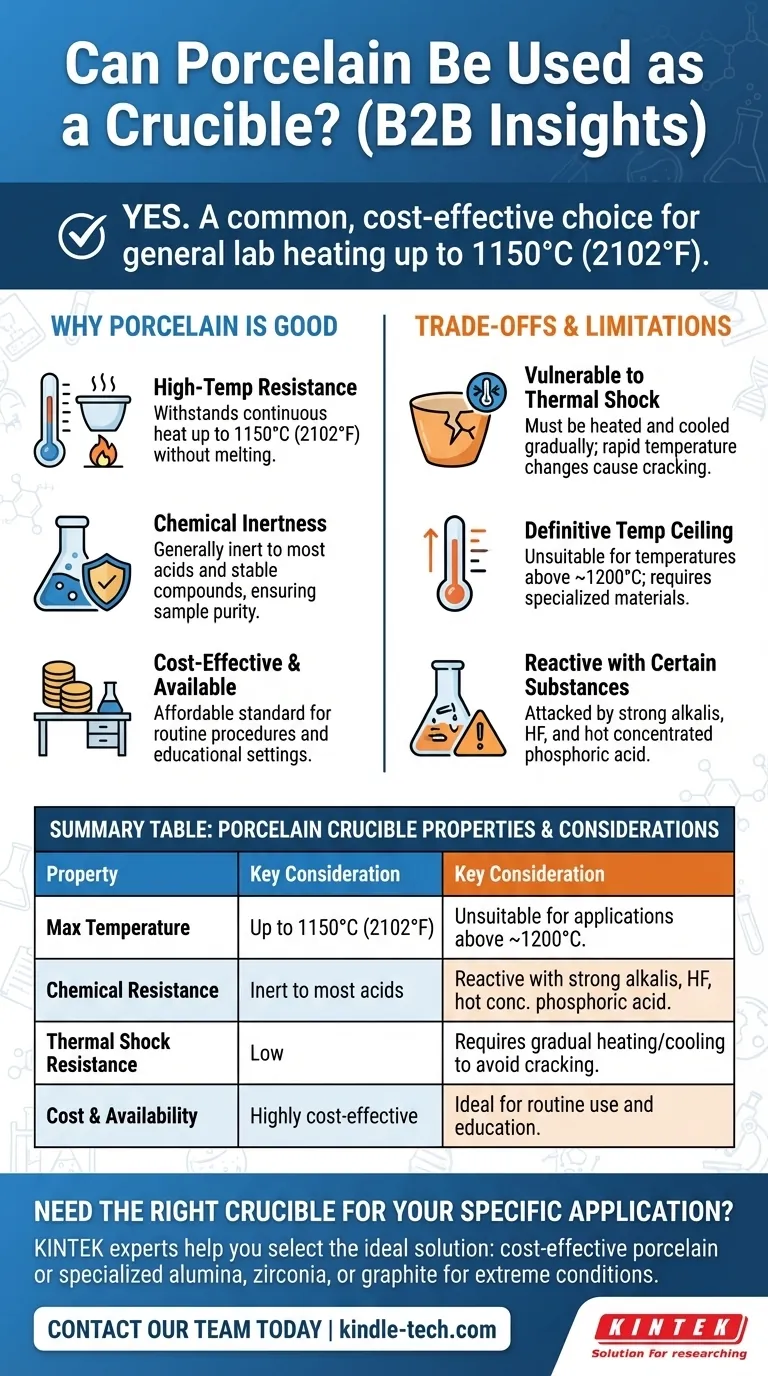
Yes, porcelain is one of the most common and widely used materials for laboratory crucibles. It is frequently employed for heating various chemical substances to high temperatures, such as determining volatile content or ashing samples. However, its suitability is not universal and depends entirely on your specific temperature requirements and the chemical nature of the substance being heated.
The core takeaway is that porcelain is a reliable and cost-effective choice for general-purpose heating up to about 1150°C (2102°F). Its primary limitations are a vulnerability to thermal shock and a lack of suitability for extremely high temperatures or highly reactive alkaline chemicals.

What Makes Porcelain a Good Crucible Material?
Porcelain's prevalence in the lab is due to a strong balance of thermal, chemical, and economic properties. It builds on the historical use of clay-based materials, refined for modern scientific needs.
High-Temperature Resistance
Porcelain can withstand continuous high temperatures without melting or deforming. Most glazed porcelain crucibles are rated for use up to 1150°C (2102°F).
Unglazed versions can sometimes tolerate slightly higher temperatures, but they are more porous.
General Chemical Inertness
For most common applications, porcelain is sufficiently inert. This means it will not react with or contaminate the sample being heated, which is a critical requirement for accurate analytical work.
It provides a clean surface that holds its integrity when exposed to most acids and stable compounds.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Compared to specialized alternatives like platinum or zirconium, porcelain crucibles are significantly more affordable and readily available.
This makes them the default choice for educational settings and routine laboratory procedures where extreme conditions are not a factor.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While versatile, porcelain is not the right tool for every job. Understanding its limitations is crucial for preventing experimental failure and ensuring safety.
Vulnerability to Thermal Shock
The most significant weakness of porcelain is its susceptibility to thermal shock. Heating or cooling a porcelain crucible too quickly can cause it to crack or shatter.
It is standard practice to heat and cool them gradually in a furnace to avoid this. They should never be placed directly on a cold surface while hot.
A Definitive Temperature Ceiling
While its heat resistance is good, it has a clear limit. For applications requiring temperatures above 1200°C, porcelain is unsuitable.
In these cases, more refractory materials like alumina, zirconia, or graphite are necessary.
Reactivity with Certain Substances
Porcelain's inertness has limits. It can be attacked by highly alkaline substances (like molten sodium hydroxide), hydrofluoric acid, and hot, concentrated phosphoric acid.
Using a porcelain crucible with these chemicals, especially at high temperatures, will damage the crucible and contaminate your sample.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct crucible material comes down to the specific goals of your procedure.
- If your primary focus is general heating, drying, or ashing samples below 1150°C: Porcelain is the ideal, cost-effective standard for these tasks.
- If your primary focus is working at temperatures above 1200°C or with strong alkalis: You must use a more specialized crucible made from alumina, zirconia, or even platinum.
- If your primary focus is ultra-trace analysis requiring zero contamination: A high-purity platinum or zirconium crucible is the professional standard to ensure the highest accuracy.
Ultimately, understanding these material properties ensures you select the right tool for a safe and successful outcome.
Summary Table:
| Property | Porcelain Crucible | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Max Temperature | Up to 1150°C (2102°F) | Unsuitable for applications above ~1200°C |
| Chemical Resistance | Inert to most acids and stable compounds | Reactive with strong alkalis, HF, and hot concentrated phosphoric acid |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Low - requires gradual heating/cooling | Can crack if temperature changes too rapidly |
| Cost & Availability | Highly cost-effective and readily available | Ideal for routine use and education |
Need the Right Crucible for Your Specific Application?
Choosing the correct crucible material is critical for your lab's safety and accuracy. The experts at KINTEK can help you select the ideal solution, whether you need cost-effective porcelain for general heating or specialized alumina, zirconia, or graphite crucibles for extreme temperatures and reactive chemicals.
Contact our team today to discuss your requirements and ensure you get the precise lab equipment and consumables for successful results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- What role do high-purity alumina crucibles play in high-temperature steam oxidation? Ensure Data Integrity up to 1350°C
- What is the function of alumina crucibles in Na3V2(PO4)2F3 synthesis? Ensure Purity in NVPF Production
- Why are high-purity alumina crucibles used for LATP? Preserve Purity and Conductivity in Sintering
- How does the use of corrosion-resistant ceramic crucibles ensure the chemical purity of materials? | KINTEK
- What are the functional advantages of using high-purity alumina crucibles? Achieve Precise Oxidation Data



















