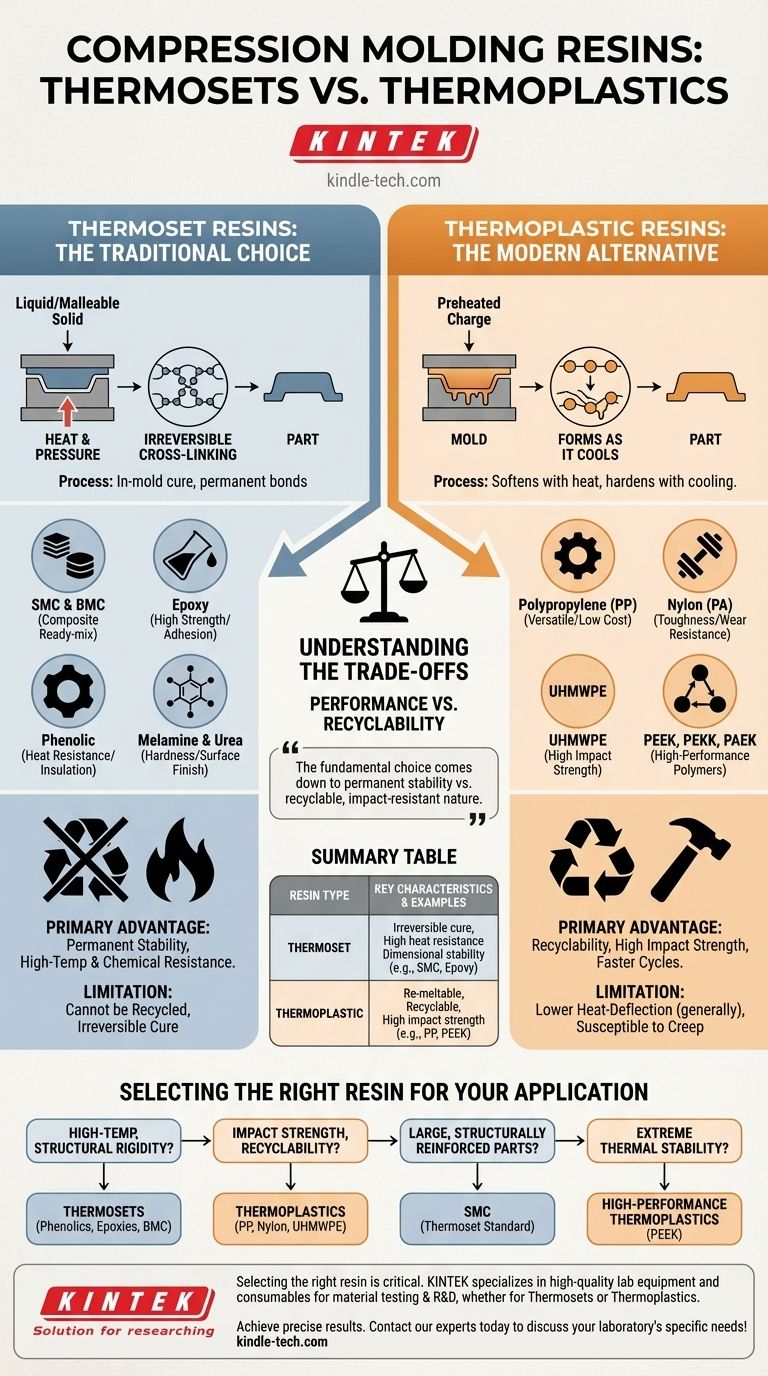
Compression molding utilizes two primary families of resins: thermosets and thermoplastics. Thermosets, such as Sheet Molding Compound (SMC), Bulk Molding Compound (BMC), and epoxies, are the traditional materials for this process, undergoing an irreversible chemical change when heated. However, thermoplastics like polypropylene, nylon, and high-performance polymers like PEEK are also commonly used, particularly for applications requiring impact resistance and recyclability.
The fundamental choice between resin types comes down to a trade-off between the permanent, high-temperature stability of thermosets and the recyclable, impact-resistant nature of thermoplastics. While both are viable, thermosets are more intrinsically suited to the "in-mold cure" nature of the compression molding process.

The Two Primary Resin Families
Compression molding's versatility stems from its ability to accommodate both major categories of polymers. The selection depends entirely on the final part's required performance characteristics, such as thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength.
Thermoset Resins: The Traditional Choice
Thermosets are polymers that begin as a liquid or malleable solid and are irreversibly cured by heat and pressure within the mold. This process, called cross-linking, creates strong covalent bonds between polymer chains.
Once cured, a thermoset part cannot be re-melted. This property is foundational to why they are so well-suited for compression molding.
Common thermoset examples include:
- Sheet Molding Compound (SMC) & Bulk Molding Compound (BMC): These are composite materials containing the resin, fillers, and reinforcing fibers (like glass fiber) that are ready to be placed in the mold.
- Epoxy: Known for exceptional strength, adhesion, and chemical resistance.
- Phenolic: Valued for its high heat resistance and electrical insulation properties.
- Melamine and Urea: Often used for electrical components and consumer goods due to their hardness and surface finish.
Thermoplastic Resins: The Modern Alternative
Thermoplastics soften when heated and harden when cooled, a process that can be repeated without chemically altering the material. This makes them inherently recyclable.
In compression molding, the thermoplastic charge is typically preheated before being placed in the mold, which is then closed to form the material as it cools and solidifies.
Common thermoplastic examples include:
- Polypropylene (PP): A versatile, low-cost polymer with good chemical resistance.
- Nylon (PA): Offers good strength, toughness, and wear resistance.
- Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE): Known for extremely high impact strength and low coefficient of friction.
- PEEK, PEKK, and PAEK: High-performance polymers used for demanding applications requiring extreme temperature and chemical resistance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right resin family involves balancing performance requirements, manufacturing considerations, and cost. Each type has distinct advantages and limitations.
Why Choose Thermosets?
Thermosets are specified when permanent stability is the primary concern. Their highly cross-linked structure gives them superior dimensional stability under heat and load.
They generally offer better resistance to high temperatures and chemical attack compared to most commodity thermoplastics. Once cured, they will not creep or deform easily.
Why Choose Thermoplastics?
The main advantages of thermoplastics are recyclability and toughness. Scrap material can be reground and reused, reducing waste.
They also typically possess superior impact strength and are less brittle than many thermoset counterparts. For certain high-volume applications, cycle times can be faster as no chemical curing time is required.
Key Limitations to Consider
Thermoset parts cannot be recycled, and the curing process is irreversible, meaning any production defects cannot be re-molded.
Most standard thermoplastics have a lower heat-deflection temperature than thermosets, though high-performance grades like PEEK are a notable exception. They can also be susceptible to creep (slow deformation under sustained load).
Selecting the Right Resin for Your Application
Your final material choice should be driven by the specific demands of the end-use environment.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature performance and structural rigidity: Thermosets like phenolics, epoxies, or BMC are the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is impact strength and recyclability: Thermoplastics like polypropylene, nylon, or UHMWPE offer significant advantages.
- If you are producing large, structurally reinforced parts for automotive or industrial use: Pre-impregnated thermoset compounds like SMC are the industry standard.
- If you require extreme thermal stability for aerospace or medical applications: High-performance thermoplastics like PEEK should be evaluated.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental difference between these two resin families empowers you to select the material that best aligns with your project's goals.
Summary Table:
| Resin Type | Key Characteristics | Common Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Thermoset | Irreversible cure (cross-linking), high heat resistance, dimensional stability | SMC, BMC, Epoxy, Phenolic |
| Thermoplastic | Re-meltable, recyclable, high impact strength | Polypropylene (PP), Nylon (PA), PEEK |
Selecting the right resin is critical for your compression molding project's success. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables to support your material testing and R&D processes. Whether you are developing with thermosets like SMC or high-performance thermoplastics like PEEK, our solutions can help you achieve precise and reliable results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Special Shape Press Mold for Lab
- Isostatic Molding Pressing Molds for Lab
- High Performance Laboratory Stirrers for Diverse Applications
- Lab Sterile Slapping Type Homogenizer for Tissue Mashing and Dispersing
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer PTFE Beaker and Lids
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a laboratory hydraulic press in rGO film fabrication? Achieve Superior EMI Shielding Density
- How much does a hydraulic press cost? A Complete Guide to Pricing from $200 to $1M+
- For what purpose are a laboratory hydraulic press and steel molds used to cold-press Diamond/Al-Cu mixed powders?
- What is a hydraulic press made of? Discover the Core Components for Immense Force
- What causes hydraulic pressure spikes? Prevent System Damage from Hydraulic Shock
- What is the cake thickness from a filter press? Optimize Your Filtration Cycle & Efficiency
- What is the principle of the hydraulic press? Harness Pascal's Law for Massive Force
- What role do laboratory hydraulic presses play in the post-processing of iron-based aerogels? Expert Compaction Guide














