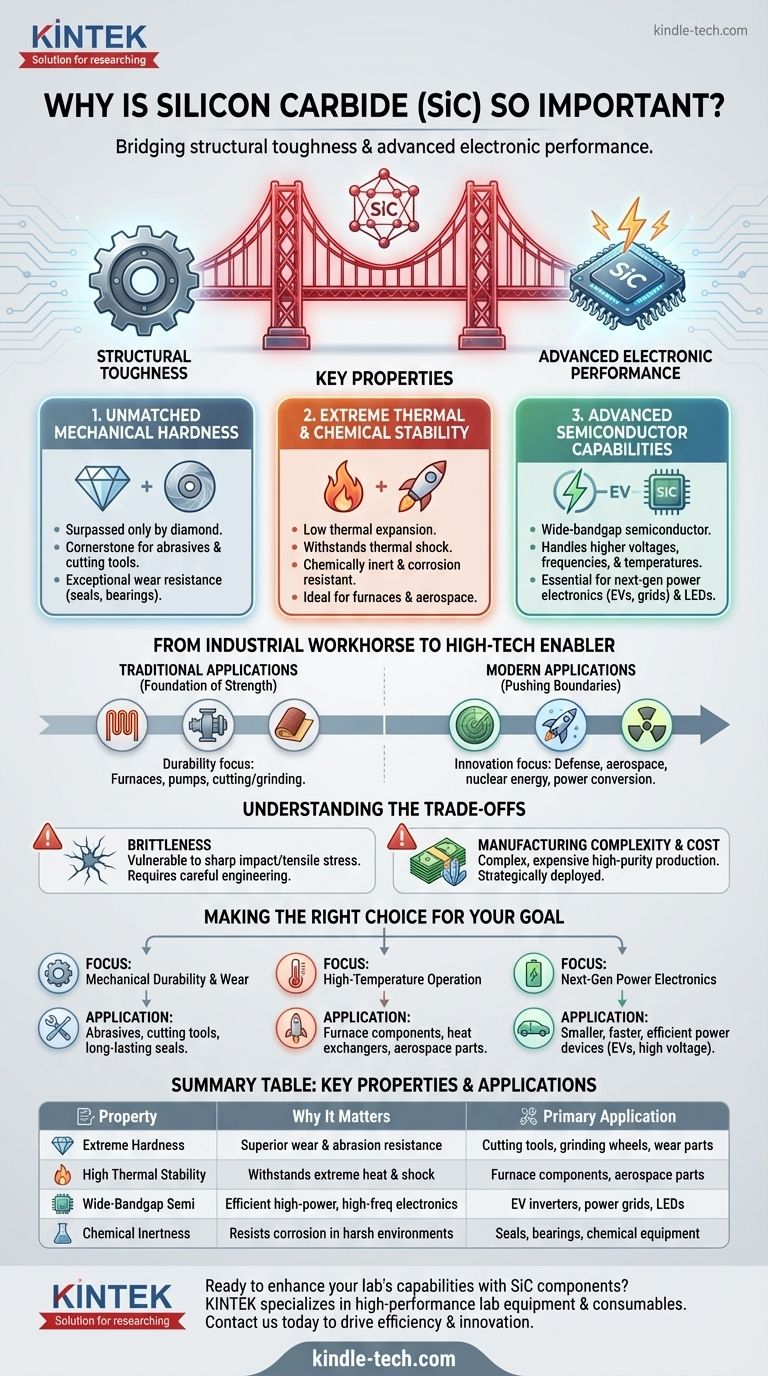
In short, silicon carbide is important because of its rare combination of superior properties. It is exceptionally hard, highly resistant to heat and chemical corrosion, and also functions as a powerful semiconductor. This versatility allows it to solve critical challenges in both traditional heavy industries and advanced high-tech fields where conventional materials like steel or silicon fall short.
Silicon carbide's true significance lies in its ability to bridge the gap between structural toughness and advanced electronic performance. It enables the creation of devices and components that are not only physically robust but also more efficient and resilient in extreme operating conditions.

The Unique Properties of Silicon Carbide
Silicon carbide's importance is rooted in a set of distinct physical and electrical characteristics that make it a superior material for a wide range of demanding applications.
Unmatched Mechanical Hardness
Silicon carbide (SiC) is one of the hardest commercially available materials, surpassed only by a few substances like diamond. This extreme hardness is why it has been a cornerstone material for abrasive and cutting applications for over a century.
Its use in sandpaper, grinding wheels, and cutting tools is a direct result of this property. This hardness also translates to exceptional wear resistance in modern applications like pump seals and bearings.
Extreme Thermal and Chemical Stability
SiC demonstrates remarkable stability when exposed to extreme conditions. It has a very low thermal expansion coefficient, meaning it does not significantly change size with temperature fluctuations.
This characteristic, combined with its ability to withstand rapid heating and cooling cycles (thermal shock), makes it ideal for high-temperature environments like industrial furnaces and rocket engine components.
Furthermore, SiC is chemically inert and highly resistant to corrosion from strong acids, ensuring longevity and reliability in harsh chemical processing environments.
Advanced Semiconductor Capabilities
While its physical toughness is impressive, SiC's role as a wide-bandgap semiconductor is what drives its importance in modern electronics. This property allows it to handle significantly higher voltages, frequencies, and temperatures than traditional silicon.
This makes SiC essential for next-generation power electronics, such as inverters for electric vehicles (EVs) and power grids, where efficiency and performance under load are critical. It is also used as a substrate for manufacturing robust and bright light-emitting diodes (LEDs).
From Industrial Workhorse to High-Tech Enabler
Silicon carbide’s journey from a simple abrasive to a key component in advanced technology highlights its unique versatility.
Traditional Applications: A Foundation of Strength
Historically, the primary uses for SiC were based on its raw physical strength and thermal endurance. It was, and still is, a go-to material for applications requiring durability.
Common examples include heating elements in industrial furnaces, wear-resistant parts for pumps, and foundational materials for cutting and grinding.
Modern Applications: Pushing Technological Boundaries
In recent decades, refinements in SiC manufacturing have unlocked its potential in high-tech fields. Its properties are now critical for innovation in sectors like defense, aerospace, and nuclear energy.
Its ability to function as a semiconductor in extreme environments allows for more powerful and resilient radar systems, more efficient power conversion in spacecraft, and sensors that can operate inside nuclear reactors.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect. While silicon carbide offers immense advantages, it's essential to understand its limitations to appreciate where it provides the most value.
The Challenge of Brittleness
Like many extremely hard ceramic materials, silicon carbide is also brittle. While it can withstand immense compressive force and surface wear, it can fracture under sharp impacts or high tensile stress, unlike metals which tend to bend.
This requires careful engineering and design considerations to ensure components are not subjected to the types of forces that could lead to catastrophic failure.
Manufacturing Complexity and Cost
Producing high-purity, single-crystal SiC suitable for semiconductor applications is a significantly more complex and expensive process than producing traditional silicon wafers.
This higher cost is a primary reason why SiC has not completely replaced silicon. Instead, it is strategically deployed in applications where its superior performance justifies the additional expense.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding to use silicon carbide depends entirely on whether its unique benefits solve your specific engineering challenge.
- If your primary focus is mechanical durability and wear resistance: SiC is an excellent choice for abrasives, cutting tools, and long-lasting seals and bearings in harsh industrial environments.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature operation: Its unmatched thermal stability makes it the ideal material for furnace components, heat exchangers, and critical aerospace parts exposed to extreme heat.
- If your primary focus is next-generation power electronics: SiC's semiconductor properties are essential for creating smaller, faster, and more efficient power devices that can operate at higher voltages and temperatures than silicon allows.
Ultimately, silicon carbide is a key enabling material, allowing engineers to push beyond the limits of conventional technology.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Why It Matters | Primary Application |
|---|---|---|
| Extreme Hardness | Superior wear and abrasion resistance | Cutting tools, grinding wheels, wear parts |
| High Thermal Stability | Withstands extreme heat and thermal shock | Furnace components, aerospace parts |
| Wide-Bandgap Semiconductor | Enables efficient high-power, high-frequency electronics | EV inverters, power grids, LEDs |
| Chemical Inertness | Resists corrosion in harsh environments | Seals, bearings, chemical processing equipment |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with silicon carbide components?
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment and consumables tailored to meet the demanding needs of modern research and industry. Whether you require durable furnace elements, advanced semiconductor substrates, or custom ceramic components, our expertise ensures you get reliable solutions that withstand extreme conditions.
Contact us today to discuss how our silicon carbide products can drive efficiency and innovation in your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Ceramic Evaporation Boat Set Alumina Crucible for Laboratory Use
- High Purity Zinc Foil for Battery Lab Applications
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
People Also Ask
- Is silicon carbide better than ceramic? Discover the Superior Technical Ceramic for Your Application
- What is the temperature resistance of silicon carbide? Withstands Extreme Heat Up to 1500°C
- What are the characteristics of SiC? Unlock High-Temp, Hard, and Chemically Inert Performance
- What is the strongest ceramics? Silicon Carbide Leads in Hardness & Thermal Strength
- What is the resistivity of silicon carbide? It's a tunable property from <0.1 ohm-cm to highly resistive.













