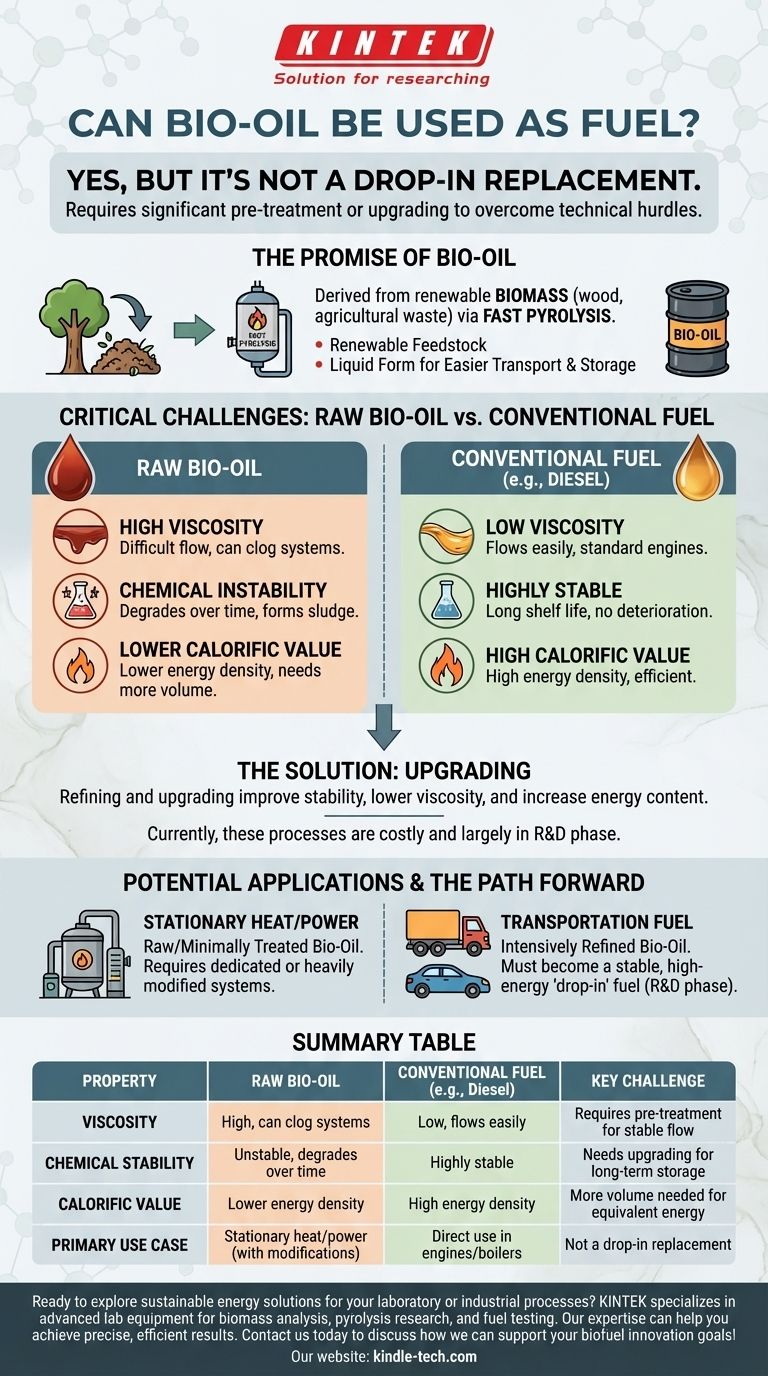
Yes, bio-oil can be used as a fuel, but it is not a simple, drop-in replacement for conventional fuels like diesel or heating oil. Its raw form has several challenging chemical and physical properties that prevent its direct use in standard engines and boilers. To be used effectively, it almost always requires significant pre-treatment or "upgrading."
While bio-oil is derived from renewable biomass, its practical application as a fuel is limited by its high viscosity, chemical instability, and lower energy content. Overcoming these technical hurdles through refining is the central challenge to its widespread adoption.

The Promise of Bio-Oil
Bio-oil is a liquid product created from the thermal decomposition of biomass, such as wood, agricultural waste, or algae, in the absence of oxygen. This process is known as fast pyrolysis.
Why Pursue Bio-Oil?
The primary driver for bio-oil development is its source material. Biomass is a renewable, widely available, and potentially carbon-neutral feedstock.
Converting solid biomass into a liquid fuel makes it much easier to transport, store, and use in existing liquid fuel infrastructure, which is a significant logistical advantage.
Potential Applications
Theoretically, bio-oil can be used in static applications like industrial boilers and furnaces for heat and power generation. It also serves as a potential intermediary product that can be refined further into transportation-grade fuels like gasoline and diesel.
Critical Challenges of Using Raw Bio-Oil
The properties of crude bio-oil are fundamentally different from those of refined petroleum products. These differences present major technical obstacles.
High Viscosity
Raw bio-oil is often thick and does not flow easily, especially at lower temperatures. This high viscosity can clog fuel lines, filters, and injectors that are designed for less viscous fossil fuels.
Chemical Instability
Bio-oil is a complex mixture that is chemically unstable. Over time, it can react with itself, leading to deterioration and an increase in viscosity, eventually forming sludge and solids that make it unusable. This makes long-term storage a significant problem.
Lower Calorific Value
Compared to fossil fuels, bio-oil has a lower calorific value, or energy density. This is largely due to its high water and oxygen content. You simply need to burn more bio-oil to generate the same amount of energy as an equivalent volume of heating oil.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The decision to use bio-oil is a balance between its environmental potential and its current technical and economic immaturity.
The Environmental Upside
The primary advantage is renewability. Using bio-oil from sustainable biomass sources can significantly reduce net greenhouse gas emissions compared to burning fossil fuels. It offers a path to valorize agricultural or forestry waste streams.
The Technical and Economic Downside
The processes for refining and upgrading bio-oil to improve its stability, lower its viscosity, and increase its energy content are not yet mature or economically feasible at a large scale. The cost and energy required for this upgrading process remain the largest barrier to competing with conventional fuels.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
The viability of bio-oil depends entirely on the intended application and the resources available for processing it.
- If your primary focus is stationary heat or power (e.g., an industrial boiler): Raw or minimally treated bio-oil could be an option, but it will likely require a dedicated or heavily modified system designed to handle its unique properties.
- If your primary focus is transportation fuel (e.g., for cars or trucks): Bio-oil must undergo intensive, multi-stage refining to be converted into a stable, high-energy "drop-in" fuel, a process that is still largely in the research and development phase.
Bio-oil holds clear potential as a renewable energy carrier, but its path from raw biomass to a practical, cost-effective fuel requires surmounting significant technical hurdles.
Summary Table:
| Property | Raw Bio-Oil | Conventional Fuel (e.g., Diesel) | Key Challenge |
|---|---|---|---|
| Viscosity | High, can clog systems | Low, flows easily | Requires pre-treatment for stable flow |
| Chemical Stability | Unstable, degrades over time | Highly stable | Needs upgrading for long-term storage |
| Calorific Value | Lower energy density | High energy density | More volume needed for equivalent energy |
| Primary Use Case | Stationary heat/power (with modifications) | Direct use in engines/boilers | Not a drop-in replacement |
Ready to explore sustainable energy solutions for your laboratory or industrial processes? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for biomass analysis, pyrolysis research, and fuel testing. Whether you're developing bio-oil refining techniques or need reliable systems for renewable energy R&D, our expertise can help you achieve precise, efficient results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your biofuel innovation goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Low-Temperature Water-Cooled Touchscreen Vibratory Ultrafine Pulverizer
- Glassy Carbon Sheet RVC for Electrochemical Experiments
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Hollow Etching Flower Basket ITO FTO Developing Glue Removal
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between grinding and pulverizing? Achieve the Perfect Particle Size for Your Application
- What is the mechanism of a cryogenic grinder? Master Polymer Powder Preparation for Additive Manufacturing
- Does milling reduce particle size? Achieve Precise Control Over Your Material's Properties
- How does a Vibratory Mill improve niobium recovery efficiency? Optimize Waste Pre-treatment for Maximum Yield
- What is sample pulverizing? The Key to Accurate and Reliable Lab Analysis







