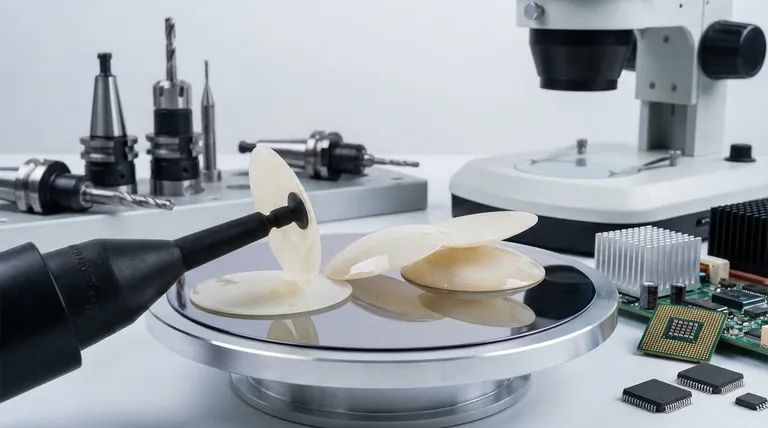
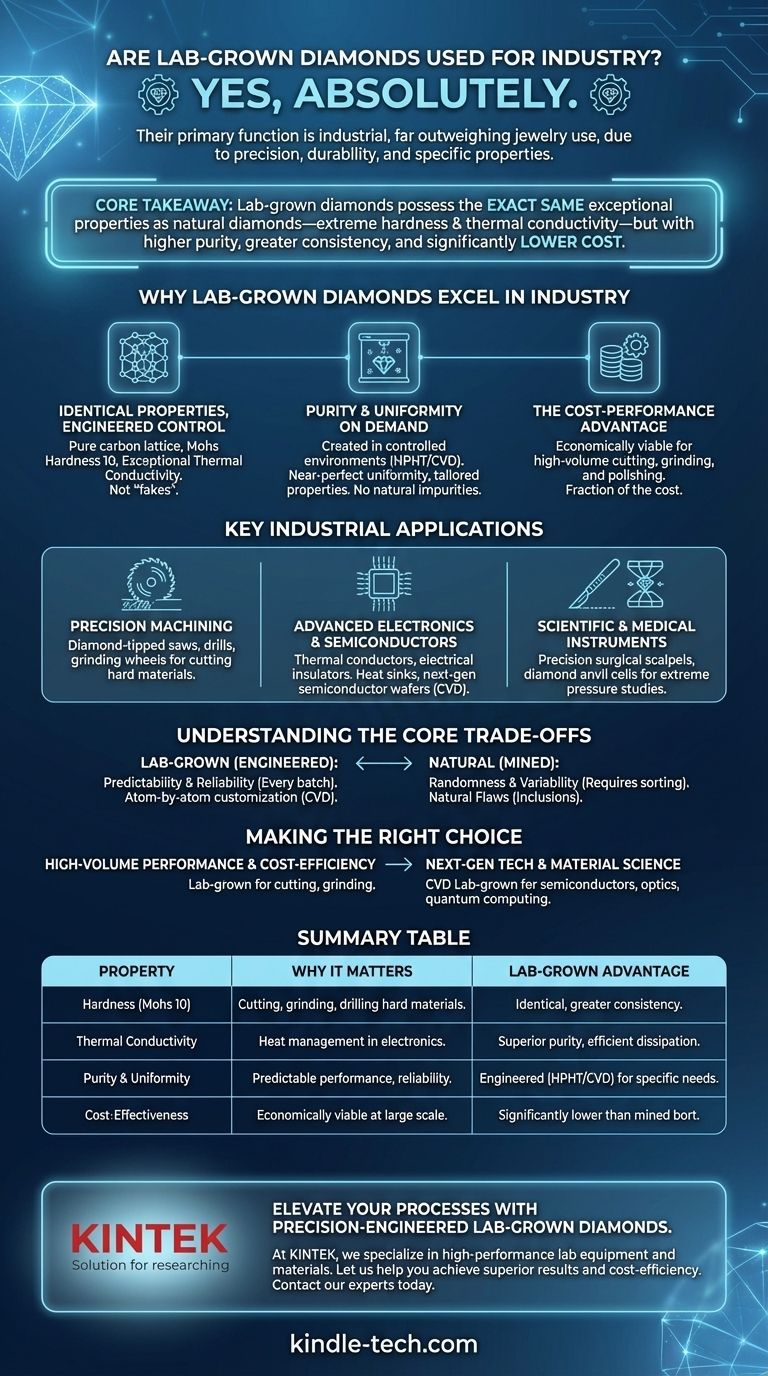
Yes, absolutely. Lab-grown diamonds are not only used for industrial purposes, but these applications are their primary function and far outweigh their use in jewelry. They are a critical component in fields where precision, durability, and specific material properties are non-negotiable, serving as a superior alternative to mined industrial diamonds.
The core takeaway is that lab-grown diamonds are favored in industry because they possess the exact same exceptional properties as natural diamonds—like extreme hardness and thermal conductivity—but can be produced with higher purity, greater consistency, and at a significantly lower cost.

Why Lab-Grown Diamonds Excel in Industry
The value of any diamond in an industrial setting is based on its physical properties, not its origin. Lab-grown diamonds deliver these properties with a level of control that nature cannot match.
Identical Properties, Engineered Control
Lab-grown diamonds are not "fakes" or simulants; they are physically and chemically identical to mined diamonds. They are made of pure carbon arranged in the same rigid crystal lattice structure.
This means they have the same Mohs hardness of 10, the highest of any known material, and the same exceptional thermal conductivity.
Purity and Uniformity on Demand
Unlike natural diamonds, which form under chaotic geological conditions and often contain impurities (inclusions), lab-grown diamonds are created in a highly controlled environment.
This allows manufacturers to produce diamonds with near-perfect uniformity and specific properties tailored to a given application, a feat impossible with mined diamonds.
The Cost-Performance Advantage
Industrial applications consume a massive volume of diamonds for cutting, grinding, and polishing. Lab-grown diamonds provide the necessary performance at a fraction of the cost of their natural counterparts.
This makes advanced materials and manufacturing processes more economically viable and accessible.
Key Industrial Applications
The unique combination of hardness, thermal management, and purity makes lab-grown diamonds essential for a range of high-tech industries.
Precision Machining and Cutting
This is the most traditional industrial use. Diamond-tipped saws, drills, and grinding wheels are used to cut and shape hard materials like rock, concrete, and metal with extreme precision.
Advanced Electronics and Semiconductors
Lab-grown diamonds are exceptional thermal conductors but electrical insulators. This unique combination makes them perfect for use as heat sinks, drawing damaging heat away from sensitive microprocessors and high-power electronics.
The purity achieved through processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) makes them a promising material for next-generation semiconductor wafers.
Scientific and Medical Instruments
The hardness and ability to be sharpened to an exceptionally fine edge make lab-grown diamonds ideal for precision surgical scalpels.
They are also used to create diamond anvil cells, which generate immense pressures to study how materials behave under extreme conditions.
Understanding the Core Trade-offs
The choice between natural and lab-grown diamonds for industrial use is not a debate; it's a settled matter of practicality and performance. The discussion is centered on cost and control.
Predictability vs. Randomness
Industrial processes require materials with consistent, predictable, and verifiable properties. Lab-grown diamonds offer this reliability in every batch.
Natural industrial-grade diamonds (bort) are highly variable in quality, size, and purity, requiring extensive sorting and processing.
Engineered Properties vs. Natural Flaws
The two primary manufacturing methods, High Pressure-High Temperature (HPHT) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), are not just about creating diamonds; they are about engineering them.
The CVD process, in particular, allows scientists to build a diamond atom-by-atom, controlling its purity and even introducing specific elements to alter its properties for specialized tasks. This level of customization is impossible with a mined resource.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision is driven entirely by the application's technical and economic requirements.
- If your primary focus is high-volume performance and cost-efficiency: Lab-grown diamonds are the definitive choice for applications like cutting, grinding, and polishing.
- If your primary focus is next-generation technology and material science: The engineered purity and customizable properties of CVD lab-grown diamonds are enabling innovations in semiconductors, optics, and quantum computing.
Ultimately, the industrial adoption of lab-grown diamonds represents the triumph of engineered materials over mined resources, prioritizing performance and predictability above all else.
Summary Table:
| Property | Why It Matters for Industry | Lab-Grown Diamond Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Mohs 10) | Essential for cutting, grinding, and drilling hard materials. | Identical to natural diamond, but with greater consistency. |
| Thermal Conductivity | Critical for heat management in electronics and high-power devices. | Superior purity allows for more efficient heat dissipation. |
| Purity & Uniformity | Ensures predictable performance and reliability in manufacturing. | Engineered in controlled environments (HPHT/CVD) for specific applications. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Makes advanced processes economically viable on a large scale. | Significantly lower cost than mined industrial diamonds (bort). |
Elevate your industrial processes with precision-engineered lab-grown diamonds.
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including materials for advanced manufacturing and research. Our expertise ensures you get the right materials for applications like precision machining, semiconductor production, and scientific instrumentation.
Let us help you achieve superior results and cost-efficiency. Contact our experts today to discuss how lab-grown diamonds can solve your specific industrial challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- CVD Diamond Dressing Tools for Precision Applications
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- CVD Diamond Optical Windows for Lab Applications
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- How is something diamond coated? A Guide to CVD Growth vs. Plating Methods
- What is the use of CVD diamond? Unlock Superior Performance in Extreme Applications
- What is the application of diamond coating? Solve Complex Wear, Heat, and Corrosion Problems
- How much does CVD diamond equipment cost? A Breakdown of Investment from Lab to Production
- What is the newly discovered mechanism for diamond formation during CVD? Explore the Graphite-to-Diamond Transition









