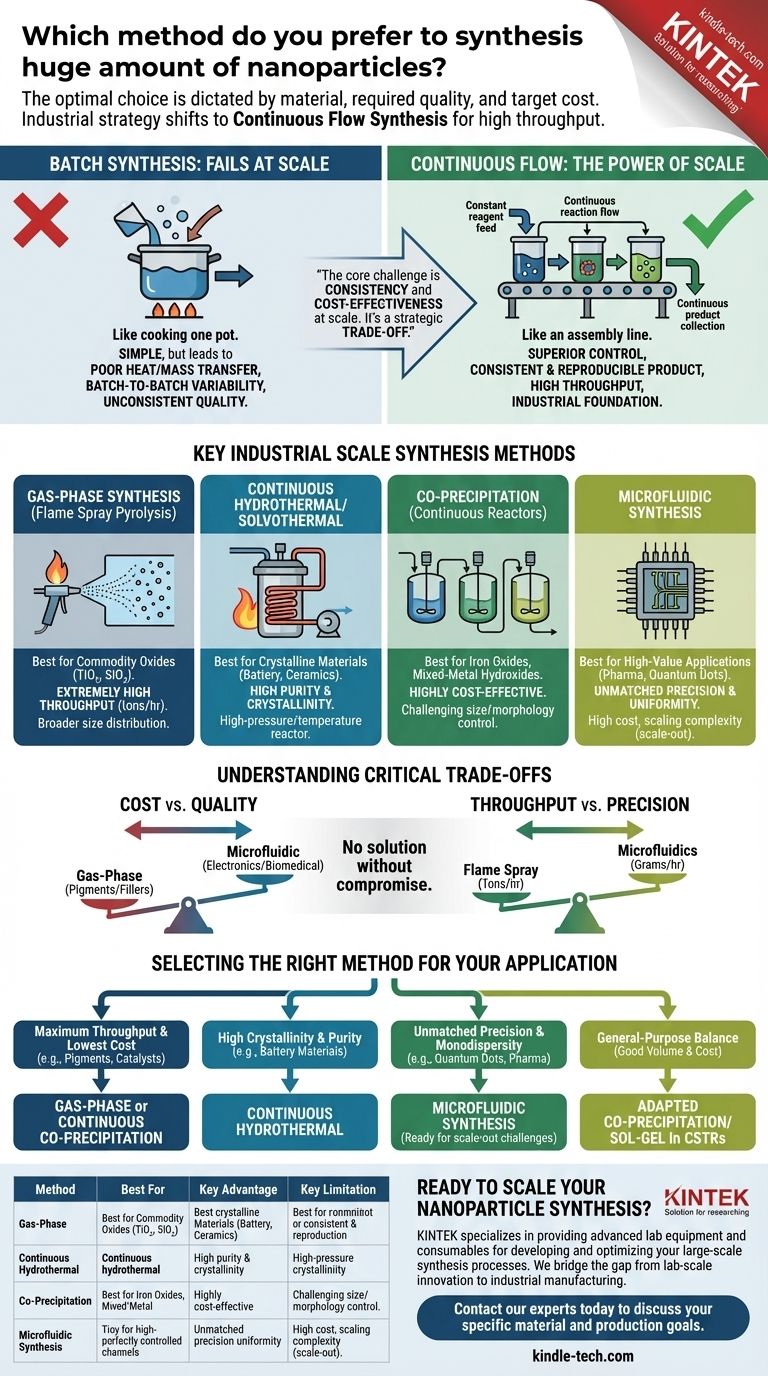
For synthesizing huge amounts of nanoparticles, there is no single "preferred" method, as the optimal choice is dictated by the specific material, required quality, and target cost. However, the dominant industrial strategy shifts away from traditional lab-scale batch processes toward continuous flow synthesis. These systems, particularly methods like gas-phase synthesis (e.g., flame spray pyrolysis) and continuous hydrothermal synthesis, are specifically engineered for high throughput and consistency at scale.
The core challenge of large-scale nanoparticle production is not simply making more, but making it consistently and cost-effectively. The most suitable method is therefore a strategic trade-off between production volume, particle precision, and economic viability.

The Fundamental Divide: Batch vs. Continuous Synthesis
To understand large-scale production, you must first distinguish between batch and continuous processing. This is the single most important factor determining scalability.
Why Batch Synthesis Fails at Scale
A batch process is like cooking a single pot of soup. You add all ingredients, let it react, and then collect the final product.
While simple for lab experiments, this model breaks down at large volumes. Scaling up a batch reactor leads to poor heat and mass transfer, resulting in temperature and concentration gradients. This creates significant batch-to-batch variability, where nanoparticles from one run differ in size, shape, and quality from the next.
The Power of Continuous Flow
Continuous flow synthesis is like an assembly line. Reagents are constantly fed into a reactor, the reaction occurs as they flow through it, and the product is continuously collected at the exit.
This approach offers superior control over reaction conditions like temperature, pressure, and mixing at every point in the reactor. The result is a highly consistent and reproducible product with significantly higher throughput, making it the foundation of industrial nanoparticle production.
Key Synthesis Methods for Industrial Scale
Several methods have been successfully adapted for continuous, large-scale production. The choice depends entirely on the type of nanoparticle you need to produce.
Gas-Phase Synthesis (Flame Spray Pyrolysis)
This is a workhorse for producing commodity oxide nanoparticles like titanium dioxide (TiO₂), silicon dioxide (SiO₂), and fumed alumina.
A precursor liquid is sprayed into a high-temperature flame, where it evaporates, decomposes, and nucleates into nanoparticles in the gas stream. It offers extremely high production rates (tons per hour) but generally produces particles with a broader size distribution.
Continuous Hydrothermal/Solvothermal Synthesis
This method is ideal for producing highly crystalline nanoparticles, especially complex metal oxides.
Reagents are mixed and pumped through a heated and pressurized reactor, often using supercritical water or other solvents. The extreme conditions accelerate the reaction and crystallization, yielding high-quality, highly pure nanoparticles at a high throughput.
Co-Precipitation in Continuous Reactors
Co-precipitation is a simple and highly cost-effective method where dissolved salts are mixed to precipitate an insoluble product.
When adapted for continuous flow using Continuous Stirred-Tank Reactors (CSTRs) in series, it allows for large-scale production of materials like iron oxides or mixed-metal hydroxides. While straightforward, achieving tight control over particle size and morphology can be challenging.
Microfluidic Synthesis
Microfluidics represents the pinnacle of precision. Reagents are pumped through micro-scale channels where mixing is perfectly controlled, leading to exceptionally uniform (monodisperse) nanoparticles.
However, scaling is achieved by "scaling out"—running thousands of microreactors in parallel—rather than "scaling up." This can lead to high capital costs and engineering complexity, reserving it for high-value applications like pharmaceuticals or quantum dots.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Choosing a large-scale synthesis method involves balancing competing priorities. There is no solution without compromise.
Cost vs. Quality
Gas-phase synthesis is often the cheapest per kilogram, making it ideal for pigments and fillers. In contrast, microfluidic synthesis offers unparalleled quality and uniformity but at a significantly higher capital and operational cost, suitable for advanced electronics or biomedical imaging agents.
Throughput vs. Precision
Flame spray pyrolysis delivers massive throughput but with less control over particle size. Continuous hydrothermal methods offer a good balance, while microfluidics prioritizes precision over raw volume, producing grams to kilograms per hour rather than tons.
Material Versatility
No single method works for all materials. Gas-phase synthesis excels with simple, stable oxides. Hydrothermal methods are versatile for a wide range of crystalline inorganic materials. Synthesis of metallic nanoparticles often requires different chemistries, such as the reduction of metal salts in continuous flow reactors.
Selecting the Right Method for Your Application
Your final decision must be guided by your ultimate goal. Analyze your project's primary driver to determine the best path forward.
- If your primary focus is maximum throughput and lowest cost (e.g., pigments, fillers, catalysts): Gas-phase synthesis like flame spray pyrolysis or a continuous co-precipitation process are your strongest candidates.
- If your primary focus is high crystallinity and purity for specialty materials (e.g., battery materials, advanced ceramics): Continuous hydrothermal or solvothermal synthesis provides the necessary quality at an industrial scale.
- If your primary focus is unmatched precision and monodispersity (e.g., quantum dots, drug delivery, medical diagnostics): Microfluidic synthesis is the superior technical choice, but you must be prepared for the challenges of scaling out.
- If your primary focus is a general-purpose balance of good volume and moderate cost: Adapting a co-precipitation or sol-gel process within a series of continuous stirred-tank reactors often hits the sweet spot.
Ultimately, the best method is the one that reliably and economically produces nanoparticles with the specific properties your application demands.
Summary Table:
| Method | Best For | Key Advantage | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gas-Phase Synthesis | Commodity Oxides (TiO₂, SiO₂) | Extremely High Throughput (tons/hour) | Broader Size Distribution |
| Continuous Hydrothermal | Crystalline Materials (Battery, Ceramics) | High Purity & Crystallinity | High-Pressure/Temperature Reactor |
| Co-Precipitation (Continuous) | Iron Oxides, Mixed-Metal Hydroxides | Highly Cost-Effective | Challenging Size/Morphology Control |
| Microfluidic Synthesis | High-Value Applications (Pharma, Quantum Dots) | Unmatched Precision & Uniformity | High Cost, Scaling Complexity |
Ready to Scale Your Nanoparticle Synthesis?
Choosing the right production method is critical to achieving the volume, consistency, and cost targets your project demands. KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables needed to develop and optimize your large-scale synthesis processes.
Our expertise supports a wide range of techniques, from robust gas-phase systems to precision microfluidic reactors. Let us help you bridge the gap from lab-scale innovation to industrial manufacturing.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific material and production goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- High Energy Vibratory Laboratory Ball Mill Grinding Mill Single Tank Type
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Containers
People Also Ask
- What is the function of PTFE reaction kettle bodies in micro-CSTR systems? Enhance Chemical Stability & Flow
- What are the four main types of sensors? A Guide to Power Source and Signal Type
- How are PTFE gaskets utilized for POEGMA electrolyte conductivity? Ensure Precision in Electrochemical Measurements
- What is the impact factor of powder metallurgy progress? A 2022 Analysis & Context
- What are the specific applications of PTFE in micro-batch slug flow systems? Enhance Your Microfluidic Reaction Purity













