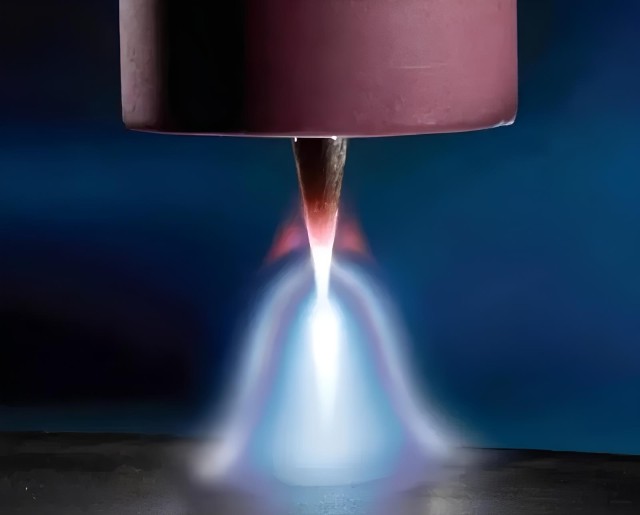
Understanding the Submerged Electric Arc Furnace Principle
The submerged electric arc furnace principle, also known as the arc resistance furnace, utilizes both the heat generated by the resistance of the charge and the heat produced by the arc between the electrode and the charge. This unique heating mechanism is pivotal in various metallurgical processes, particularly in the smelting of metals without altering their chemical properties.

Composition and Working Principle
The submerged arc furnace is constructed using ore with high resistivity as its raw material. During operation, the lower part of the electrode is typically submerged within the charge. Key components of the submerged arc furnace include:
- Power Supply System: This comprises the submerged arc furnace transformer, high-current conductor (short net), electrode, electric furnace body, cooling system, feeding system, discharging system, and dust removal system.
Charge Composition
The primary component of the charge during metal smelting in an arc furnace is steel scrap, supplemented with iron ore pellets. The recycling of steel in electric arc furnaces demands specific material quality, including:
- Minimal impurities of non-ferrous metals
- Low oxidation levels, free from rust
- Phosphorus content not exceeding 0.05%
Additionally, there is a growing trend in the utilization of primary iron ore processing products such as sponge iron and metallized pellets in electric arc furnaces.
Arc Melting Furnace
The Arc Melting Furnace operates on principles akin to an arc-welding machine, where an electrical arc is generated between two electrodes. This high-energy arc produces temperatures ranging from 3,000 to 7,000 degrees Celsius, forming a highly ionized gas known as "plasma." The plasma can be precisely directed onto a material specimen.
Arc Melting Furnace Types and Applications
Arc melting furnaces come in various types, primarily categorized into alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) operated electric furnaces. These furnaces are instrumental in metallurgical processes, particularly in the production of steel, where they are utilized for melting metal ore or scrap metal without altering the metal's chemical properties.
Conclusion
The submerged electric arc furnace principle plays a crucial role in modern metallurgy, enabling the efficient smelting of metals while maintaining their chemical integrity. With advancements in technology and the growing adoption of innovative furnace designs, the arc melting process continues to drive progress in the steel industry.
Types of Electric Furnaces
Electric furnaces play a crucial role in various industrial processes, providing the high temperatures necessary for material preparation and production. This section examines the two primary types of electric furnaces: alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) operated electric furnaces. We will highlight their differences and applications, focusing on how they contribute to various industrial processes.
Alternating Current (AC) Electric Furnaces
AC electric furnaces are widely used in industrial processes for their versatility and reliability. These furnaces operate by utilizing alternating current to generate heat. They are commonly employed in applications such as:
-
Melting Metals: AC electric furnaces are commonly used for melting metals, making them a crucial component in metal refining processes.
-
Graphitization: The Acheson-type graphitization furnace is based on AC technology. Although AC furnaces have been the industry standard for many years, they have certain limitations compared to DC furnaces.
Advantages of AC Electric Furnaces:
-
Wide Application: AC electric furnaces are suitable for a variety of industrial applications, including metal melting and graphitization.
-
Proven Technology: AC electric furnaces have been widely used and perfected over the years, making them a reliable choice for industrial heating processes.
Direct Current (DC) Electric Furnaces
DC electric furnaces have emerged as a more advanced option compared to AC furnaces, offering several advantages in terms of capacity, product quality, and energy consumption. These furnaces operate by utilizing direct current to generate heat. They are commonly employed in applications such as:
-
Graphitization: DC electric furnaces have revolutionized the graphitization process, offering significant advantages over AC furnaces.
-
Plasma Furnaces: Various DC plasmatrons are used in plasma furnaces, providing more homogeneous heating, particularly in large-scale operations.
Advantages of DC Electric Furnaces:
-
Large Capacity: DC electric furnaces offer a larger capacity compared to AC furnaces, making them suitable for high-volume industrial processes.
-
Improved Product Quality: DC electric furnaces contribute to better product quality due to their advanced technology and precise temperature control.
-
Energy Efficiency: DC electric furnaces have lower energy consumption compared to AC furnaces, resulting in cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
Types of DC Electric Arc Furnaces:
-
Single Metal Anode Arrangement: In this arrangement, a single metal anode is placed at the bottom of the furnace. It is water-cooled to prevent overheating.
-
Conducting Hearth with C-MgO Lining: The anode serves as the conducting hearth, lined with C-MgO. Cooling is achieved by air circulation.
-
Metal Rods as Anode: Metal rods act as the anode, embedded in MgO mass.
-
Thin Sheets as Anode: Thin sheets serve as the anode, also entrenched in MgO mass.
Electric furnaces are a critical component of various industrial processes, providing the high temperatures necessary for material preparation and production. Whether utilizing AC or DC technology, these furnaces play a vital role in modern manufacturing and refining processes.
Working Principles and Applications
Explore the working principles of arc melting furnaces and their diverse applications in laboratory settings. Discuss the significance of arc heating and induction heating modes, emphasizing their roles in metal smelting, heat treatment, and characteristic research.
The principle of operation of electric arc furnaces
Electric arc furnaces operate on three-phase electric current. Metal smelting in an arc furnace occurs by forming an electric arc between the graphitized electrodes and the charge to be melted. Such equipment is called a straight arc furnace. There are also electric arc furnaces of indirect action, in which the arc is at some distance from the heated metal.
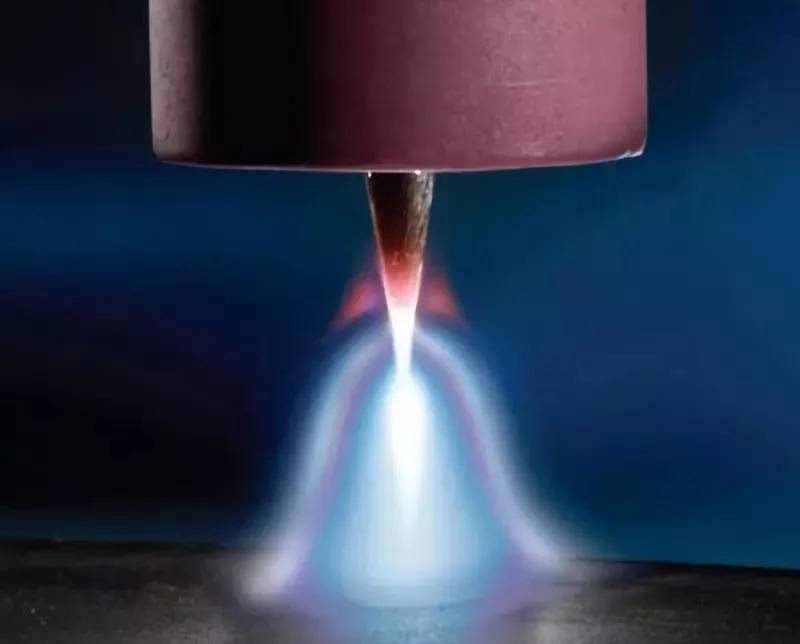

The use of vacuum in electric arc and induction furnaces allows the smelting of refractory metals and the production of special corrosion-resistant and heat-resistant alloys. Vacuum arc furnace assumes that the electric arc burns under reduced pressure, and the temperature is 3700 °C. Electric arc furnaces of this type require a constant current, which ensures the stability of the burning of the electrodes. This is primarily a straight arc furnace in which the function of the cathode is performed by the electrode, and the charge to be melted is the anode.
Steel smelting in electric arc furnaces is one of two main methods:
- Other Aspects
- Alloy element smelting: The induction furnace has a higher metal recovery rate than the arc furnace.
- Alloy element smelting burn-out ratio: This is lower in the induction furnace process than the arc furnace process.
- Environmental concerns: Induction furnaces are better for the environment, in part because arc furnace steelmaking results in a lot of waste residue, exhaust gas, noise, and energy. Since no graphite electrodes are used in an induction furnace, there is no carbon pick up.
Working principle and use method of melting furnace in laboratory
The melting furnace can be divided into arc melting furnace and induction heating furnace according to the heating method.
The smelting furnace is mainly used for metal smelting, heat treatment, and characteristic research of laboratories. Smelting is the process of melting solid metal into liquid by the heating furnace and tempering it. It is also one of the casting production processes. Melting and re-cooling of metals involve complex crystallization processes that can significantly alter the properties of the metal. The melting furnace has two heating modes of arc heating and induction heating.
Advantages of Arc Melting Furnaces
Arc melting furnaces offer several distinct advantages in the steelmaking process, making them a preferred choice for many industries. Let's delve into these advantages:

Larger Size and Power
One of the notable advantages of arc melting furnaces is their substantial size and power capacity. Compared to other types of melting furnaces, arc furnaces tend to be larger and more powerful. This characteristic enables them to handle larger quantities of scrap steel and melt it efficiently.
Quick Construction and Fast Cost Recovery
Arc furnaces are known for their relatively quick construction process compared to other types of furnaces. This swift setup allows for faster deployment and integration into steelmaking facilities. Additionally, the fast construction translates to rapid cost recovery, making arc furnaces an economically viable option for steel manufacturers.
Precise Temperature Control
Temperature control is crucial in steelmaking processes to ensure the desired quality and properties of the final product. Arc melting furnaces excel in this aspect by offering precise temperature control mechanisms. Operators can accurately regulate the temperature within the furnace, allowing for optimal smelting conditions and consistent steel quality.
Versatility in Smelting Various Steels
Arc furnaces boast versatility in smelting different types of steels, including those containing refractory elements such as tungsten (W) and molybdenum (Mo). This capability enables the production of a wide range of steel compositions tailored to specific industrial requirements. Moreover, arc furnaces can efficiently remove toxic gases and inclusions while deoxidizing and desulfurating the molten steel, contributing to enhanced product purity.
Environmental Benefits
In addition to their operational advantages, arc melting furnaces offer environmental benefits. They provide an efficient means to significantly reduce carbon emissions in steel production compared to traditional methods. By employing Best Available Control Technology (BACT) and Maximum Achievable Control Technology (MACT), arc furnaces can effectively capture, control, and mitigate emissions, aligning with sustainability goals and regulatory standards.
High Flexibility
Arc furnaces demonstrate high flexibility in production processes, allowing for continuous or intermittent operation as needed. This flexibility enables steel manufacturers to adapt to varying demand levels and production requirements efficiently. Whether engaging in continuous mass production or intermittent specialized runs, arc melting furnaces offer the versatility to meet diverse operational needs.
In summary, arc melting furnaces stand out for their larger size and power capacity, quick construction, precise temperature control, versatility in smelting various steels, environmental benefits, and high flexibility in production. These advantages make arc furnaces a preferred choice for steelmakers seeking efficient and sustainable steel production solutions.
Electric Arc Furnace: Steel Industry Application
Electric Arc Furnace and its Functionality
An Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) stands as a cornerstone in the steel industry's arsenal of melting furnaces. Its primary function revolves around the utilization of electrical energy to melt scrap metal, thereby facilitating steelmaking processes. Operating at staggering temperatures of up to 3000°F, these furnaces ensure precise temperature control, crucial for both safety and efficiency.

Advantages of Electric Arc Furnace for Steel-making
Industrial Versatility
Electric arc furnaces exhibit a wide range of sizes tailored to various industrial needs. Ranging from petite units with capacities of a few dozen grams, commonly found in research laboratories and dental practices, to mammoth units capable of handling up to 400 tons, predominantly used in secondary steelmaking. The average capacity typically falls within the range of 80 to 120 metric tons.
Temperature Capabilities
In the realm of industrial electric arc furnaces, temperatures soar up to 1,800°C (3,272°F), while their laboratory counterparts can exceed a blistering 3,000°C (5,432°F). Such extreme temperatures are instrumental in achieving the desired steel properties and purity levels.
Widely Adopted Technology
Electric arc furnaces reign supreme as the most prevalent steel furnace worldwide. Their adaptability allows for the smelting of high-quality steel and specialty alloys, catering to diverse industrial requirements.
Efficiency in Scrap Recycling
A notable application of electric arc furnaces lies in the recycling of steel scrap. These furnaces excel in re-melting steel scrap, contributing significantly to sustainable steel production practices. Smaller units find utility in producing cast-iron products, underscoring the versatility of this technology.
Operational Mechanism
Electric arc furnaces operate on the principle of utilizing electric arcs to generate heat. The arc initiates an electrical breakdown of gases, leading to a phenomenon known as "plasma discharge." This process expedites the melting of materials, ensuring rapid and efficient steel production. The furnace chamber facilitates direct contact between the material and the arc, enabling temperatures to reach remarkable levels, often surpassing 3275°F (1800°C).
Electrode Utilization
Central to the operation of electric arc furnaces are electrodes, which conduct electrical currents through the metal within the furnace. Foundries predominantly employ these furnaces for processing large slabs, beams, and shredded scrap. Upon filling the furnace tank with metal, electrodes are inserted, initiating an arc of electricity between them to induce melting. Additionally, oxygen may be introduced into the process to enhance efficiency and refine steel quality.
In essence, electric arc furnaces represent a pinnacle of innovation in the steel industry, blending efficiency, versatility, and sustainability to meet the ever-evolving demands of modern steelmaking processes.
For those seeking steel melting induction furnaces, the industrial landscape offers a plethora of options. Steel finds extensive usage across various sectors, with mechanical equipment and automotive applications constituting significant segments of its consumption. Up to 16% of the world's steel is channeled into mechanical equipment, including robotics and manufacturing, while the automotive industry accounts for approximately 13% of global steel usage.
Conclusion
The Arc Melting Furnace stands out for its high temperature capabilities, operational efficiency, and environmental benefits. It exemplifies a crucial tool in material science research and industrial applications, enabling precise control over the treatment of materials at extremely high temperatures. This furnace not only supports advanced research but also contributes to sustainable industrial practices. Through its versatile design and control features, it offers a robust solution for a wide range of melting and treatment processes, maintaining a high degree of purity and operational safety.
Related Products
- Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- Horizontal High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
Related Articles
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace: Principle, Advantages, and Applications
- Vacuum Induction Furnace Fault Inspection: Essential Procedures and Solutions
- Vacuum Laboratory Furnaces in Advanced Materials Research
- Exploring Tungsten Vacuum Furnaces: Operation, Applications, and Advantages
- Melting process and maintenance of vacuum induction melting furnace









