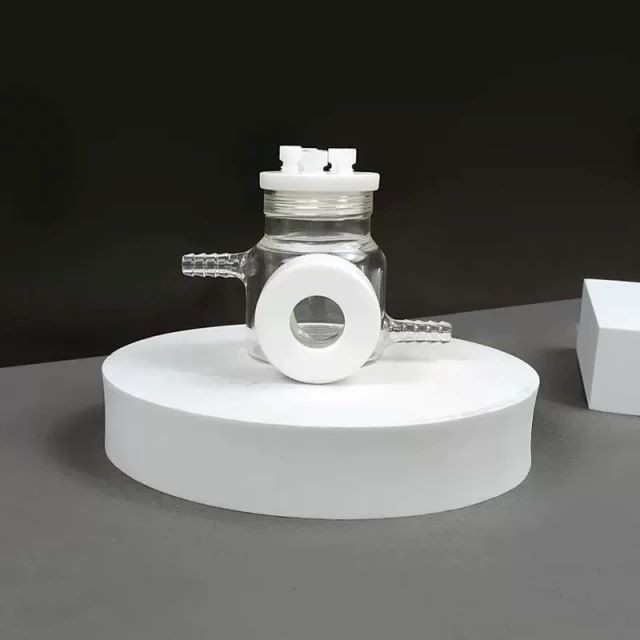

Electrochemical Consumables
Optical Water Bath Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
Item Number : ELCWO
Price varies based on specs and customizations
$249.00 / set
- Specifications
- 50ml ~ 250ml
- Applicable temperature range
- 0 ~ 60℃
- Material
- boron glass + PTFE
Shipping:
Contact us to get shipping details Enjoy On-time Dispatch Guarantee.
Why Choose Us
Easy ordering process, quality products, and dedicated support for your business success.
This is an optical water bath with a constant temperature, sealed electrolytic cell. The temperature is controllable. It also has excellent corrosion resistance and comes in complete specifications. Additionally, it can be customized to meet specific requirements.
Technical specifications
Optical water bath sealed electrolytic cell
| Specifications | 50ml ~ 250ml |
| Applicable temperature range | 0 ~ 60℃ |
| Sealing form | Thread + Apron |
| Material | boron glass + PTFE |
| Electrolytic cell opening | three electrode holes (6mm), two air holes (3mm), can be customized |
Optical water bath unsealed electrolytic cell
| Specifications | 50ml ~ 250ml |
| Applicable temperature range | 0 ~ 60℃ |
| Material | boron glass + PTFE |
| Electrolytic cell opening | three electrode holes (6mm), can be customized |
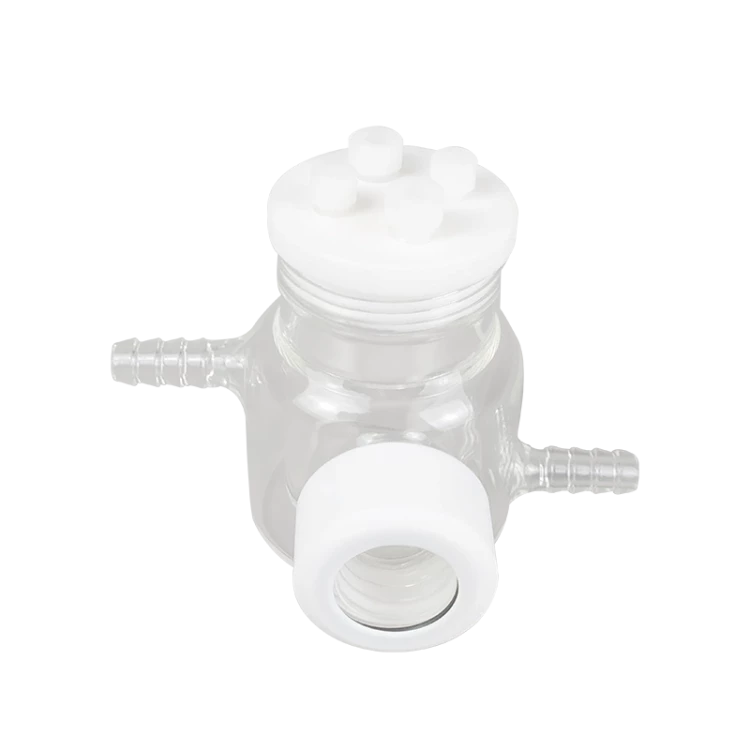
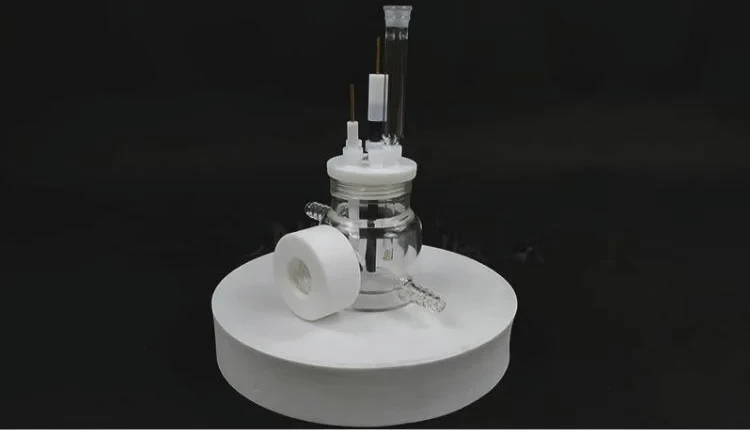
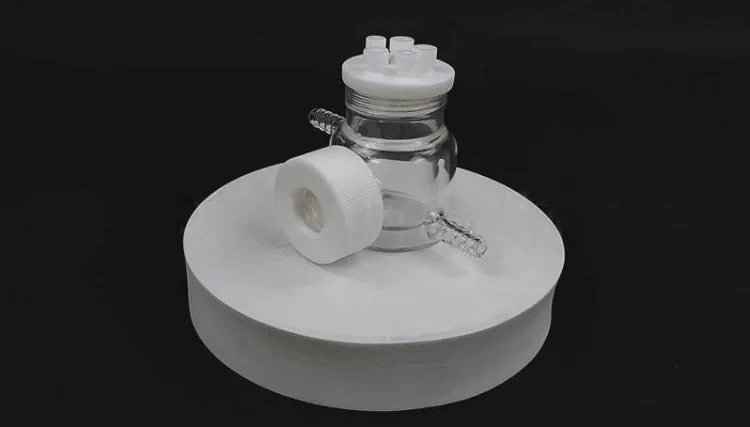
Detail & Parts
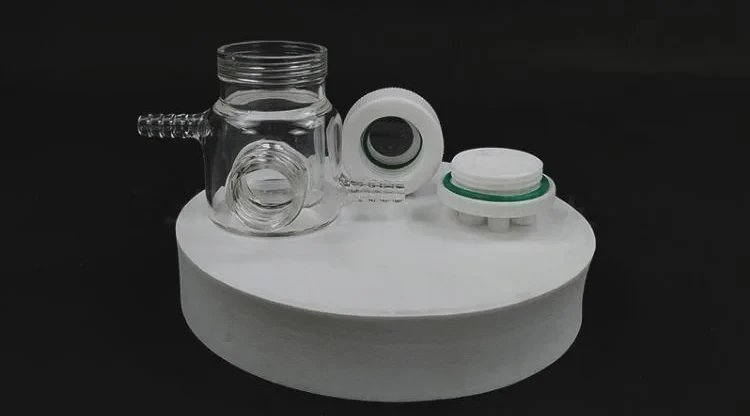
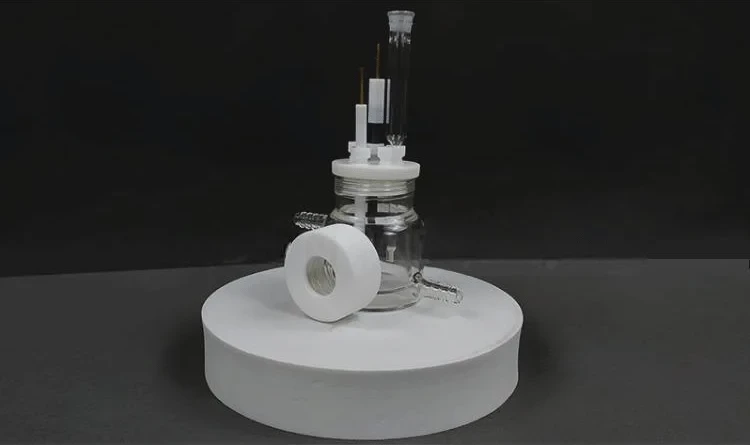
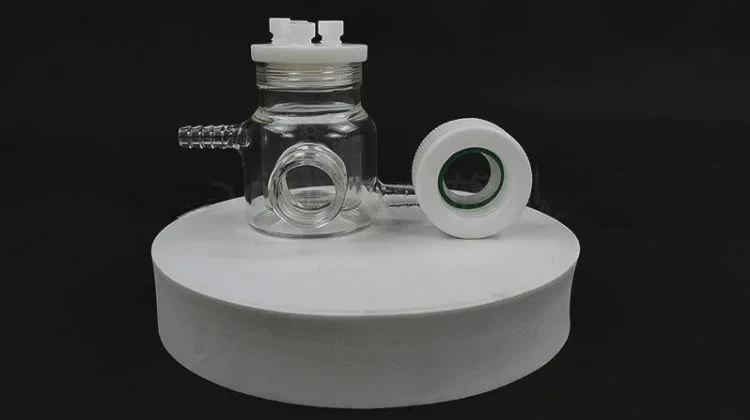


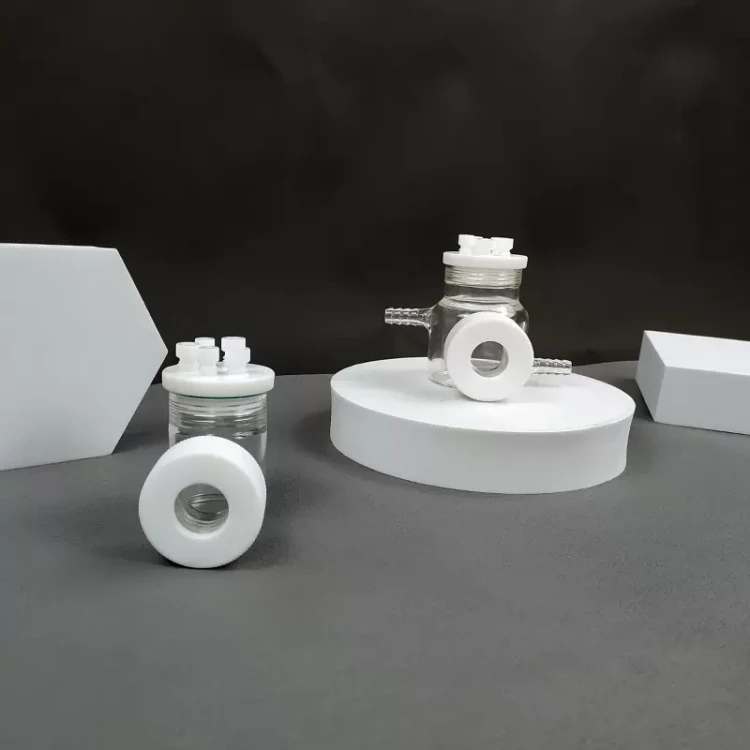







Operating steps

1. The optical water bath electrolytic cell is composed of a sealing rubber ring, a sealing plug, a polytetrafluoroethylene cover, a quartz wide window and a cell body.

2. When installing, insert the electrode and gas pipe into the electrolytic cell, then install the sealing ring and cover the cover

3. The optical water bath electrolytic cell is installed
Designed for You
KinTek provide deep custom made service and equipment to worldwide customers, our specialized teamwork and rich experienced engineers are capable to undertake the custom tailoring hardware and software equipment requirements, and help our customer to build up the exclusive and personalized equipment and solution!
Would you please drop your ideas to us, our engineers are ready for you now!
Trusted by Industry Leaders

FAQ
What Are Electrolytic Cells Used For?
What Are The Materials Used In Electrochemical Cell?
What Is The Difference Between Galvanic Cell And Electrolytic Cell?
What Are The Examples Of Electrochemical Material?
What Is An Electrolytic Cell And How Does It Work?
What Are The Two Points Of Difference Between Electrochemical And Electrolytic Cells?
What Is The Example Of Electrolytic Cell?
Are Electrolytic Cells Spontaneous?
4.8 / 5
This device has exceeded my expectations for quality. It has been a great addition to our lab, and we appreciate the fast delivery.
4.9 / 5
The optical water bath electrolytic cell is an amazing piece of equipment. It's easy to use and provides consistent, accurate results. I highly recommend it!
4.7 / 5
The Optical water bath electrolytic cell has been a valuable addition to my lab. It's well-made, easy to use, and provides reliable results. I highly recommend it.
4.6 / 5
I'm very impressed with the optical water bath electrolytic cell. It's a great value for the price and has helped me to improve the efficiency of my lab work.
5.0 / 5
The optical water bath electrolytic cell is a great product. It's easy to use and clean, and it provides accurate results. I highly recommend it.
4.8 / 5
I'm very happy with the optical water bath electrolytic cell. It's a great value for the price and has helped me to improve the accuracy of my experiments.
4.9 / 5
The optical water bath electrolytic cell is a great product. It's easy to use and provides consistent results. I highly recommend it!
4.7 / 5
The optical water bath electrolytic cell is a great value for the price. It's easy to use and has helped me to improve the efficiency of my lab work.
4.6 / 5
I'm very impressed with the optical water bath electrolytic cell. It's a great value for the price and has helped me to improve the accuracy of my experiments.
5.0 / 5
The optical water bath electrolytic cell is a great product. It's easy to use and clean, and it provides accurate results. I highly recommend it.
4.8 / 5
I'm very happy with the optical water bath electrolytic cell. It's a great value for the price and has helped me to improve the efficiency of my lab work.
4.9 / 5
The optical water bath electrolytic cell is a great product. It's easy to use and provides consistent results. I highly recommend it!
4.7 / 5
The optical water bath electrolytic cell is a great value for the price. It's easy to use and has helped me to improve the efficiency of my lab work.
4.6 / 5
I'm very impressed with the optical water bath electrolytic cell. It's a great value for the price and has helped me to improve the accuracy of my experiments.
5.0 / 5
The optical water bath electrolytic cell is a great product. It's easy to use and clean, and it provides accurate results. I highly recommend it.
4.8 / 5
I'm very happy with the optical water bath electrolytic cell. It's a great value for the price and has helped me to improve the efficiency of my lab work.
REQUEST A QUOTE
Our professional team will reply to you within one business day. Please feel free to contact us!
Related Products

Multifunctional Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell Water Bath Single Layer Double Layer
Discover our high-quality Multifunctional Electrolytic Cell Water Baths. Choose from single or double-layer options with superior corrosion resistance. Available in 30ml to 1000ml sizes.

Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell Gas Diffusion Liquid Flow Reaction Cell
Looking for a high-quality gas diffusion electrolysis cell? Our liquid flow reaction cell boasts exceptional corrosion resistance and complete specifications, with customizable options available to suit your needs. Contact us today!

Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Five-Port
Streamline your laboratory consumables with Kintek's Electrolytic Cell with five-port design. Choose from sealed and non-sealed options with customizable electrodes. Order now.

PTFE Electrolytic Cell Electrochemical Cell Corrosion-Resistant Sealed and Non-Sealed
Choose our PTFE Electrolytic Cell for reliable, corrosion-resistant performance. Customize specifications with optional sealing. Explore now.

Quartz Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Electrochemical Experiments
Looking for a reliable quartz electrochemical cell? Our product boasts excellent corrosion resistance and complete specifications. With high-quality materials and good sealing, it's both safe and durable. Customize to meet your needs.

Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
Looking for corrosion-resistant coating evaluation electrolytic cells for electrochemical experiments? Our cells boast complete specifications, good sealing, high-quality materials, safety, and durability. Plus, they're easily customizable to meet your needs.

H Type Electrolytic Cell Triple Electrochemical Cell
Experience versatile electrochemical performance with our H-type Electrolytic Cell. Choose from membrane or non-membrane sealing, 2-3 hybrid configurations. Learn more now.

Super Sealed Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
Super-sealed electrolytic cell offers enhanced sealing capabilities, making it ideal for experiments that require high airtightness.

Flat Corrosion Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
Discover our flat corrosion electrolytic cell for electrochemical experiments. With exceptional corrosion resistance and complete specifications, our cell guarantees optimal performance. Our high-quality materials and good sealing ensure a safe and durable product, and customization options are available.
Related Articles

The Art of Resistance: Why Your Electrolytic Cell Needs Breathing Room
Short circuits in electrolytic cells aren't just accidents; they are geometry failures. Learn how to control the electrical path and protect your lab equipment.

The Architecture of Precision: Mastering Electrolytic Cell Maintenance
Reliable data starts with disciplined maintenance. Discover the psychological and technical approach to preserving electrolytic cells for peak performance.

The Glass Heart of the Experiment: Precision Through Systematic Care
Routine maintenance of double-layer electrolytic cells isn't just cleaning—it's calibration. Discover the systematic protocol for reproducible electrochemical data.

Exploring the Multifunctional Electrolytic Cell Water Bath: Applications and Benefits
Discover the versatile applications of multifunctional electrolytic cell water baths in various industries. Learn about their benefits, components, and how they facilitate chemical reactions and temperature control.

The Architecture of Reaction: Selecting the Right Electrolytic Cell Body
Discover how cell volume and sealing impact electrochemical data. Learn to balance scarcity, scale, and sensitivity with the right lab equipment choices.

The Architecture of Precision: Why the Invisible Details Define Electrochemical Success
Master the art of pre-use inspection for electrolytic cells. From physical integrity to electrode purity, learn why the invisible details dictate experimental safety.

Advanced Electrolytic Cell Techniques for Cutting-Edge Lab Research
Electrolytic cells are devices that utilize an electric current to induce a non-spontaneous chemical reaction.

The Quiet Discipline: Mastering the Post-Use Protocol for Five-Port Electrolytic Cells
Learn the methodical post-use care for five-port water bath electrolytic cells. Prevent corrosion, ensure safety, and protect your experimental data.

The Transparency Paradox: Mastering the Fragile Art of Electrolytic Cells
Glass electrolytic cells are precision instruments, not simple containers. Learn the systematic approach to handling glass to ensure safety and data integrity.

Understanding Electrolytic Cells and Their Role in Copper Purification and Electroplating
Electrolytic cells play a crucial role in various industrial processes, including copper purification and electroplating. These cells utilize an external power source to drive chemical reactions, resulting in the decomposition of substances. Through the process of electrolysis, an electric current is passed through a liquid or solution containing ions, causing them to break down.

Comparing the Features of Laboratory Waterbaths: A Guide to Finding the Right Waterbath for Your Needs
Water bath is a common piece of laboratory equipment that is used to heat samples or substances to a specific temperature.

Optical Quartz Plate: A Comprehensive Guide to Applications, Specifications, and Usage
Discover the versatility of optical quartz plates, exploring their uses in various industries, key specifications, and factors that differentiate them from glass. Gain insights into their applications in ultraviolet transmission, precision optics, and more.