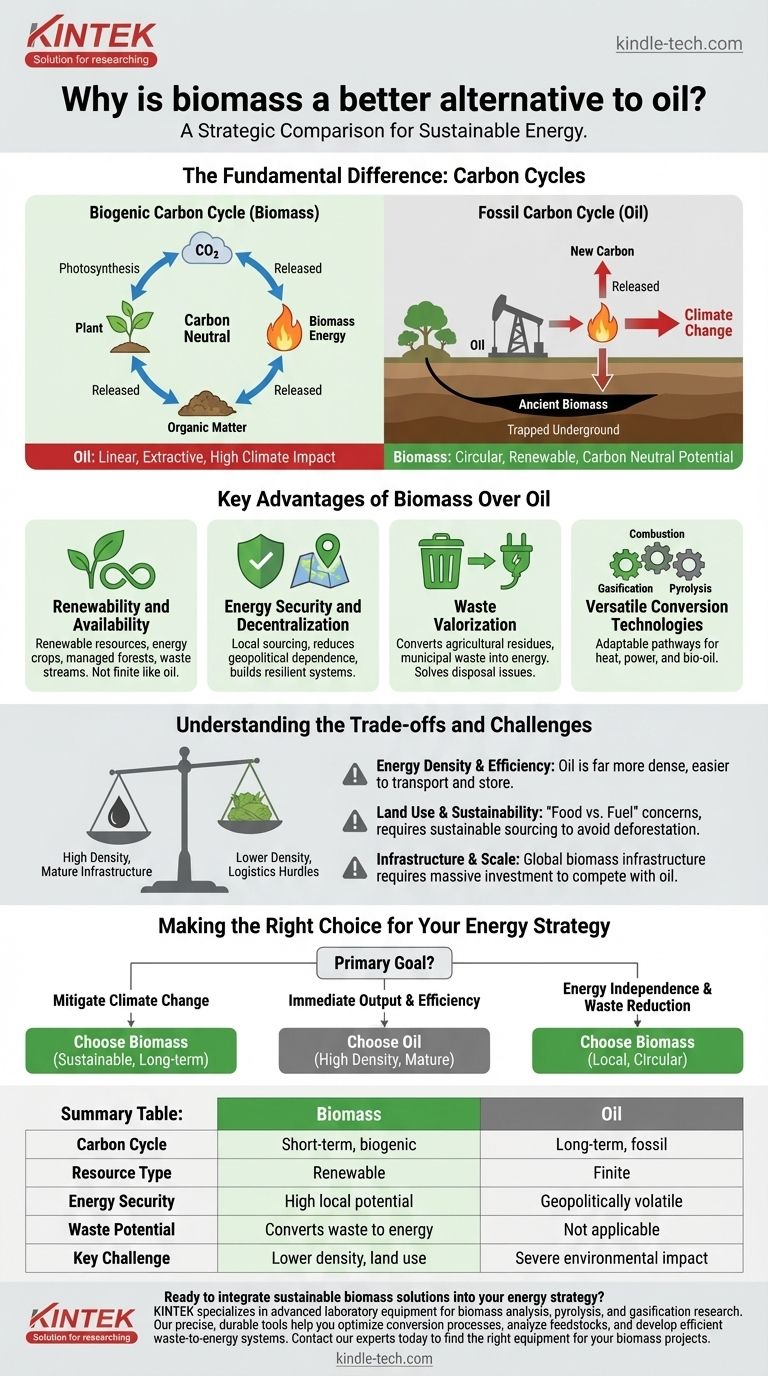
From a sustainability standpoint, biomass is considered a better alternative to oil primarily because it is a renewable resource that operates within the current biogenic carbon cycle. Oil is a finite fossil fuel that releases ancient, sequestered carbon into the atmosphere. This fundamental difference gives biomass key advantages in carbon neutrality, energy security, and waste reduction, even though it faces challenges in energy density and scale.
The choice between biomass and oil is a choice between two entirely different energy models. Oil represents a linear, extractive system with high efficiency but finite reserves and significant climate impact. Biomass represents a circular, renewable system that recycles carbon but requires careful management to be truly sustainable and effective.
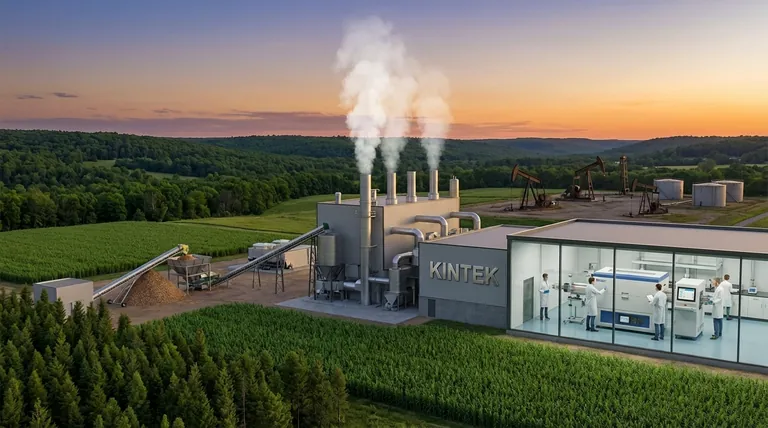

The Fundamental Difference: Carbon Cycles
The core distinction between biomass and oil lies in how they interact with the Earth's carbon cycle. Understanding this is critical to evaluating their environmental impact.
The Biogenic Carbon Cycle (Biomass)
Biomass energy comes from organic matter like plants, wood, and waste. As plants grow, they absorb carbon dioxide (CO₂) from the atmosphere through photosynthesis.
When this biomass is used for energy, it releases that same amount of CO₂ back into the atmosphere. This creates a relatively short-term, closed loop, making it carbon neutral in principle.
The Fossil Carbon Cycle (Oil)
Oil is also derived from organic matter, but it is ancient biomass that has been trapped underground for millions of years. Its carbon has been out of the atmospheric cycle for eons.
Burning oil releases this long-sequestered carbon into the current atmosphere. This adds new carbon to the system, disrupting the planet's energy balance and driving climate change.
Key Advantages of Biomass Over Oil
Beyond the carbon cycle, biomass offers several strategic benefits that position it as a favorable long-term alternative to petroleum.
Renewability and Availability
Biomass sources are renewable. Energy crops can be grown, forests can be managed sustainably, and waste streams from agriculture and cities are constantly generated.
Oil, by contrast, is a finite resource. Its extraction becomes more difficult and expensive over time as easily accessible reserves are depleted.
Energy Security and Decentralization
Biomass can often be sourced locally or regionally. This reduces dependence on a small number of oil-producing nations and insulates economies from geopolitical instability and volatile global energy markets.
This decentralized model empowers communities and countries to build more resilient and independent energy systems.
Waste Valorization
A significant advantage of biomass is its ability to convert waste into energy. Agricultural residues, forestry by-products, and even municipal solid waste can be used as fuel.
This process, known as waste-to-energy, solves a disposal problem while simultaneously generating valuable heat and power.
Versatile Conversion Technologies
Biomass is not limited to a single use. It can be converted into energy through several different technological pathways.
These include direct combustion (burning for heat), gasification (converting to a combustible gas), and pyrolysis (decomposing with heat to create bio-oil). This flexibility allows it to be adapted for various energy needs.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
To be objective, it is crucial to acknowledge that biomass is not a perfect solution and comes with its own set of significant challenges.
Energy Density and Efficiency
Oil is incredibly energy-dense. A small volume of oil contains a massive amount of energy, making it easy to store and transport.
Biomass is much bulkier and has a lower energy content by weight and volume. This creates logistical hurdles for transportation, storage, and processing at a large scale.
Land Use and Sustainability
The "food vs. fuel" debate is a major concern. Using arable land to grow energy crops can compete with food production, potentially impacting food security and prices.
Furthermore, if biomass is not sourced sustainably—for example, through clear-cutting forests—it can lead to deforestation, habitat loss, and a net increase in carbon emissions. The carbon footprint of harvesting, processing, and transportation must also be factored in.
Infrastructure and Scale
The global oil industry is supported by a century of investment in highly efficient infrastructure for extraction, refining, and distribution.
Building a comparable global infrastructure for biomass would require a monumental and costly effort. Most biomass operations today remain localized and are not yet able to compete with oil on a global scale.
Making the Right Choice for Your Energy Strategy
Your preference for biomass or oil depends entirely on your primary goals, as each serves different strategic priorities.
- If your primary focus is mitigating climate change: Biomass is the superior long-term choice due to its potential for carbon neutrality, provided it is sourced and processed sustainably.
- If your primary focus is immediate energy output and logistical efficiency: Oil remains the dominant fuel due to its high energy density and mature global infrastructure, though its environmental costs are severe.
- If your primary focus is energy independence and waste reduction: Biomass offers a clear advantage by enabling localized energy production and turning waste streams into valuable resources.
Ultimately, transitioning from oil to biomass is a strategic investment in a more sustainable and circular energy future.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Biomass | Oil |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Cycle | Short-term, biogenic (carbon neutral) | Long-term, fossil (adds new carbon) |
| Resource Type | Renewable | Finite |
| Energy Security | High potential for local/regional production | Geopolitically volatile, centralized |
| Waste Potential | Converts waste streams into energy | Not applicable |
| Key Challenge | Lower energy density, land use concerns | Severe environmental impact, resource depletion |
Ready to integrate sustainable biomass solutions into your energy strategy? KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment for biomass analysis, pyrolysis, and gasification research. Our precise, durable tools help you optimize conversion processes, analyze feedstocks, and develop efficient waste-to-energy systems. Whether you're in R&D or scaling up production, we provide the reliable technology you need to pioneer the future of renewable energy. Contact our experts today to find the right equipment for your biomass projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why is an Alumina Ceramic Tube Support Necessary for 1100°C Experiments? Ensure Data Accuracy and Chemical Inertness
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material
- What tube is used for tubular furnace? Choose the Right Material for Temperature & Atmosphere
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- What is the pressure on a tube furnace? Essential Safety Limits for Your Lab



















