Inclusions in laboratory-grown diamonds are a direct result of their manufacturing process. Unlike natural diamonds, which trap tiny mineral crystals from deep within the Earth, lab diamonds contain signatures of their controlled creation. The most common inclusions are remnants of metallic flux from the HPHT process or small, dark spots of non-diamond carbon from the CVD process.
The core takeaway is that inclusions are not just flaws; they are forensic evidence of a diamond's origin. While natural diamonds contain other minerals, lab-grown diamonds contain artifacts from the specific high-tech environment in which they were formed.

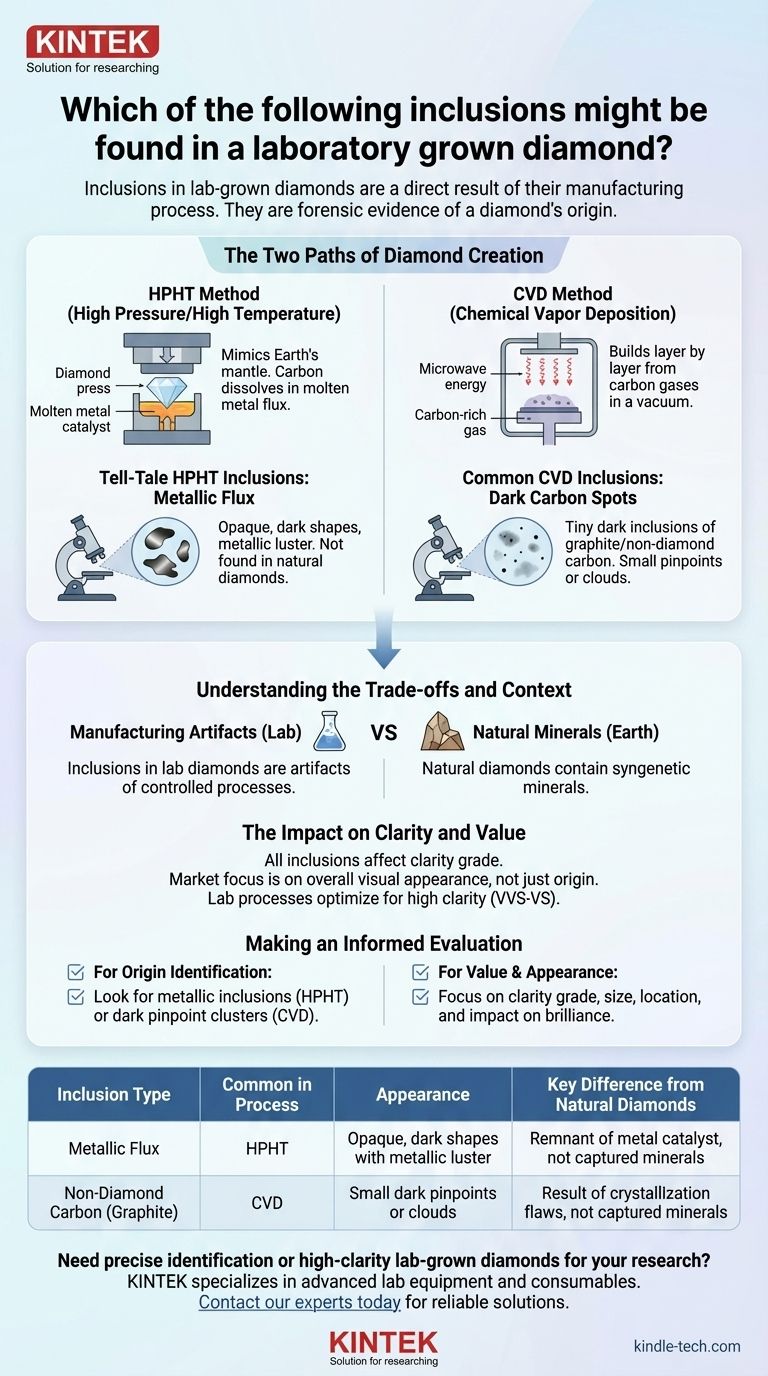
The Two Paths of Diamond Creation
To understand the inclusions, you must first understand the two primary methods used to grow diamonds in a lab: High Pressure/High Temperature (HPHT) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). Each method leaves a distinct trail.
The HPHT Method (High Pressure/High Temperature)
The HPHT process mimics the natural diamond-forming conditions of the Earth's mantle. It uses a large press to apply immense pressure and high temperatures to a carbon source.
This carbon source is dissolved in a molten metal catalyst, or flux, which allows the carbon atoms to crystallize into a diamond around a small diamond seed.
Tell-Tale HPHT Inclusions: Metallic Flux
During the HPHT growth process, small droplets of the molten metal flux can become trapped within the diamond crystal.
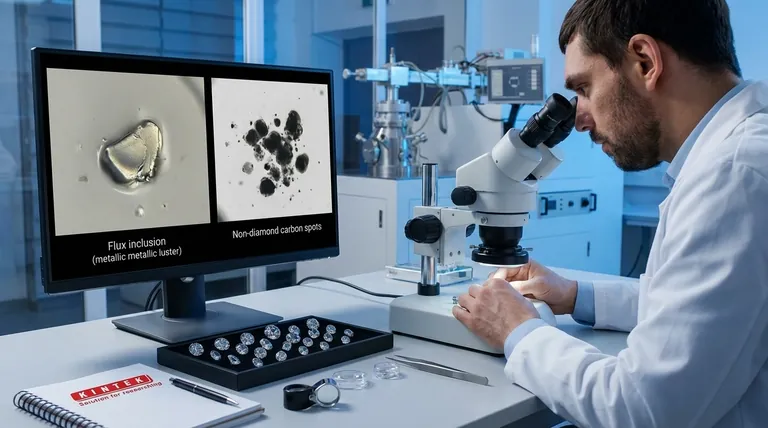
These metallic flux inclusions are the most definitive sign of an HPHT-grown diamond. They appear as opaque, dark shapes with a subtle metallic luster under a microscope, something not found in natural diamonds.
The CVD Method (Chemical Vapor Deposition)
The CVD method builds a diamond layer by layer in a vacuum chamber. The chamber is filled with carbon-rich gases (like methane) and heated to extreme temperatures.
Microwave energy breaks down the gas, allowing carbon atoms to rain down and deposit onto a diamond seed plate, slowly growing a larger diamond crystal.
Common CVD Inclusions: Dark Carbon Spots
The CVD process is not always perfect. Interruptions or inconsistencies in the atomic layering can result in carbon atoms that fail to crystallize properly into the diamond structure.
These form tiny, dark inclusions of graphite or other non-diamond carbon. They often appear as small pinpoints or dark clouds within the stone, which can be difficult to distinguish from certain natural inclusions without advanced gemological testing.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Context
While "inclusion" often has a negative connotation, its meaning differs significantly between natural and lab-grown stones. The presence of an inclusion is less important than what that inclusion tells you.
Manufacturing Artifacts vs. Natural Minerals
The fundamental difference is this: inclusions in lab diamonds are manufacturing artifacts. They are remnants of a controlled, man-made process, like the metal flux.
Inclusions in natural diamonds are syngenetic minerals, such as tiny crystals of garnet or peridot. They are pieces of the Earth's mantle that were captured as the diamond formed over billions of years.
The Impact on Clarity and Value
Regardless of origin, all inclusions affect a diamond's clarity grade. A large, centrally located inclusion—whether it's a natural crystal or a metallic spot—will lower the diamond's grade and value.
The market generally does not penalize a lab diamond for having a manufacturing-related inclusion any more than it penalizes a natural diamond for having a mineral inclusion. The focus remains on the overall visual appearance.
The Goal of a Controlled Environment
Because lab processes are controlled, manufacturers can optimize for high clarity. Diamonds with significant, visible inclusions are often screened out and used for industrial purposes rather than for jewelry.
This is why many lab-grown diamonds on the market have very high clarity grades (VVS to VS), as the process is geared towards minimizing these tell-tale signs.
Making an Informed Evaluation
Your interpretation of an inclusion should depend entirely on your goal, whether it's academic identification or a practical purchase decision.
- If your primary focus is identifying a diamond's origin: Look for opaque, metallic inclusions (a strong sign of HPHT) or clusters of dark pinpoints (common in CVD), which are distinct from the mineral crystals found in natural stones.
- If your primary focus is purchasing for value and appearance: Focus on the diamond's overall clarity grade from a reputable grading report. The origin of an inclusion matters far less than its size, location, and impact on the stone's brilliance.
Ultimately, understanding a diamond's inclusions empowers you to look beyond its sparkle and appreciate the unique story of its creation.
Summary Table:
| Inclusion Type | Common in Process | Appearance | Key Difference from Natural Diamonds |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metallic Flux | HPHT | Opaque, dark shapes with metallic luster | Not found in natural diamonds; remnant of metal catalyst |
| Non-Diamond Carbon (Graphite) | CVD | Small dark pinpoints or clouds | Result of crystallization flaws, not captured minerals |
Need precise identification or high-clarity lab-grown diamonds for your research or application? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables, serving the exact needs of laboratories and gemologists. Our expertise ensures you have the right tools for accurate analysis and sourcing. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific requirements with reliable, high-performance solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- Square Lab Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
People Also Ask
- What machine is used to make lab-grown diamonds? Discover the HPHT & CVD Technologies
- What are the applications of microwave plasma? From Diamond Synthesis to Semiconductor Fabrication
- How does microwave plasma work? Unlock Precision Material Synthesis for Advanced Manufacturing
- What are the limitations of diamonds? Beyond the Myth of Perfection
- How do lab-grown diamonds compare to natural diamonds? Uncover the Truth About Origin, Price, and Value













