Introduction to Molecular Distillation and High Purity Metals
Demand for High Purity Metals
High purity metals are experiencing a surge in demand, driven by their critical roles in cutting-edge technologies across multiple sectors. These metals are indispensable in the development of new energy solutions, where their high conductivity and low impurity levels are essential for efficient energy conversion and storage. In the electronics industry, high purity metals are fundamental to the performance and reliability of semiconductors, ensuring optimal functionality in devices ranging from smartphones to advanced computing systems.
In the optoelectronics field, the precise control of metal purity enables the creation of materials with superior optical properties, crucial for applications in lasers, LEDs, and photovoltaic cells. The medical sector also benefits from high purity metals, which are used in the fabrication of medical devices that require exceptional biocompatibility and durability. Additionally, the aerospace industry relies on these metals for their superior strength and resistance to corrosion, ensuring the safety and longevity of structures exposed to extreme conditions.
The increasing demand for high purity metals underscores their irreplaceable value in modern technology, where even trace impurities can significantly impact performance and reliability. This growing need is expected to drive further innovation and investment in purification technologies, such as molecular distillation, to meet the stringent purity requirements of these high-stakes applications.
Role of Molecular Distillation
Molecular distillation stands as a pivotal separation technology in the realm of high purity metal preparation. Operating under extremely low pressures, typically below 0.01 torr (1.3 Pa), this technique leverages the free molecular flow regime where the mean free path of molecules is comparable to the size of the equipment. This unique operating condition ensures that the gaseous phase exerts minimal pressure on the substance being evaporated, thereby decoupling the rate of evaporation from pressure.
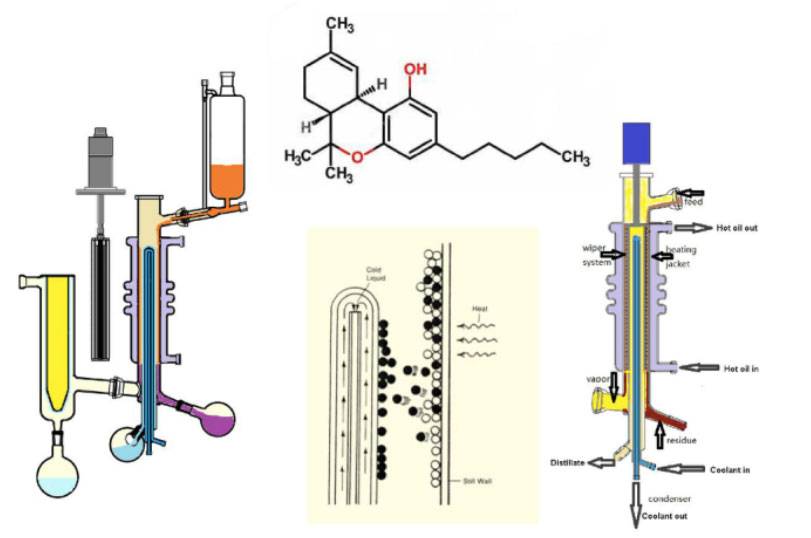
In molecular distillation, the process involves heating the substances to evaporate them, followed by immediate cooling and condensing the evaporated material. This sequence allows for the separation of different components based on their boiling points, a critical aspect in achieving high purity levels. The short path between the hot and cold surfaces, often facilitated by a high purity graphite crucible and a cold plate with a clear line of sight, is essential to maintain the efficiency and effectiveness of the distillation process.
The advantages of molecular distillation are manifold, particularly in the context of high purity metal preparation. Firstly, it avoids the toxicity issues associated with solvents used in traditional separation methods. Secondly, the process minimizes thermal decomposition losses by operating under reduced pressures and temperatures. Additionally, molecular distillation can be integrated into continuous feed processes, allowing for uninterrupted distillate harvesting without breaking the vacuum. This stability is crucial for maintaining the integrity of thermally sensitive, high molecular weight materials, ensuring that their purity and structural properties are preserved throughout the purification process.
Furthermore, the application of molecular distillation extends beyond just metal purification. It is extensively used in various industries, including electronics, solar cells, optoelectronics, medical devices, and aerospace. In each of these sectors, the ability to achieve and maintain high purity levels is paramount, underscoring the indispensable role of molecular distillation in modern industrial processes.
Mechanism and Advantages of Molecular Distillation
Separation and Purification Process
Molecular distillation is a sophisticated process that involves heating substances to their boiling points, causing them to evaporate. The evaporated material is then rapidly cooled and condensed, allowing for the separation of different components based on their distinct boiling points. This method is particularly effective for high purity metal preparation due to the significant differences in boiling points among various metal compounds.
The process can be broken down into several key steps:
-
Heating: The substances are heated under vacuum conditions to facilitate evaporation. The vacuum reduces the pressure on the substances, lowering their boiling points and preventing decomposition.
-
Evaporation: As the substances reach their boiling points, they vaporize. The speed of this process is crucial; rapid evaporation ensures that the components do not have time to interact with each other, maintaining their purity.
-
Cooling and Condensation: The vapor is then rapidly cooled and condensed into a liquid form. This step is critical for separating the components based on their boiling points, as each component will condense at a specific temperature.
This method leverages the large differences in boiling points to evaporate and condense components separately, achieving effective separation and purification. The result is a highly purified metal that meets the stringent requirements of various industries, from electronics to aerospace.
Advantages in High Purity Metal Preparation
Molecular distillation offers several distinct advantages in the preparation of high purity metals, primarily due to its ability to leverage significant differences in boiling points. This technique involves heating the metal compounds to a point where they evaporate, followed by rapid cooling and condensation of these vapors. By carefully controlling the temperature and pressure during this process, it is possible to separate and purify components based on their unique boiling points.
This method is particularly effective for metals that have impurities with markedly different boiling points. For instance, the process can efficiently remove low-boiling-point impurities by evaporating them first, while high-boiling-point impurities are left behind. This selective evaporation and condensation not only enhance the purity of the metal but also preserve its structural integrity, which is crucial for applications in industries such as electronics, aerospace, and medical devices.
Moreover, molecular distillation allows for continuous and large-scale operations, making it a scalable solution for industrial production. The ability to handle high volumes of material without compromising on purity levels is a significant advantage, especially in sectors where high throughput is necessary. This scalability ensures that the technology can meet the growing demand for high purity metals across various industries, from electronics to aerospace.

In summary, the advantages of molecular distillation in high purity metal preparation lie in its precision, scalability, and effectiveness in achieving high levels of purity by exploiting the natural differences in boiling points of different metal components.
Applications of Molecular Distillation in Various Industries
Preparation of Electronic Materials
Molecular distillation plays a pivotal role in the purification of metal materials, significantly enhancing the performance of electronic components. By improving the purity of these materials, molecular distillation ensures that electronic devices operate more efficiently and reliably. This process is particularly crucial in the manufacturing of semiconductors and other sensitive electronic components, where even trace impurities can lead to significant performance degradation.
The enhanced purity achieved through molecular distillation results in several key benefits for electronic materials:
- Increased Conductivity: High purity metals exhibit superior electrical conductivity, which is essential for minimizing energy loss in electronic circuits.
- Improved Thermal Stability: Purified metals are less prone to thermal degradation, ensuring that electronic components can withstand higher temperatures without compromising performance.
- Enhanced Reliability: The removal of impurities reduces the likelihood of defects and failures, leading to more durable and reliable electronic devices.
In summary, molecular distillation is not merely a purification process but a critical step in the production of high-performance electronic materials, contributing to the advancement of modern electronics.
Solar Cell Preparation
The application of molecular distillation in the preparation of solar cells significantly enhances the energy conversion efficiency by refining the purity of semiconductor materials. This technology plays a crucial role in the purification process, ensuring that the semiconductor materials are free from impurities that could otherwise hinder optimal performance.
Molecular distillation operates by heating the semiconductor materials to their evaporation point, followed by rapid cooling and condensation. This process effectively separates the pure semiconductor components from any contaminants, leveraging the substantial differences in boiling points between the desired materials and impurities. The result is a highly purified semiconductor material that is essential for the efficient operation of solar cells.
Moreover, the benefits of molecular distillation extend beyond mere purification. The technique also contributes to the structural integrity and crystalline properties of the semiconductor materials, further boosting their performance. This dual advantage ensures that solar cells not only convert sunlight into electricity more efficiently but also maintain their durability and longevity under various environmental conditions.
In summary, molecular distillation is a pivotal technology in the preparation of solar cells, offering a comprehensive solution to both purification and structural enhancement, thereby significantly improving the overall efficiency and reliability of solar energy conversion systems.
Optoelectronic Materials
Molecular distillation plays a pivotal role in the production of optoelectronic materials, which are essential for devices such as LEDs, photodetectors, and optical fibers. By refining the purity and crystal structure of metals, this advanced separation technique significantly enhances the optical properties of these materials.
The process begins with the careful selection of raw materials, which are then subjected to molecular distillation. This method involves heating the substances to their evaporation points and subsequently condensing the vapor to separate and purify the components based on their distinct boiling points. The result is a material with reduced impurities and a more uniform crystal structure, both of which are critical for optimal optical performance.
For instance, in the case of indium tin oxide (ITO), a common material used in transparent conductive coatings, molecular distillation can remove trace elements that might otherwise degrade its transparency and conductivity. Similarly, in the production of gallium arsenide (GaAs) for high-efficiency solar cells, the technique ensures that the semiconductor material is free from contaminants that could lower its energy conversion efficiency.
The benefits of molecular distillation extend beyond just purity; it also contributes to the structural integrity of the materials. A well-ordered crystal structure is crucial for minimizing light scattering and maximizing the transmission of photons, which is essential for optoelectronic applications. This dual enhancement in purity and structure makes molecular distillation an indispensable process in the fabrication of high-performance optoelectronic materials.
Medical Device Preparation
Molecular distillation plays a pivotal role in ensuring the safety and stability of medical devices by achieving the high purity required for these critical applications. The technology is particularly essential in the production of components that directly interact with biological systems, such as surgical instruments, implants, and diagnostic equipment.
The purification process facilitated by molecular distillation involves the precise separation of impurities, which can compromise the functionality and safety of medical devices. By leveraging large differences in boiling points, this technique effectively evaporates and condenses components separately, thereby achieving a level of purity that is crucial for medical applications.
Moreover, the high purity metals obtained through molecular distillation are instrumental in enhancing the durability and reliability of medical devices. This is particularly important in environments where even trace amounts of contaminants can lead to adverse effects, such as in the human body or in sensitive diagnostic processes. The use of molecular distillation ensures that medical devices not only meet regulatory standards but also exceed them, providing an added layer of assurance for both manufacturers and end-users.
In summary, molecular distillation is indispensable in the preparation of medical devices, offering a robust solution for achieving the stringent purity requirements necessary for their safe and effective use.
Aerospace Industry
High purity metal materials play a pivotal role in enhancing the durability and reliability of aerospace structures. These materials are meticulously refined through processes like molecular distillation, which strip away impurities to leave metals with unparalleled strength and corrosion resistance. This purification process is crucial for aerospace applications, where materials must withstand extreme conditions such as high altitudes, intense temperature fluctuations, and corrosive atmospheric elements.
In the context of aerospace engineering, the use of high purity metals ensures that components such as fuselage panels, engine parts, and landing gear can endure the rigors of flight without compromising structural integrity. For instance, titanium alloys, known for their high strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, are often employed in critical areas of aircraft. These alloys are typically subjected to molecular distillation to achieve the necessary purity levels, thereby enhancing their performance and longevity.
Moreover, the enhanced corrosion resistance of high purity metals is particularly vital in aerospace applications. Corrosion can lead to significant structural degradation over time, posing safety risks and necessitating costly maintenance. By utilizing high purity metals, aerospace manufacturers can mitigate these risks, ensuring that aircraft remain safe and operational for extended periods. This not only enhances the overall safety of air travel but also reduces the operational costs associated with frequent maintenance and repairs.
In summary, the integration of high purity metal materials, refined through advanced techniques like molecular distillation, is essential for the aerospace industry. These materials not only bolster the mechanical properties of aerospace structures but also ensure their resilience against the harsh environmental conditions encountered during flight.
Conclusion
Future Prospects of Molecular Distillation
Molecular distillation holds immense potential for future advancements, particularly in the realm of metal materials. As technology continues to evolve, the capabilities of molecular distillation are expected to expand, offering more efficient and effective methods for separation and purification. This technology is poised to play a pivotal role in enhancing the quality and reliability of various products, from fine chemicals to high-purity metals.
One of the key advantages of molecular distillation is its ability to operate under reduced pressure, which significantly lowers the boiling points of substances. This characteristic is particularly beneficial for heat-sensitive materials, such as tocopherols, lactic acid, and omega-3 fatty acids, which can be denatured at high temperatures. By maintaining optimal conditions for extraction, molecular distillation preserves the chemical integrity of these compounds, ensuring higher quality end products.
Moreover, the application of molecular distillation in the production of high-purity metals is set to grow. The technique's effectiveness in separating components based on their boiling points makes it an ideal choice for refining metals used in electronics, solar cells, optoelectronics, medical devices, and aerospace structures. As industries demand materials with superior purity and performance, molecular distillation stands to become an indispensable tool in meeting these requirements.
Despite the higher initial costs associated with molecular distillation equipment compared to standard distillation methods, the long-term benefits far outweigh the investment. The high efficiency and reduced maintenance time contribute to lower overall distillation costs, making it a cost-effective solution in the long run. Additionally, the continuous improvement and expansion of molecular distillation technology, driven by ongoing research and development, promise to unlock new applications and further enhance its efficiency.
In summary, the future prospects of molecular distillation are both broad and significant, with the potential to revolutionize various industries by providing superior separation and purification processes. As technological advancements continue to unfold, molecular distillation is expected to remain at the forefront of innovation, driving progress in the field of metal materials and beyond.
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Wall Mounted Water Distillation Unit
Related Articles
- The Furnace Dilemma: Choosing Between Precision and Scale in Thermal Processing
- Vacuum Laboratory Furnaces in Advanced Materials Research
- Exploring Tungsten Vacuum Furnaces: Operation, Applications, and Advantages
- Why Your High-Temperature Processes Fail: The Hidden Enemy in Your Vacuum Furnace
- Materials Science with the Lab Vacuum Furnace





