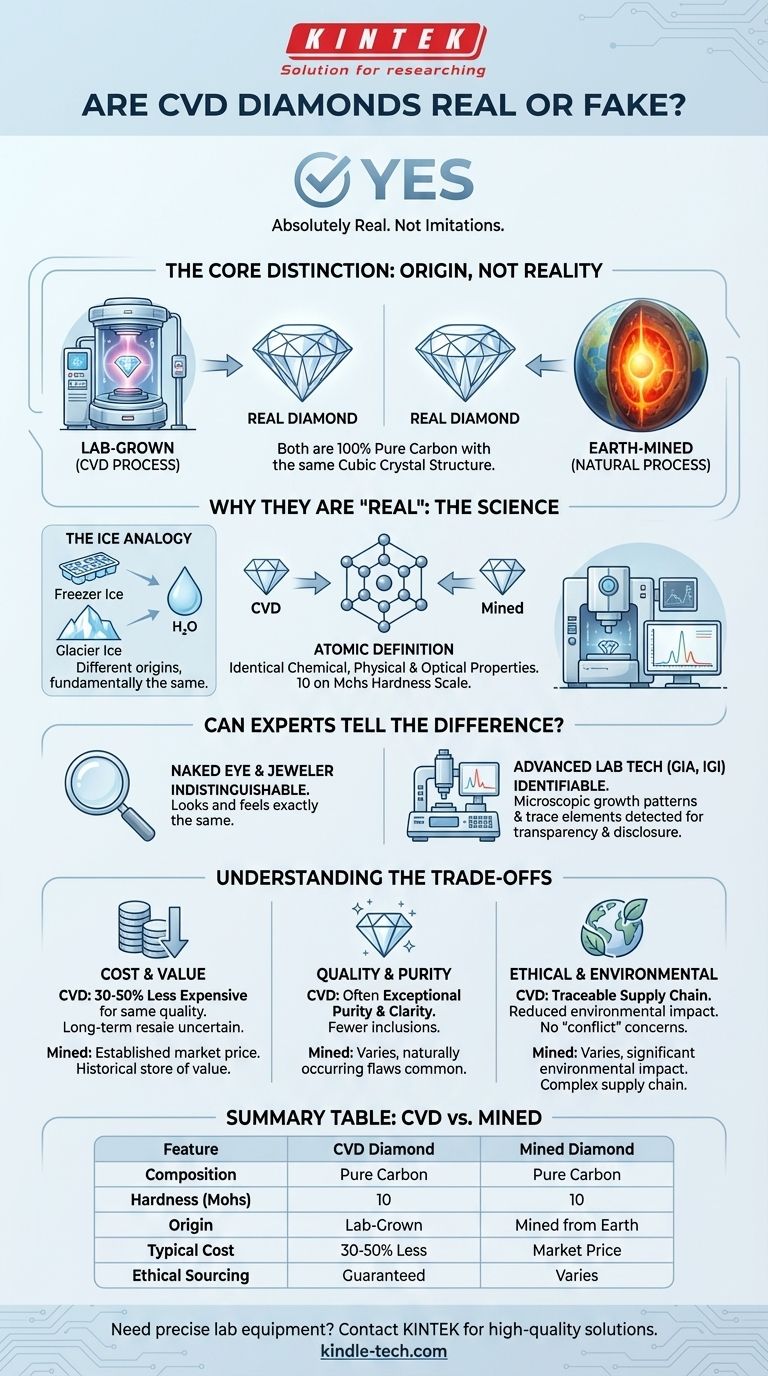
Yes, CVD diamonds are absolutely real diamonds. They are not imitations like cubic zirconia or moissanite. A diamond created via Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is physically, chemically, and optically identical to a diamond mined from the Earth, a fact recognized by official bodies like the U.S. Federal Trade Commission (FTC).
The core distinction is not between "real" and "fake," but between origin: one is grown in a lab and the other is extracted from the earth. Both are composed of pure carbon in the same crystal structure that defines a diamond.

What Makes a Diamond "Real"?
The "realness" of a diamond is determined by its atomic structure and chemical composition, not by how it was formed. Understanding this is key to seeing why CVD diamonds are not imitations.
The Atomic Definition of a Diamond
A diamond is defined by its material: carbon atoms arranged in a specific cubic crystal lattice. This unique structure is what gives a diamond its unparalleled hardness, brilliance, and fire.
Whether these carbon atoms were organized under immense pressure deep within the Earth's mantle or meticulously layered in a controlled lab environment, the resulting material is chemically identical.
The CVD Process vs. Nature's Process
Natural diamonds form over billions of years under extreme heat and pressure. The CVD process replicates the final stages of diamond formation in a highly controlled and accelerated manner.
The process starts with a tiny "seed" crystal, which is a very thin slice of a diamond. This seed is placed in a vacuum chamber filled with carbon-rich gases. When heated, these gases break apart, and the carbon atoms deposit onto the seed, growing the diamond layer by layer.
Identical Properties, Different Origin
The end product of the CVD process is a rough diamond that possesses the exact same properties as a mined rough diamond. It has the same hardness (10 on the Mohs scale), the same refractive index, and the same chemical purity.
An effective analogy is ice: ice from a freezer is just as real as ice from a glacier. They have different origins and formation stories, but they are both fundamentally frozen water (H₂O).
Can Experts Tell the Difference?
While CVD and mined diamonds are identical in composition, their different growth processes leave microscopic traces that can be identified with advanced technology.
Indistinguishable to the Naked Eye
It is impossible for anyone, even a trained jeweler, to distinguish a CVD diamond from a high-quality natural diamond using only a magnifying loupe or microscope. They look and feel exactly the same.
The Role of Gemological Labs
Major gemological laboratories like the Gemological Institute of America (GIA) and the International Gemological Institute (IGI) use sophisticated scientific equipment to determine a diamond's origin.
This equipment can detect subtle differences in the crystal growth patterns and trace elements that are characteristic of lab-grown diamonds. For this reason, reputable lab-grown diamonds are always sold with a certificate that clearly states their origin.
Why Identification Matters
The purpose of identifying a diamond as lab-grown is for transparency and market disclosure, not to label it as inferior or "fake." This allows consumers to know exactly what they are purchasing and allows the market to price the two categories of diamonds differently based on rarity and production cost.
Understanding the Trade-offs: CVD vs. Mined
Choosing between a CVD and a mined diamond involves weighing a clear set of trade-offs related to cost, value, and ethics.
Cost and Value
This is the most significant difference for most buyers. A CVD diamond is typically 30-50% less expensive than a mined diamond of the exact same size, cut, color, and clarity.
However, while mined diamonds have a long-established history as a store of value, the long-term resale value of lab-grown diamonds is less certain as production technology continues to evolve.
Quality and Purity
Because they are created in a meticulously controlled environment, CVD diamonds often exhibit exceptional purity and clarity. It is common for them to have fewer of the inclusions and blemishes (known as "flaws") that are frequently found in natural diamonds.
Ethical and Environmental Considerations
Lab-grown diamonds offer a clear and traceable supply chain. This completely sidesteps the concerns associated with "conflict diamonds" and reduces the significant environmental impact of large-scale mining operations.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should be based on your personal priorities. Both options result in a beautiful, genuine diamond.
- If your primary focus is maximizing size and quality for your budget: A CVD diamond delivers significantly more carat weight and clarity for the same price.
- If your primary focus is traditional symbolism and potential long-term resale value: A mined diamond with a reputable certificate is the established and conventional choice.
- If your primary focus is ethical and environmental transparency: A lab-grown diamond provides a clear and accountable origin story.
Ultimately, the choice is not between a real diamond and a fake one, but between two authentic diamonds with different histories and market values.
Summary Table:
| Feature | CVD Diamond | Mined Diamond |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Pure Carbon | Pure Carbon |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 10 | 10 |
| Origin | Lab-Grown | Mined from Earth |
| Typical Cost | 30-50% Less | Market Price |
| Ethical Sourcing | Guaranteed | Varies |
Need precise, reliable equipment for your laboratory? At KINTEK, we specialize in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, ensuring your research and production processes are efficient and accurate. Whether you're working with advanced materials or conducting critical analyses, our solutions are designed to meet your specific needs. Contact us today to learn how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- Why are carbon nanotubes important in industry? Unlocking Next-Generation Material Performance
- Are carbon nanotubes stronger than graphene? Choosing the Right Carbon Nanomaterial for Your Application
- What are the advantages of ion beam sputtering? Achieve Superior Thin Film Quality and Precision
- What are the methods of measuring thickness of thin films? A Guide to In-Situ and Ex-Situ Techniques
- What is deposition process in chemistry? A Guide to Thin-Film Engineering
- What is thickness uniformity of sputtering? The Key to Consistent Thin Film Quality
- What is the unit of deposition rate? Mastering Thin-Film Control for Precision Manufacturing
- What is sputter coating SEM? Achieve Clear, High-Resolution Imaging for Non-Conductive Samples



















