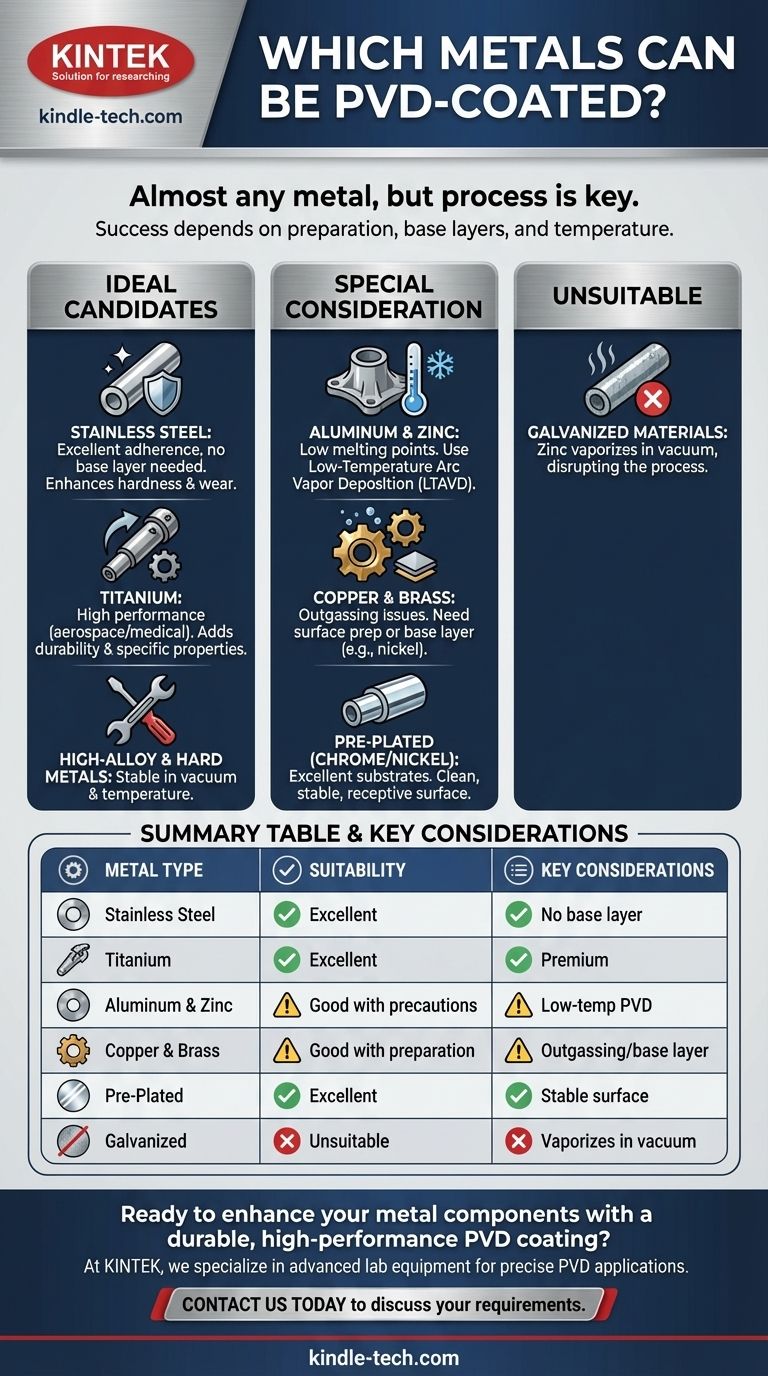
In short, almost any metal can be PVD-coated. The list of suitable materials is extensive, including all families of steel, titanium, aluminum, copper, and their alloys. Even previously chrome or nickel-plated products serve as excellent substrates for Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) coating.
The critical takeaway is not which metals can be coated, but how a specific metal's properties dictate the process. Success with PVD depends entirely on selecting the correct preparation, potential base layers, and coating temperature for the chosen metal substrate.

The Ideal Candidates for PVD Coating
Certain metals are inherently well-suited for the PVD process due to their stability and surface properties. These materials typically require less preparation and yield highly reliable results.
Stainless Steel: The Prime Example
Stainless steel is one of the most advantageous materials for PVD coating. Its surface provides excellent adherence for coating substances without the need for an intermediate layer.
Because it is already durable and corrosion-resistant, the PVD coating primarily enhances its surface hardness, wear resistance, and aesthetic appearance, making it an economically sound choice.
Titanium: For High-Performance Applications
Titanium is another popular choice, particularly in the aerospace and medical industries where high performance is non-negotiable.
Its inherent strength, low weight, and corrosion resistance make it a premium substrate. PVD coatings are used to further protect it from wear and to achieve specific surface properties or colors.
Other Well-Suited Metals
Materials like high-alloy steels, high-speed steels, and other hard metals are also excellent candidates. They are stable in the vacuum environment and at the temperatures required for standard PVD processes.
Coating Metals That Require Special Consideration
While most metals are compatible, some require specific techniques or preparatory steps to ensure a high-quality, durable coating. Ignoring these requirements is a common cause of failure.
Aluminum and Zinc: The Need for Low Temperatures
Substrates like aluminum and zinc castings have lower melting points and cannot withstand the heat of traditional PVD processes.
For these materials, a specialized technique called Low-Temperature Arc Vapor Deposition (LTAVD) is necessary to apply the coating without damaging or deforming the part.
Copper and Brass: The Importance of Preparation
Copper and brass can be successfully coated, but they are more challenging. These metals can release trace amounts of gas in the vacuum chamber, a process known as outgassing, which can interfere with coating adhesion.
Proper surface preparation or the application of a base layer, such as nickel, is often required to create a stable foundation for the PVD coating and prevent future corrosion.
Pre-Plated Surfaces (Chrome & Nickel)
Parts that have already been plated with chrome or nickel are excellent substrates for PVD. The plated layer provides a clean, stable, and highly receptive surface for the PVD coating to bond with.
Understanding the Pitfalls and Limitations
The primary challenges in PVD coating are not related to the metal itself, but to how it behaves under vacuum and heat. Understanding these limitations is key to avoiding costly errors.
The Problem of Outgassing
The PVD process takes place in a high-vacuum chamber. Some materials, particularly porous or untreated ones like raw brass, can trap atmospheric gases that are released under vacuum. This outgassing disrupts the coating process, leading to poor adhesion and defects.
Why Galvanized Materials Are Unsuitable
Galvanized materials are coated with a layer of zinc for corrosion protection. Zinc has a high vapor pressure, meaning it turns into a gas very easily inside a vacuum chamber. This makes galvanized parts fundamentally incompatible with the PVD process.
The Necessity of Base Layers
For certain metals, a PVD coating applied directly to the surface may not adhere well or provide sufficient corrosion resistance. In these cases, an intermediate base layer of nickel or chromium is applied first, adding a step and cost to the overall process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Your choice of metal substrate should be guided by your project's performance requirements, budget, and aesthetic goals.
- If your primary focus is simplicity and cost-effectiveness: Choose stainless steel, as it requires no base layer and provides an excellent, durable finish.
- If your primary focus is high performance and low weight: Use titanium, accepting that it is a premium material for demanding applications.
- If you are working with heat-sensitive metals like aluminum or zinc: Ensure your PVD provider uses a specialized low-temperature process to avoid damaging the part.
- If you plan to use copper or brass: Factor in the need for meticulous surface preparation and a potential base layer to ensure coating adhesion and long-term stability.
Ultimately, a successful PVD outcome begins with a well-informed choice of the metal underneath.
Summary Table:
| Metal Type | Suitability for PVD | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Excellent | No base layer needed; ideal for hardness & wear resistance. |
| Titanium | Excellent | Premium choice for aerospace/medical; enhances durability. |
| Aluminum & Zinc | Good (with precautions) | Requires low-temperature PVD (LTAVD) to avoid damage. |
| Copper & Brass | Good (with preparation) | Prone to outgassing; may need a nickel base layer. |
| Pre-Plated (Chrome/Nickel) | Excellent | Stable surface; minimal preparation required. |
| Galvanized Materials | Unsuitable | Zinc vaporizes in vacuum, disrupting the coating process. |
Ready to enhance your metal components with a durable, high-performance PVD coating?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables for precise PVD applications. Whether you're working with stainless steel, titanium, or heat-sensitive metals like aluminum, our expertise ensures optimal coating adhesion, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic results.
Let us help you select the right substrate and process for your project's needs. Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and achieve superior surface performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
People Also Ask
- How do you calculate coating coverage? A Practical Guide to Accurate Material Estimation
- How do CVD diamonds grow? A Step-by-Step Guide to Lab-Grown Diamond Creation
- What is microwave plasma CVD? A Guide to High-Purity Diamond and Material Synthesis
- What is direct current DC magnetron sputtering? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the hot filament chemical vapour deposition of diamond? A Guide to Synthetic Diamond Coating



















