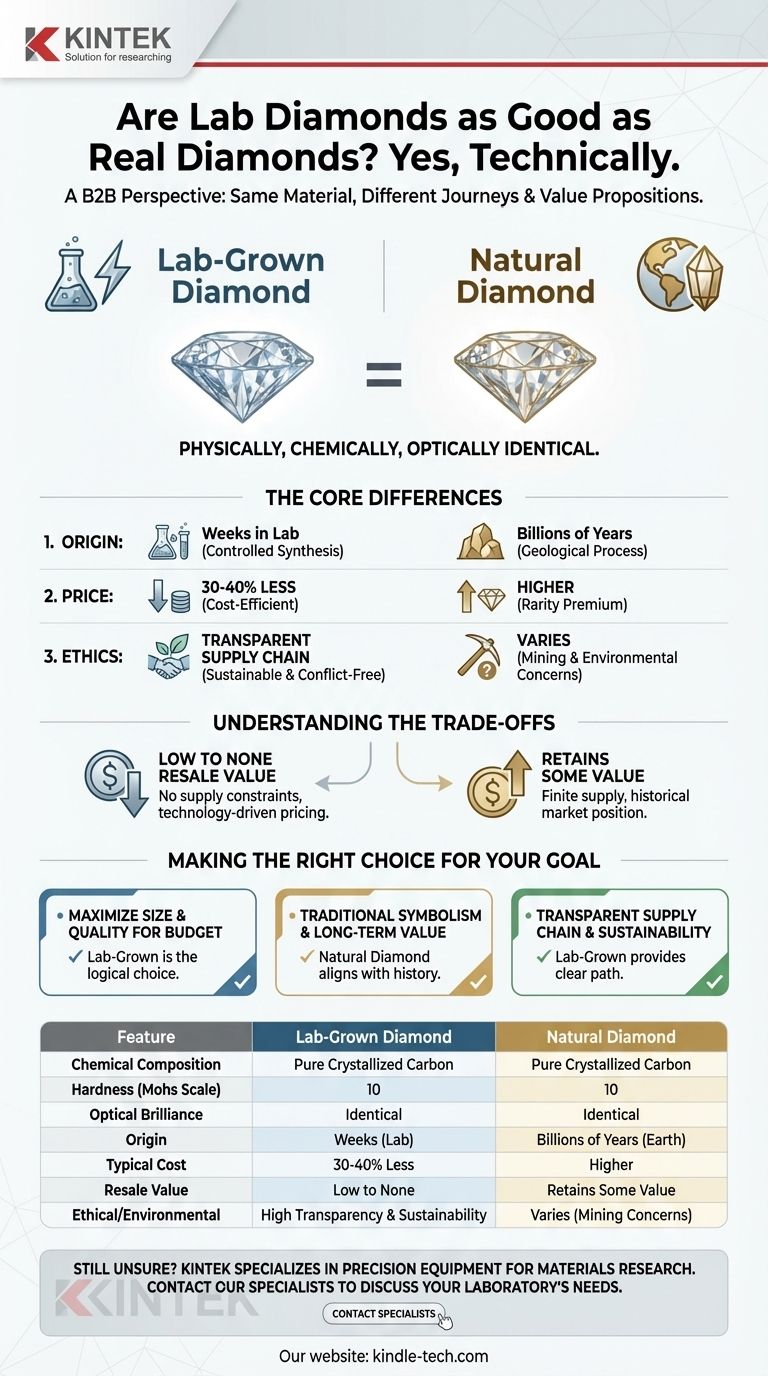
From a technical standpoint, yes. A lab-grown diamond is physically, chemically, and optically identical to a diamond mined from the earth. They possess the same crystal structure, hardness, and brilliance, making them indistinguishable to the naked eye and qualifying them as real diamonds in every scientific sense.
The question is not whether a lab diamond is as good as a natural diamond—they are physically the same material. The real choice is between the value of geological rarity and tradition versus the value of modern technology, cost efficiency, and supply chain transparency.
What Defines a "Real" Diamond?
At its core, a diamond is defined by its material properties, not its origin. A lab-grown diamond meets every technical requirement to be considered a genuine diamond.
Identical Chemical and Physical Structure
Both lab-grown and natural diamonds are crystallized carbon. They share the exact same chemical composition and crystal lattice structure, which is what gives them their exceptional hardness (10 on the Mohs scale) and durability.
Identical Optical Properties
A diamond's sparkle, or "fire," comes from the way it refracts and disperses light. Because lab-grown diamonds have the same refractive index and optical properties as natural ones, they exhibit the exact same brilliance and sparkle when cut to the same quality standards.
Indistinguishable to the Naked Eye
Side-by-side, there is no visual difference between a lab-grown and a natural diamond of the same carat, cut, color, and clarity. The only way to differentiate them is with specialized gemological equipment that can detect subtle variations in crystal growth patterns or trace elements.
The Core Differences: Origin and Price
While the final products are identical, their journeys from carbon to gemstone are vastly different. These differences are the true basis for comparison.
A Tale of Two Origins
A natural diamond is the result of a geological process taking billions of years, formed under immense heat and pressure deep within the earth. A lab-grown diamond is created in a highly controlled environment, replicating those same conditions over a matter of weeks.
The Impact on Cost
The primary advantage of lab-grown diamonds for most buyers is cost. By removing the immense expense, rarity, and uncertainty of mining, lab-grown diamonds can be 30-40% less expensive than natural diamonds of comparable size and quality.
The Ethical and Environmental Angle
Lab-grown diamonds offer a transparent and shorter supply chain. This eliminates the concerns over "conflict diamonds" and can offer a more sustainable alternative, especially when the labs are powered by renewable energy.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between a lab-grown and a natural diamond involves evaluating non-physical factors. Objectivity requires acknowledging the arguments for both.
The Question of Resale Value
This is the most significant financial trade-off. Natural diamonds, due to their finite supply and long-held market position, tend to retain a portion of their value over time. Lab-grown diamonds, being a product of technology with no supply constraints, currently have very little to no resale value.
The Perception of Rarity and Romance
For many, the value of a natural diamond is tied to its billion-year-old story and its status as a rare, natural treasure. This mystique and tradition are powerful emotional factors that technology cannot replicate.
An Evolving Market
The technology to produce lab-grown diamonds is constantly improving, and production is scaling. This means prices for lab-grown diamonds may continue to decrease over time, further distinguishing their market behavior from that of natural diamonds.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "better" option depends entirely on your personal priorities. Once you define your primary goal, the choice becomes clear.
- If your primary focus is maximizing carat size and quality for your budget: A lab-grown diamond is the logical choice, offering a significantly larger or higher-grade stone for the same price.
- If your primary focus is traditional symbolism and potential long-term value retention: A natural diamond better aligns with the historical significance and established market for fine jewelry.
- If your primary focus is a transparent supply chain and minimizing environmental impact: A lab-grown diamond provides a clear and accountable path from creation to consumer.
Ultimately, the "best" diamond is the one that perfectly reflects your own values, budget, and story.

Summary Table:
| Feature | Lab-Grown Diamond | Natural Diamond |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Pure Crystallized Carbon | Pure Crystallized Carbon |
| Hardness (Mohs Scale) | 10 | 10 |
| Optical Brilliance | Identical | Identical |
| Origin | Created in Weeks (Lab) | Billions of Years (Earth) |
| Typical Cost | 30-40% Less | Higher |
| Resale Value | Low to None | Retains Some Value |
| Ethical/Environmental | High Transparency & Sustainability | Varies (Mining Concerns) |
Still unsure which diamond is right for your needs? At KINTEK, we specialize in precision equipment and consumables for laboratories, including technology used in advanced material synthesis. Whether you're researching gemology or developing new materials, our expertise ensures you have the right tools for accurate analysis and innovation. Contact our specialists today to discuss how KINTEK can support your laboratory's specific requirements with reliable, high-performance solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- CVD Diamond Dressing Tools for Precision Applications
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between CVD and original diamond? Choose the Right Diamond for Your Needs
- What is the future of CVD diamond? Unlocking Next-Gen Electronics & Thermal Management
- What is the fluorescence of a CVD diamond? A Guide to Its Unique Glow and Purpose
- What is the future value of lab grown diamond? Understanding Its Depreciating Financial Worth
- Are CVD diamonds fake? Discover the Truth About Lab-Grown Diamonds












