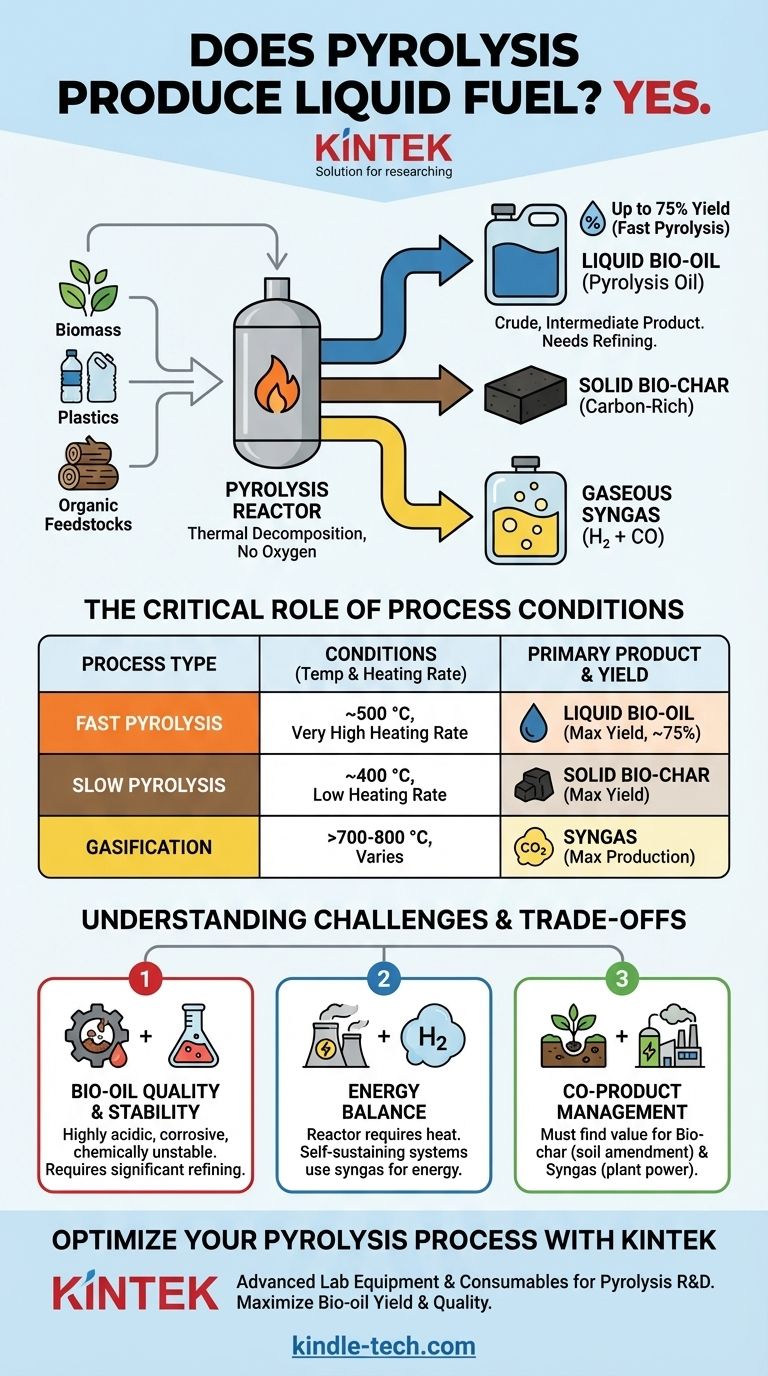
Yes, pyrolysis is a well-established process that produces liquid fuel. This liquid, commonly known as bio-oil or pyrolysis oil, is one of the three primary outputs of the thermal decomposition of organic material, alongside a solid product (bio-char) and a gaseous one (syngas). The specific quantity and quality of the liquid fuel depend heavily on the input material and the precise conditions under which the pyrolysis is performed.
The central takeaway is that pyrolysis reliably creates a liquid fuel from organic feedstocks like biomass or plastics. However, this "bio-oil" is not a simple drop-in replacement for gasoline or diesel; it is a crude, intermediate product that requires further refining for most modern applications. The key to a successful pyrolysis operation is managing the process to maximize the desired output, whether it's liquid, solid, or gas.

How Pyrolysis Creates Liquid Fuel
Pyrolysis is fundamentally a process of thermal decomposition in the absence of oxygen. Think of it not as burning, but as "baking" a material at high temperatures until its complex molecules break down into simpler, smaller components.
Defining Bio-oil
Bio-oil (also called pyrolysis oil or biocrude) is a dark, viscous, and complex mixture of oxygenated organic compounds. It is the liquid fraction that results from rapidly cooling the hot gases and vapors produced during pyrolysis.
Its composition can include hundreds of different chemical compounds, such as acids, alcohols, aldehydes, and phenols. This complexity is what distinguishes it from conventional petroleum crude oil.
The Critical Role of Process Conditions
The outcome of pyrolysis is not fixed; it is a direct result of the process parameters. The most important variable is temperature, combined with the heating rate.
- Fast Pyrolysis: This process uses moderate temperatures (around 500 °C) with a very high heating rate. These conditions are optimized to maximize the yield of liquid bio-oil, often reaching up to 75% of the product by weight.
- Slow Pyrolysis: This method uses lower temperatures (around 400 °C) over a much longer period. These conditions are designed to maximize the yield of solid bio-char, the carbon-rich charcoal-like substance.
- Gasification: At much higher temperatures (above 700-800 °C), the process favors breaking down molecules even further, maximizing the production of syngas, a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide.
The Importance of the Feedstock
The type of material you put into the reactor fundamentally changes the output.
While biomass, wood, agricultural waste, and certain plastics are excellent feedstocks for producing liquid bio-oil, other materials yield different results. For example, the pyrolysis of methane produces solid carbon and gaseous hydrogen, with no liquid fuel involved.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While pyrolysis is a powerful technology, it is crucial to understand its practical limitations. The liquid fuel it produces is not a simple solution.
Bio-oil Quality and Stability
Pyrolysis-derived bio-oil is not a "drop-in" fuel for conventional engines. It is highly acidic, corrosive to standard pipes and engine parts, and can be chemically unstable, thickening over time.
To be used as a transportation fuel, bio-oil must undergo significant upgrading and refining—a process that adds cost and complexity. More commonly, it is used directly as an industrial heating fuel in boilers or furnaces designed to handle it.
The Energy Balance
A pyrolysis plant requires a significant amount of heat to operate. In a self-sustaining system, this heat is typically generated by burning the syngas that is co-produced during the process.
The overall energy efficiency of the system depends on successfully balancing the energy required to prepare the feedstock (e.g., drying) and run the reactor with the energy contained in the final products.
Co-Product Management
A pyrolysis plant does not just produce liquid fuel. It creates a complete product stream—liquid, solid, and gas. A viable business model must find value for all three outputs.
The solid bio-char has valuable applications in agriculture as a soil conditioner and for carbon sequestration. The syngas is essential for powering the plant itself. Ignoring these co-products makes the economics of liquid fuel production far more challenging.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "best" pyrolysis setup is entirely dependent on your primary objective. By adjusting the process parameters, you can steer the output to meet your specific needs.
- If your primary focus is maximizing liquid fuel production: Employ fast pyrolysis of a consistent biomass feedstock at moderate temperatures (around 500 °C) with rapid vapor cooling.
- If your primary focus is carbon sequestration or soil amendment: Utilize slow pyrolysis at lower temperatures to maximize the yield and quality of stable bio-char.
- If your primary focus is producing hydrogen gas from natural gas: Methane pyrolysis is the correct pathway, which produces solid carbon and hydrogen, not liquid fuel.
Ultimately, mastering pyrolysis means understanding that you are not just making one product, but managing a chemical process to yield a specific ratio of valuable outputs.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Type | Temperature | Heating Rate | Primary Product | Yield |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fast Pyrolysis | ~500 °C | Very High | Liquid Bio-oil | Up to 75% |
| Slow Pyrolysis | ~400 °C | Low | Solid Bio-char | High |
| Gasification | >700 °C | Varies | Syngas | High |
Ready to optimize your pyrolysis process for high-quality liquid fuel production? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and development. Whether you're working with biomass, plastics, or other feedstocks, our precise heating systems and analytical tools help you maximize bio-oil yield and quality. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your renewable energy projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
People Also Ask
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success



















