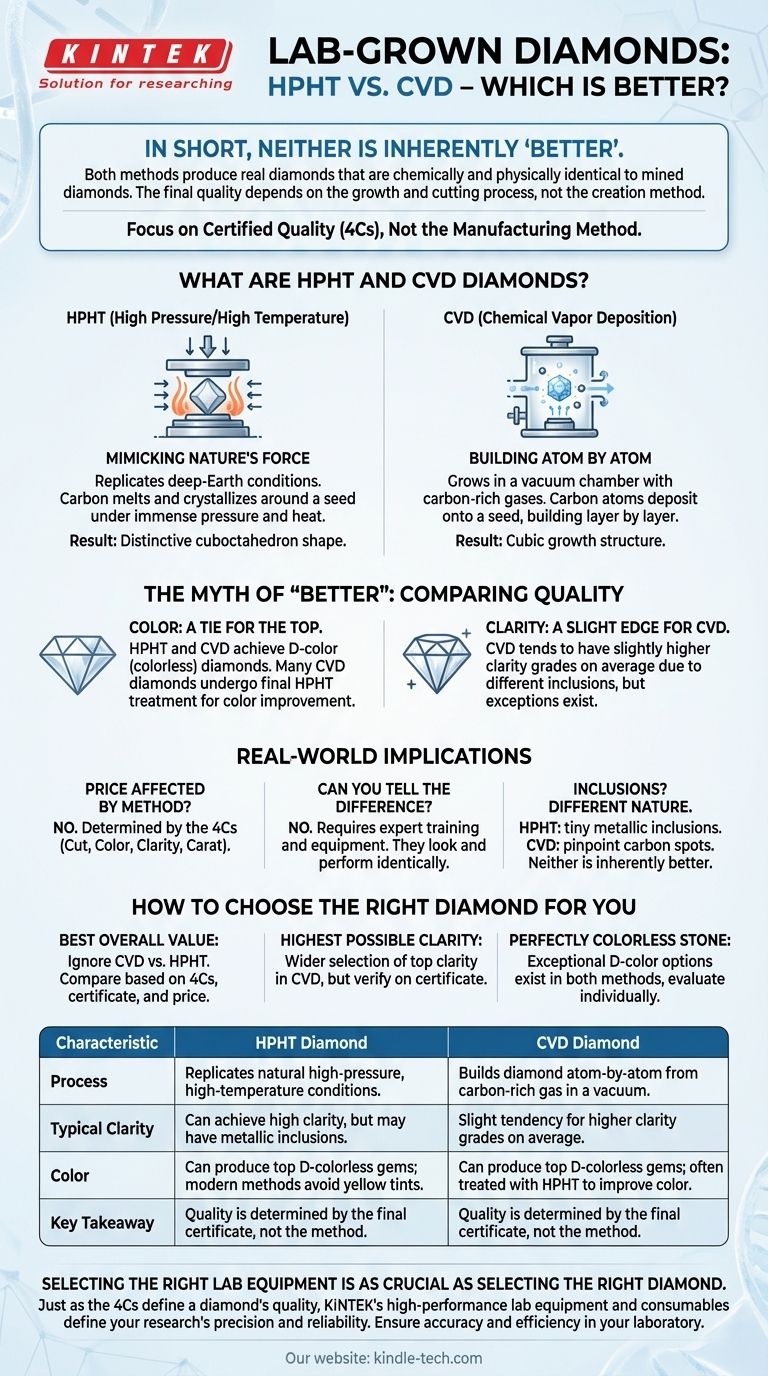
In short, neither HPHT nor CVD is an inherently "better" method for creating a lab-grown diamond. Both processes produce real diamonds that are physically and chemically identical to mined diamonds, and both can yield flawless, colorless gems. The final quality of the stone is determined by the specific outcome of its growth and cutting process, not the method of its creation.
The debate over HPHT versus CVD is largely a distraction for the end consumer. Your focus should not be on the manufacturing method, but on the diamond's certified quality—its Cut, Color, Clarity, and Carat weight—which is the true measure of its value and beauty.

What Are HPHT and CVD Diamonds?
HPHT and CVD are the two primary methods used to grow diamonds in a laboratory. The end product is a diamond in either case, but the journey from a carbon source to a crystal is fundamentally different.
HPHT: Mimicking Nature's Force
The High Pressure/High Temperature (HPHT) method replicates the natural conditions under which diamonds form deep within the Earth.
A small diamond seed is placed in a chamber with pure carbon. This chamber is then subjected to immense pressure and extreme heat, causing the carbon to melt and crystallize around the seed, forming a new, larger diamond. The crystal grows outwards in multiple directions, creating a distinctive cuboctahedron shape.
CVD: Building a Diamond Atom by Atom
The Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) method grows a diamond in a completely different environment.
A diamond seed is placed in a vacuum chamber filled with carbon-rich gases, like methane. These gases are heated, breaking down their molecular bonds and allowing carbon atoms to "rain" down and deposit onto the diamond seed, building the crystal layer by layer. This process results in a cubic growth structure.
The Myth of "Better": Comparing Quality Characteristics
While gemologists can identify the origin method through magnification, these differences are not visible to the naked eye. For a buyer, the only thing that matters is the final result as graded on a certificate.
Color: A Tie for the Top
Both HPHT and CVD methods can produce the highest D-color (colorless) diamonds. While HPHT diamonds were historically associated with yellowish tints, modern advancements mean they now consistently produce high-color gems.
Interestingly, many CVD diamonds undergo a final HPHT treatment to improve their color, blurring the lines between the two methods.
Clarity: A Slight Edge for CVD
On average, CVD diamonds tend to achieve slightly higher clarity grades. This is due to the different types of inclusions that can form during the growth process.
However, this is only an average tendency. It is entirely possible to find an HPHT diamond with higher clarity than a CVD diamond. The final clarity grade on the certificate is the only reliable guide.
Understanding the Real-World Implications
When purchasing a diamond, the technical details of its origin are far less important than its certified performance and appearance.
Does the Method Affect the Price?
No. The wholesale price and retail value of a lab-grown diamond are determined by its 4Cs (Cut, Color, Clarity, Carat), not its growth method. An F-color, VS1-clarity HPHT diamond will be priced similarly to an F-color, VS1-clarity CVD diamond of the same carat and cut quality.
Can You Tell the Difference?
No. Without a gemological microscope and expert training, you cannot distinguish between an HPHT and a CVD diamond. They look and perform identically. The choice between them has no bearing on the diamond's brilliance, fire, or durability.
What About Inclusions?
Both methods can create inclusions, but their nature differs. HPHT diamonds may have tiny metallic inclusions from the growth press, while CVD diamonds may have pinpoint carbon spots. Neither type is inherently better or worse; their impact is measured solely by the diamond's official clarity grade.
How to Choose the Right Diamond for You
Instead of focusing on the manufacturing process, concentrate on the tangible results you can see and verify.
- If your primary focus is getting the best overall value: Ignore whether it's CVD or HPHT and compare diamonds based solely on their 4Cs, certificate, and price.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible clarity: You may find a wider selection of top-clarity grades among CVD diamonds, but you must still verify this on the certificate.
- If your primary focus is finding a perfectly colorless stone: You will find exceptional D-color options created by both methods, so evaluate each diamond individually.
Ultimately, a beautiful, high-quality diamond is defined by its certified characteristics, not its origin story.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | HPHT Diamond | CVD Diamond |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Replicates natural high-pressure, high-temperature conditions. | Builds diamond atom-by-atom from carbon-rich gas in a vacuum. |
| Typical Clarity | Can achieve high clarity, but may have metallic inclusions. | Slight tendency for higher clarity grades on average. |
| Color | Can produce top D-colorless gems; modern methods avoid yellow tints. | Can produce top D-colorless gems; often treated with HPHT to improve color. |
| Key Takeaway | Quality is determined by the final certificate, not the method. | Quality is determined by the final certificate, not the method. |
Selecting the right lab equipment is as crucial as selecting the right diamond.
Just as the 4Cs define a diamond's quality, the precision and reliability of your lab equipment define the quality of your research and results. KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables to support your critical work, ensuring accuracy and efficiency in your laboratory.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory's unique needs and elevate your research to the next level.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What function does CVD equipment serve in rhodium-modified coatings? Achieve Deep Diffusion and Microstructural Precision
- How high of temperature do carbon nanotubes in air have the ability to sustain? Understanding the Oxidation Limit
- What are the advantages of industrial CVD for solid boriding? Superior Process Control and Material Integrity
- Why are carbon nanotubes important in industry? Unlocking Next-Generation Material Performance
- What is the floating catalyst method? A Guide to High-Yield CNT Production



















