In short, tungsten is used in high-temperature furnaces because it has the highest melting point of any metal, allowing it to remain solid and structurally stable at extreme temperatures where other materials would fail. This unique property makes it indispensable for constructing the critical internal components of furnaces that must operate well above 2000°C.
The core reason for using tungsten is its unparalleled heat resistance. However, this advantage comes with a critical requirement: tungsten must be protected from oxygen at high temperatures, necessitating its use in a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere.

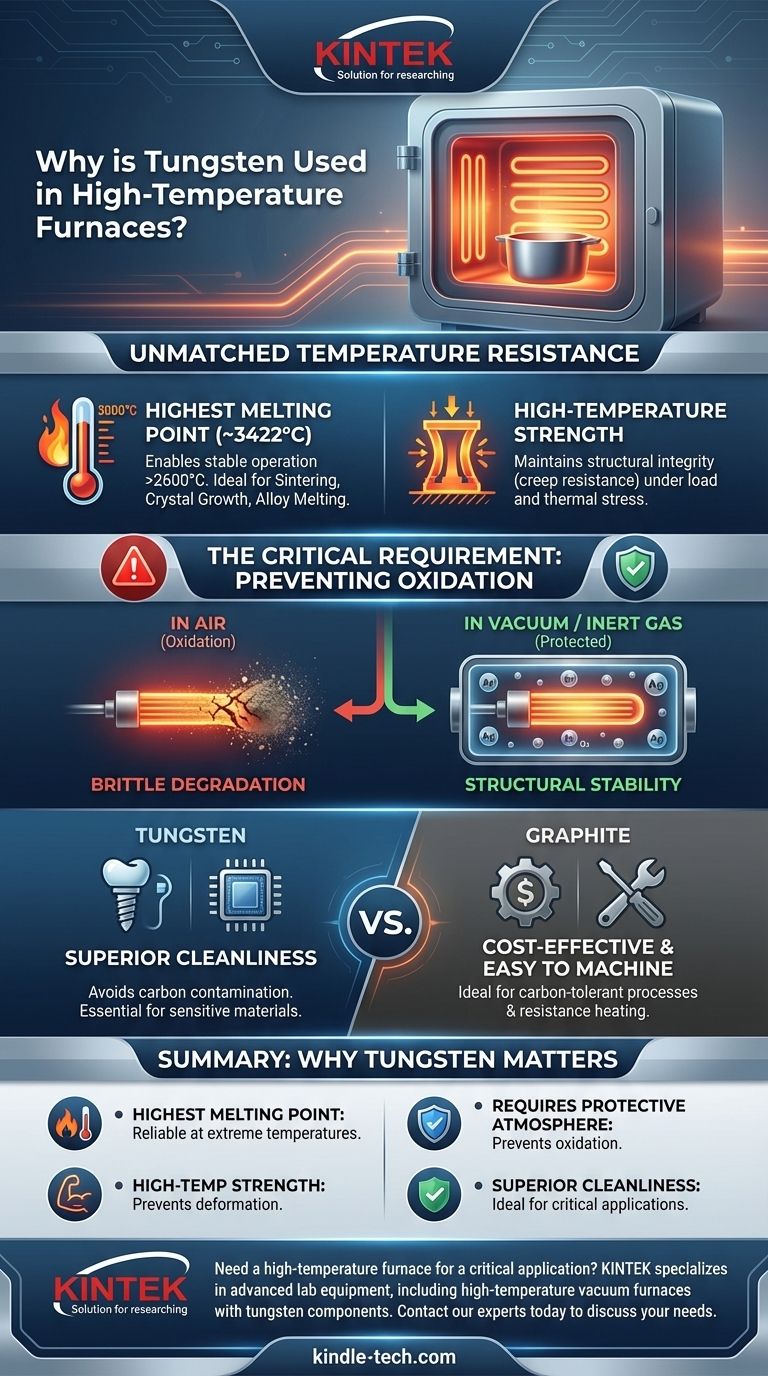
The Defining Property: Unmatched Temperature Resistance
The primary driver for selecting tungsten in furnace applications is its ability to withstand extreme heat without compromising its physical form. This thermal stability is foundational to creating environments for advanced material processing.
The Highest Melting Point of Any Metal
Tungsten's melting point is approximately 3422°C (6192°F), the highest of all metallic elements. This allows furnaces built with tungsten components, such as heating elements and heat shields, to reliably operate at temperatures up to 2600°C or even higher.
These extreme operating temperatures are essential for processes like sintering refractory metals, growing artificial crystals, and melting high-temperature alloys.
Maintaining Structural Integrity
Beyond simply not melting, tungsten maintains significant strength and stiffness at very high temperatures. This property, known as hot strength or creep resistance, is critical.
Furnace components like supports, racks, and heating elements must hold their shape under load and thermal stress. Where other metals would sag or deform, tungsten remains rigid, ensuring the furnace's structural integrity and operational precision.
The Critical Operating Environment
While tungsten's heat resistance is its greatest strength, it also has a significant vulnerability that dictates the entire design of a tungsten furnace.
The Achilles' Heel: Oxidation
At elevated temperatures, tungsten reacts readily with oxygen in the air. This process, known as oxidation, causes it to become brittle and rapidly degrade, completely negating its structural benefits.
Because of this, a tungsten furnace cannot be operated in a standard air atmosphere at high temperatures. The tungsten components would be destroyed.
The Solution: Vacuum or Inert Gas
To protect the tungsten, furnaces must operate in a controlled atmosphere. This is typically achieved in one of two ways.
First is a high vacuum, where pumps remove nearly all air and, critically, the residual oxygen. Second is by backfilling the chamber with a non-reactive, inert gas like argon or a reducing gas like hydrogen, which displaces the oxygen.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Tungsten vs. Graphite
Tungsten is not the only material used for high-temperature furnace construction. Graphite is a common alternative, and understanding the difference is key to material selection.
When to Choose Tungsten
Tungsten is the superior choice for applications demanding an exceptionally clean operating environment. Graphite can "outgas," releasing carbon particles or vapor that can contaminate sensitive materials.
Therefore, tungsten is preferred for processing medical implants, electronic components, and other materials where even minute contamination is unacceptable. Its high density also makes it an excellent material for heat shielding.
When to Choose Graphite
Graphite is often more cost-effective and significantly easier to machine than tungsten, which is notoriously hard and brittle.
Graphite is the ideal choice for processes where the presence of carbon is acceptable or even desirable, such as in graphitization furnaces. It is also an excellent electrical conductor, making it a very effective material for resistance heating elements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision between tungsten and other refractory materials depends entirely on the process requirements for temperature, cleanliness, and cost.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature and ultimate cleanliness: Choose a tungsten furnace to avoid carbon contamination in a high-vacuum environment.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for a carbon-tolerant process: Choose a graphite furnace for its lower material cost and ease of manufacturing.
- If you are sintering reactive metals or medical-grade alloys: A tungsten furnace is essential to maintain the purity and integrity of the final product.
Ultimately, understanding the properties of tungsten allows you to leverage its unmatched temperature resistance while controlling its environment to ensure reliable, high-performance results.
Summary Table:
| Property | Why It Matters for Furnaces |
|---|---|
| Highest Melting Point (~3422°C) | Enables stable operation at extreme temperatures (>2600°C) where other metals fail. |
| High-Temperature Strength | Maintains structural integrity (creep resistance) under load and thermal stress. |
| Requires Protective Atmosphere | Must operate in a vacuum or inert gas to prevent oxidation at high temperatures. |
| Superior Cleanliness | Avoids carbon contamination, ideal for sensitive processes like medical implant sintering. |
Need a high-temperature furnace for a critical application?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including high-temperature vacuum furnaces with tungsten components. Our solutions are designed for processes requiring extreme heat and ultimate material purity, such as sintering reactive metals or growing artificial crystals.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK tungsten furnace can provide the reliability and cleanliness your laboratory demands.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between muffle furnace and air oven? Choose the Right Tool for Your Thermal Process
- What apparatus is used for heating in a lab? A Guide to Choosing the Right Tool
- How is the ash content determined in a muffle furnace? Master the Gravimetric Analysis Method
- What is the highest temperature of a furnace? Unlocking the Limits of Extreme Heat
- How do you measure ash content? Choose the Right Method for Accurate Results



















