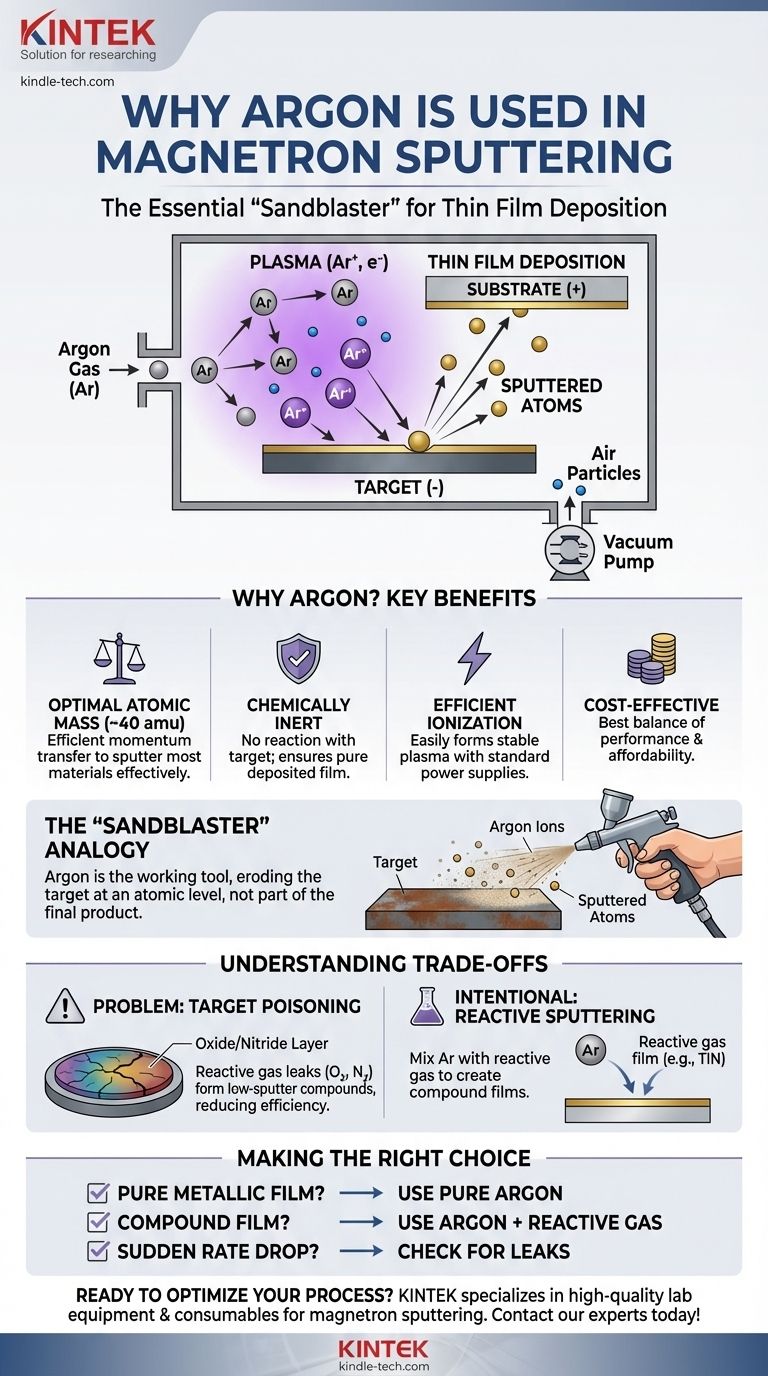
In magnetron sputtering, argon is used because it is a chemically inert gas with a sufficient atomic mass to effectively function as a "bombardment" particle. When ionized into a plasma, argon ions are accelerated into a target material, physically knocking atoms off its surface. This process allows those dislodged atoms to travel and deposit onto a substrate, forming a thin film, without the argon chemically interfering with the process.
The core principle is this: argon is not part of the final product, but rather the essential working tool that makes the physical sputtering process possible. It is chosen for its ideal balance of atomic weight and chemical inertness, serving as the "sandblaster" that erodes the target at an atomic level.

The Core Mechanism: How Sputtering Works
The Role of Plasma
Magnetron sputtering takes place inside a vacuum chamber to ensure process purity and control.
First, the chamber is evacuated to remove most air particles. Then, it is backfilled with a small, controlled amount of a working gas, which is typically argon.
A high voltage is applied between the substrate holder and the material to be deposited, known as the target. This electrical potential, combined with a magnetic field from the magnetron, ignites the argon gas into a plasma.
Ionization and Acceleration
The plasma consists of a mix of neutral argon atoms, positively charged argon ions (Ar+), and free electrons.
The target is given a negative charge (acting as a cathode). This powerfully attracts the positively charged argon ions from the plasma.
These Ar+ ions accelerate across the electric field, gaining significant kinetic energy before they collide with the surface of the target.
The Bombardment Process
The high-energy impact of an argon ion transfers momentum to the atoms of the target material, much like a cue ball striking a rack of billiard balls.
If the momentum transfer is sufficient, it can eject, or "sputter," atoms from the target surface.
These sputtered atoms travel through the vacuum chamber and condense on the substrate, gradually building up a thin, uniform film.
Why Argon is the Industry Standard
While other noble gases can be used, argon provides the best combination of performance, safety, and cost for the vast majority of applications.
Optimal Atomic Mass
Argon's atomic mass (around 40 amu) is heavy enough to efficiently transfer momentum and sputter most materials effectively.
Lighter gases like helium would be less efficient, while heavier gases like xenon or krypton can provide higher sputter rates but are significantly more expensive.
Chemical Inertness
As a noble gas, argon is chemically inert. This is a critical property.
It means the argon ions will not chemically react with the target material during bombardment. This ensures that the sputtered material arriving at the substrate is pure, preserving the desired properties of the final film.
Efficient Ionization
Argon has a relatively low ionization potential, meaning it does not require an extreme amount of energy to be converted into a plasma.
This allows for the creation of a stable, dense plasma using standard DC or RF power supplies, leading to a consistent and controllable deposition process.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Complications
The choice and purity of the working gas are critical for process stability and film quality. Introducing other gases, whether intentionally or not, can dramatically change the outcome.
The Problem of Reactive Gases
A common issue is target poisoning. This occurs if a reactive gas, like oxygen or nitrogen from a small leak, enters the system.
These reactive gases can form compounds on the target surface (e.g., oxides or nitrides). These compounds often have a much lower sputter rate than the pure material.
This "poisoned" layer reduces deposition efficiency and can lead to defects or instability in the plasma, such as arcing.
Intentional Reactive Sputtering
This same principle is harnessed in a process called reactive sputtering.
In this technique, a reactive gas (like nitrogen or oxygen) is intentionally mixed with the argon.
This allows for the deposition of compound films. For example, by sputtering a titanium target in an argon/nitrogen atmosphere, you can create a hard, gold-colored film of titanium nitride (TiN) on the substrate.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The selection of the process gas is fundamental to achieving the desired film characteristics.
- If your primary focus is a pure metallic film: Argon is almost always the correct choice due to its inertness, efficiency, and low cost.
- If your goal is to create a compound film (e.g., an oxide or nitride): You will use argon as the primary sputtering gas but intentionally introduce a controlled amount of a reactive gas (O₂ or N₂) to form the compound.
- If you are experiencing a sudden drop in deposition rate: Your first step should be to check for system leaks that could be introducing reactive gases and poisoning your target.
Ultimately, viewing argon not as a simple consumable but as a critical component of the sputtering engine is key to mastering the deposition process.
Summary Table:
| Property | Why It Matters for Sputtering |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Prevents reactions with the target, ensuring pure film deposition. |
| Optimal Atomic Mass (~40 amu) | Efficiently transfers momentum to sputter target atoms effectively. |
| Low Ionization Potential | Easily forms a stable plasma with standard power supplies. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Provides the best balance of performance and affordability compared to other noble gases. |
Ready to optimize your thin film deposition process?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for magnetron sputtering and other advanced laboratory applications. Whether you need reliable argon gas systems, sputtering targets, or expert advice to troubleshoot issues like target poisoning, our solutions are designed to enhance your lab's efficiency and ensure film purity.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory needs and help you achieve superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is plasma CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for Sensitive Materials
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating
- What is the plasma CVD process? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















