals (like titanium and some grades of stainless steel) to form undesirable nitrides, which can make the material brittle.
The Special Case of Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
Carbon dioxide is often used in welding and is sometimes referred to as an inert gas, but this is not technically correct.
At the high temperatures of a welding arc, CO2 can break down into carbon monoxide and oxygen, leading to a more reactive and slightly oxidizing atmosphere compared to true inert gases. It is very cheap but offers lower-quality protection than an argon-based mixture.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's specific requirements will determine the best atmospheric gas.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity and weld quality on sensitive metals: Use pure Argon or a high-purity Argon/Helium mixture.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, general-purpose shielding: Nitrogen is an excellent choice, provided your material and process temperatures are not susceptible to nitride formation.
- If your primary focus is active oxide removal during furnace heat treating: A Hydrogen/Nitrogen mixture is the industrial standard, but it demands strict safety protocols.
- If your primary focus is low-cost steel welding where appearance is secondary: A CO2 or Argon/CO2 mixture is a common economic choice.
Ultimately, selecting the right gas is about matching the chemical properties of the atmosphere to the needs of your material and process.
Summary Table:
| Gas Type | Primary Gases | Key Mechanism | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inert Shielding | Argon (Ar), Nitrogen (N2) | Displaces oxygen with a non-reactive barrier | Maximum purity, sensitive metals, general-purpose use |
| Reducing (Active) | Hydrogen (H2), H2/N2 mixtures | Actively reacts with and removes oxygen | Oxide removal, high-temperature heat treating |
| Economic (Semi-Inert) | Carbon Dioxide (CO2) | Low-cost shielding (can be slightly oxidizing at high temps) | Low-cost steel welding |
Need to select the perfect gas for your application? KINTEK specializes in providing the ideal lab equipment and consumables to create controlled atmospheres for your specific materials and processes. Whether you require high-purity inert gases for sensitive work or robust systems for active reducing atmospheres, our experts can help you achieve oxidation-free results. Contact our team today to discuss your needs and enhance your lab's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of using an atmosphere-controlled heating furnace for Cu reduction? Achieve Active Catalytic States
- What provides an inert atmosphere? Achieve Safety and Purity with Nitrogen, Argon, or CO2
- Can nitrogen be used for brazing? Key Conditions and Applications Explained
- What is an example of an inert atmosphere? Discover the Best Gas for Your Process
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes



















