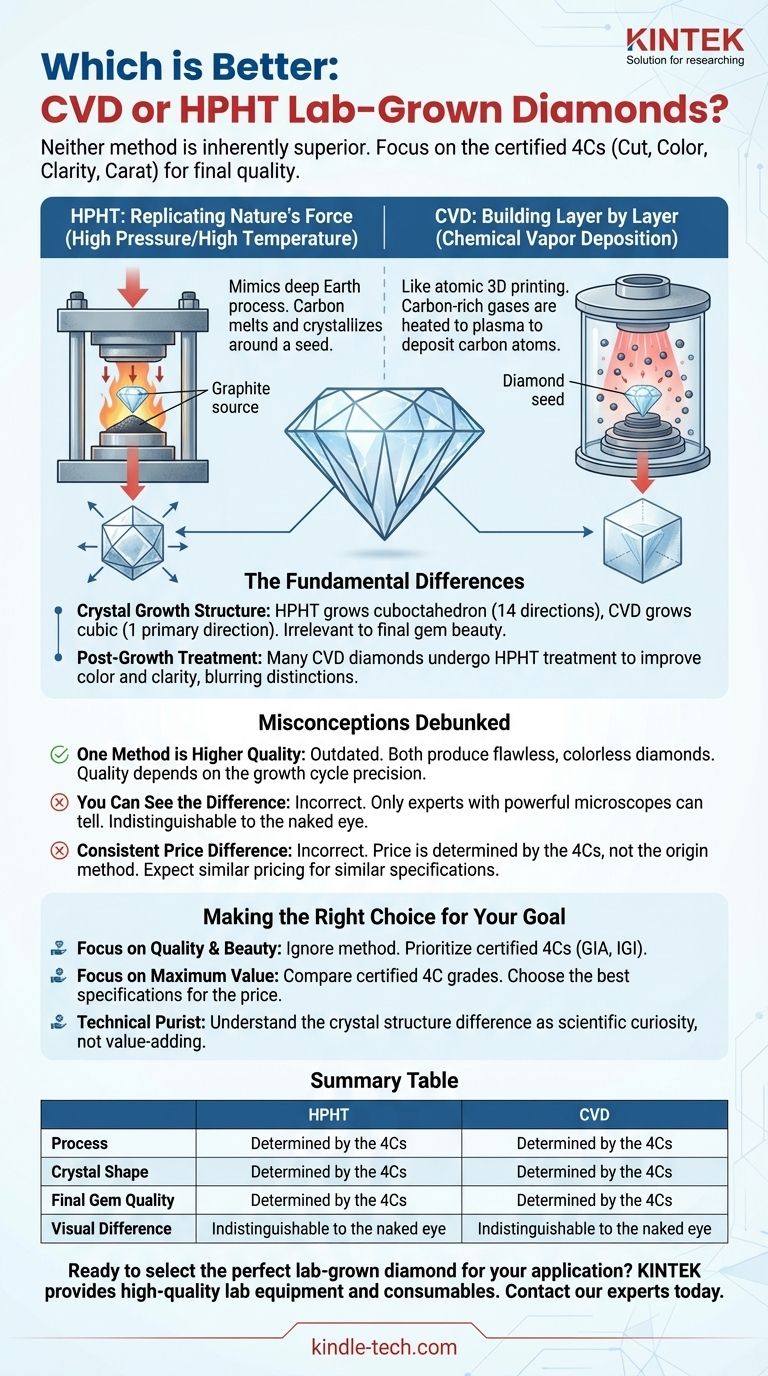
Neither method is inherently superior. In today's market, both HPHT and CVD processes produce high-quality, visually stunning diamonds that are indistinguishable from one another to the naked eye. The final quality of the stone, as detailed in its official certification, is far more important than the specific method used to grow it.
The distinction between HPHT and CVD is now primarily a technical one relevant to gemologists. For the buyer, the focus should be on the diamond's certified 4Cs (cut, color, clarity, and carat), as both methods produce physically and chemically real diamonds of exceptional quality.

The Two Paths to a Lab-Grown Diamond
Understanding the two creation methods helps clarify why the end products are so similar. Both start with a tiny diamond "seed" but use fundamentally different processes to grow it.
HPHT: Replicating Nature's Force
HPHT stands for High Pressure/High Temperature. This method mimics the natural diamond-growing process found deep within the Earth.
A diamond seed is placed in a large mechanical press along with a carbon source, like graphite. It is then subjected to immense pressure and extremely high temperatures, causing the carbon to melt and crystallize around the seed, forming a new, larger diamond.
CVD: Building Diamond Layer by Layer
CVD stands for Chemical Vapor Deposition. This method builds a diamond in a way that can be compared to 3D printing on an atomic level.
A diamond seed is placed in a vacuum chamber filled with carbon-rich gases (like methane). These gases are heated to a plasma state, which causes the carbon atoms to separate and deposit onto the diamond seed, building the diamond layer by layer.
How They Fundamentally Differ
While the finished gems are visually identical, the underlying growth process creates subtle differences that a trained expert can identify under magnification.
Crystal Growth Structure
The most significant technical difference is the shape of their crystal growth. HPHT diamonds grow in a cuboctahedron shape with 14 distinct growth directions. In contrast, CVD diamonds grow in a cubic shape with only one primary growth direction.
This structural difference has no impact on the diamond's beauty, brilliance, or durability once it has been cut and polished.
The Post-Growth Treatment Reality
A critical point is that many CVD diamonds undergo an HPHT treatment after they are grown. This additional step is used to improve the diamond's color and clarity, effectively erasing any subtle visual distinctions.
This common practice blurs the lines between the two methods, making the initial growth process less relevant to the final quality of the gem you purchase.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Misconceptions
When choosing a lab-grown diamond, it's easy to get lost in technical details that have little practical impact. It's more important to focus on what truly matters.
Misconception 1: One Method is "Higher Quality"
This is outdated information. While early HPHT diamonds sometimes had a yellowish tint, modern advancements allow both methods to produce flawless, colorless diamonds. The quality is determined by the precision of the specific growth cycle, not the method itself.
Misconception 2: You Can See the Difference
An expert with a powerful microscope can identify the growth method by analyzing the diamond's internal structure. However, to the naked eye, a top-grade CVD diamond and a top-grade HPHT diamond are absolutely identical.
Misconception 3: There is a Consistent Price Difference
The price of a lab-grown diamond is determined by its 4Cs, not its origin method. A D-color, VVS1-clarity diamond will be priced based on those specifications, regardless of whether it was created via HPHT or CVD. You should not expect to pay more or less based on the growth technique alone.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should not be about choosing a superior technology, but about selecting the best diamond for your needs based on its certified merits.
- If your primary focus is quality and beauty: Ignore the growth method entirely. Concentrate solely on the diamond's official grading report (from an institution like GIA or IGI) and select the best cut, color, and clarity within your budget.
- If your primary focus is maximum value: Compare the prices of certified diamonds with similar 4C grades. Choose the stone that offers the best specifications for the price, regardless of whether it is labeled HPHT or CVD.
- If you are a technical purist: You might find the unique crystal structure of one method more interesting than the other, but recognize this is a scientific curiosity with no bearing on the gem's appearance or worth.
Ultimately, you are choosing a specific diamond, not a manufacturing process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | HPHT Diamond | CVD Diamond |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Mimics natural conditions (High Pressure/High Temperature) | Builds diamond layer-by-layer in a vacuum chamber |
| Crystal Shape | Cuboctahedron (14 growth directions) | Cubic (1 primary growth direction) |
| Final Gem Quality | Determined by the 4Cs (Cut, Color, Clarity, Carat) | Determined by the 4Cs (Cut, Color, Clarity, Carat) |
| Visual Difference | Indistinguishable to the naked eye | Indistinguishable to the naked eye |
Ready to select the perfect lab-grown diamond for your application?
Whether your laboratory requires materials for research, industrial abrasives, or high-precision components, the certified quality of the diamond is paramount. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables. Our expertise ensures you get the right materials for your specific laboratory needs.
Let us help you make an informed decision. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your project with the right solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- How is something diamond coated? A Guide to CVD Growth vs. Plating Methods
- What is the specific function of the metal filament in HF-CVD? Key Roles in Diamond Growth
- What machine is used to make lab-grown diamonds? Discover the HPHT & CVD Technologies
- How are reactants introduced into the reaction chamber during a CVD process? Mastering Precursor Delivery Systems
- How does PACVD equipment improve DLC coatings? Unlock Low Friction and High Heat Resistance



















