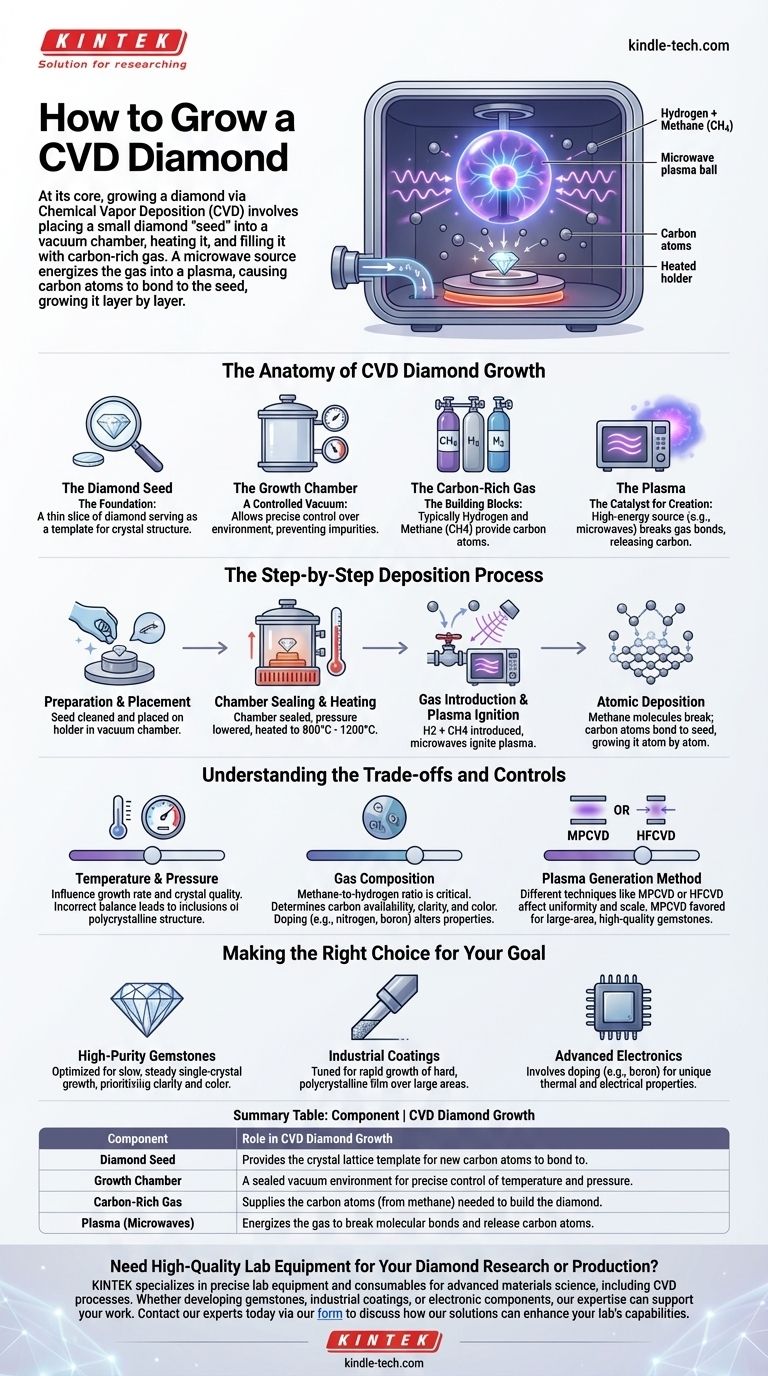
At its core, growing a diamond via Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) involves placing a small diamond "seed" into a vacuum chamber. This chamber is then heated and filled with a carbon-rich gas, like methane. A high-energy source, typically microwaves, energizes the gas into a plasma, which causes carbon atoms to rain down and bond to the diamond seed, growing it layer by layer.
The fundamental challenge of creating a diamond is arranging carbon atoms into a specific crystal lattice. CVD achieves this not with immense pressure, but with precise chemistry, using a superheated gas to "deposit" carbon atoms onto a template under highly controlled conditions.

The Anatomy of CVD Diamond Growth
To understand the process, you must first understand its essential components. Each element plays a critical role in transforming simple gas into one of the hardest materials known to man.
The Diamond Seed: The Foundation
A thin slice of a previously grown diamond—either another lab-grown diamond or a natural one—serves as the diamond seed. This seed acts as the template, providing the crystal structure for the new carbon atoms to bond to.
The Growth Chamber: A Controlled Vacuum
The entire process takes place within a sealed vacuum chamber. This allows for precise control over pressure, temperature, and atmospheric composition, preventing any impurities from contaminating the diamond.
The Carbon-Rich Gas: The Building Blocks
A specific mixture of gases is pumped into the chamber. This is typically hydrogen and a carbon-containing gas, most commonly methane (CH4). The methane provides the carbon atoms that will form the diamond.
The Plasma: The Catalyst for Creation
To break the strong molecular bonds in the methane gas, a significant amount of energy is needed. This is usually supplied by microwave beams, which excite the gas into a plasma—an ionized cloud of gas. This plasma is the key to releasing individual carbon atoms.
The Step-by-Step Deposition Process
With the core components in place, the growth process follows a meticulous, automated sequence that can last several weeks.
Preparation and Placement
The diamond seed is thoroughly cleaned to remove any microscopic dust or residue. It is then placed on a holder inside the vacuum chamber.
Chamber Sealing and Heating
The chamber is sealed and the pressure is lowered to create a near-perfect vacuum. The interior is then heated to a precise temperature, typically between 800°C and 1200°C.
Gas Introduction and Plasma Ignition
The hydrogen and methane gas mixture is introduced into the chamber. Microwaves are then activated, igniting the gas into a glowing ball of plasma.
Atomic Deposition
Within the plasma, methane molecules (CH4) break apart. The resulting carbon atoms are drawn down to the cooler surface of the diamond seeds. They bond to the seed's crystal lattice, extending its structure one atom at a time. This is the "deposition" in Chemical Vapor Deposition.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Controls
The true expertise in CVD is not just in making a diamond, but in making the right kind of diamond. The final properties of the stone are dictated entirely by the parameters controlled during growth.
The Impact of Temperature and Pressure
Slight adjustments to temperature and pressure inside the chamber can influence the growth rate and the quality of the crystal structure. An incorrect balance can lead to inclusions or a polycrystalline structure instead of a desired single crystal.
The Role of Gas Composition
The ratio of methane to hydrogen is critical. It determines the availability of carbon atoms and influences the final clarity and color of the diamond. Introducing other gases, like nitrogen or boron, can be used to intentionally dope the diamond, altering its color and electrical conductivity for specific applications.
The Plasma Generation Method
Different techniques exist to generate the plasma, such as Microwave Plasma CVD (MPCVD) or Hot Filament CVD (HFCVD). MPCVD is favored for its ability to produce highly uniform, large-area diamond films, making it suitable for industrial-scale production of high-quality gemstones.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the CVD process reveals that "lab-grown diamond" is not a monolithic category. The production method is tuned based on the intended application.
- If your primary focus is high-purity gemstones: The process is optimized for slow, steady growth of a single-crystal structure with minimal impurities, prioritizing clarity and color.
- If your primary focus is industrial coatings: The process may be tuned for rapid growth of a hard, polycrystalline diamond film over a large surface area, where hardness is more important than optical clarity.
- If your primary focus is advanced electronics: The process involves intentionally introducing dopants like boron to create a semiconductor with unique thermal and electrical properties.
By mastering these chemical and physical parameters, the CVD process allows for the creation of diamonds engineered for a specific purpose.
Summary Table:
| Component | Role in CVD Diamond Growth |
|---|---|
| Diamond Seed | Provides the crystal lattice template for new carbon atoms to bond to. |
| Growth Chamber | A sealed vacuum environment for precise control of temperature and pressure. |
| Carbon-Rich Gas | Supplies the carbon atoms (from methane) needed to build the diamond. |
| Plasma (Microwaves) | Energizes the gas to break molecular bonds and release carbon atoms. |
Need High-Quality Lab Equipment for Your Diamond Research or Production?
KINTEK specializes in the precise lab equipment and consumables essential for advanced materials science, including CVD processes. Whether you are developing gemstones, industrial coatings, or electronic components, our expertise can support your work.
Contact our experts today via our form to discuss how our solutions can enhance your lab's capabilities and help you achieve superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- How does RF magnetron sputtering work? A Complete Guide to Thin-Film Deposition
- What is the ion beam sputtering method? Achieve Unmatched Precision in Thin Film Deposition
- What is the MOCVD method? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Deposition
- What is the main difference between CVD and natural diamond? Origin, Purity, and Value Explained
- What is the temperature of LPCVD? Optimize Your Thin-Film Deposition Process
- What gases are used in sputtering? Choose the Right Gas for Your Thin Film Deposition
- What is chemical Vapour deposition in simple words? A Simple Guide to 'Painting' with Gas
- What is vapor deposition of graphene? A Guide to Scalable, High-Quality Production



















