At its core, a centrifuge is a machine that separates mixtures. It achieves this by spinning samples at high speeds, generating a powerful force that sorts components based on their density, size, and shape. This process, known as centrifugation, is a fundamental technique for isolating particles suspended in a liquid or for separating immiscible liquids.
A centrifuge doesn't create a new force; it leverages extreme angular velocity to amplify the effect of gravity. This allows for the rapid separation of substances that would otherwise take hours, days, or even years to separate on their own.

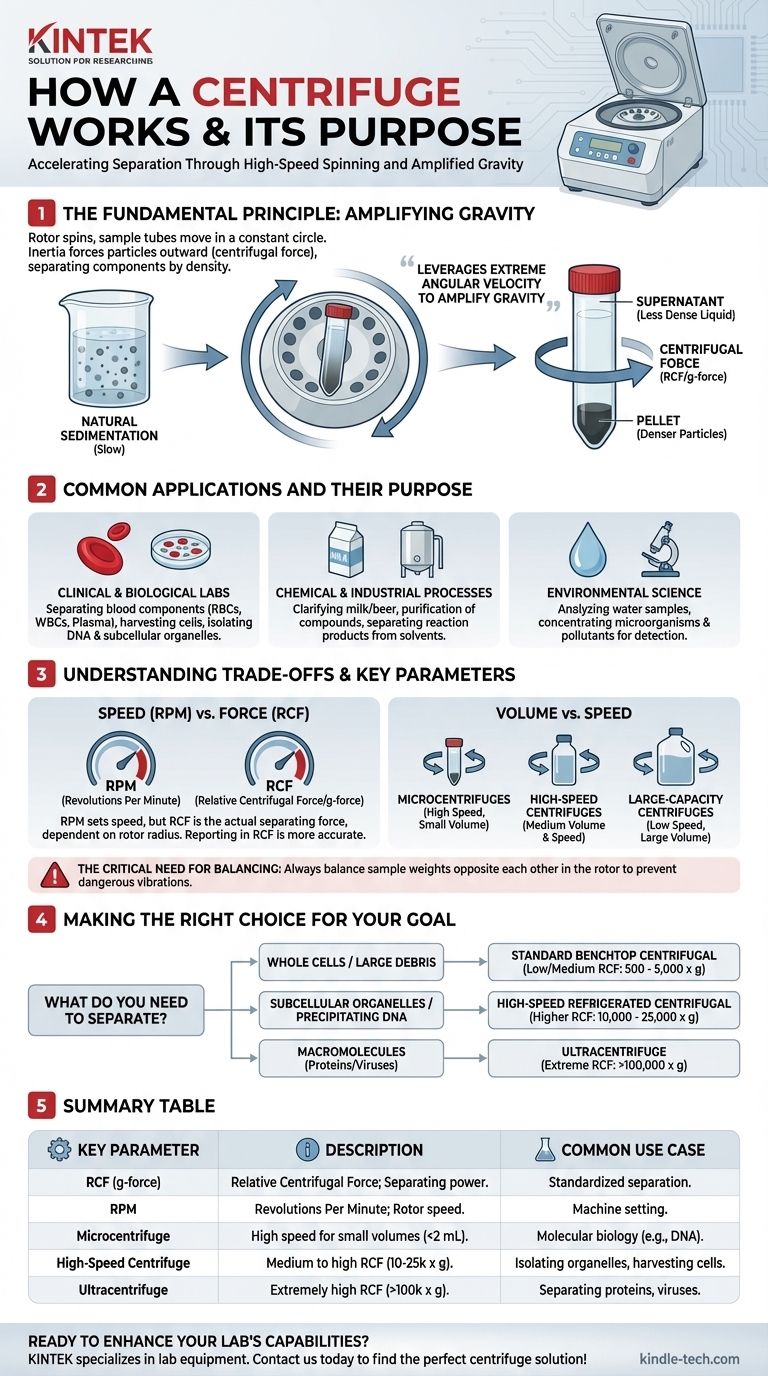
The Fundamental Principle: Amplifying Gravity
From Gravity to G-Force
Under normal conditions, gravity causes denser particles to settle out of a liquid over time. Think of sand settling at the bottom of a glass of water.
This natural process, called sedimentation, is often too slow for practical applications in science and industry. A centrifuge dramatically accelerates this process.
The Role of Inertia and Force
As the central part of the centrifuge, the rotor, spins, the sample tubes are forced to move in a constant circle. The particles within the sample have inertia—they resist this change in direction and attempt to continue in a straight line.
Because the tube wall is curved, this outward-moving inertia forces the particles toward the bottom of the tube. This effect, often referred to as centrifugal force, is measured in multiples of Earth's gravitational force (g-force or RCF).
How Separation Occurs
This intense g-force acts on every particle in the mixture, but it affects denser and larger particles more strongly.
As a result, the densest components migrate to the bottom of the tube fastest, forming a tightly packed solid layer called the pellet.
The less dense liquid left behind is known as the supernatant. This clear separation allows the two components to be easily isolated.
Common Applications and Their Purpose
In Clinical and Biological Labs
Centrifugation is indispensable in life sciences. A primary use is separating whole blood into its constituent parts: red blood cells, white blood cells, and plasma.
It is also used to harvest cells from a culture medium, isolate DNA during extraction protocols, or separate subcellular components like mitochondria from the rest of the cell's contents.
In Chemical and Industrial Processes
Industries rely on large-scale centrifuges for purification and separation. This includes separating cream from milk in the dairy industry and clarifying wine or beer by removing yeast cells.
The chemical and pharmaceutical industries use centrifugation to purify compounds and separate reaction products from residual solvents.
In Environmental Science
Environmental analysts use centrifuges to analyze water samples. By spinning the water, they can concentrate microorganisms, microplastics, or pollutants into a small, measurable pellet, making them easier to detect and study.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Parameters
Speed (RPM) vs. Force (RCF)
While speed is set in Revolutions Per Minute (RPM), the actual separating force is the Relative Centrifugal Force (RCF), or g-force.
RCF depends on both the RPM and the radius of the rotor (the distance from the center of rotation to the sample). Reporting separation parameters in RCF is more scientifically accurate and reproducible than using RPM alone.
Volume vs. Speed
Different centrifuges are designed for different tasks, creating a trade-off between the volume of the sample and the maximum speed.
- Microcentrifuges spin small tubes (under 2 mL) at high speeds for molecular biology tasks.
- Large-capacity centrifuges spin larger bottles or blood bags at lower speeds.
- Ultracentrifuges are a specialized class that achieves immense RCF (over 100,000 x g) to separate very small particles like viruses or individual proteins.
The Critical Need for Balancing
The most common operational mistake is failing to balance the rotor. An unbalanced load at high speed will cause violent vibrations that can destroy the machine and pose a serious safety hazard.
Every sample must be balanced by another sample of the exact same weight placed directly opposite it in the rotor.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The type of centrifuge and the settings you use depend entirely on what you need to separate.
- If your primary focus is separating whole cells or large debris: A standard benchtop centrifuge at a lower to medium RCF (500 - 5,000 x g) is sufficient.
- If your primary focus is isolating subcellular organelles or precipitating DNA: You will need a high-speed refrigerated centrifuge to generate higher g-forces while protecting samples from heat (10,000 - 25,000 x g).
- If your primary focus is separating macromolecules like proteins or viruses: An ultracentrifuge is required to generate the extreme forces (over 100,000 x g) needed to pellet these tiny particles.
Ultimately, understanding centrifugation is about recognizing it as a powerful tool for accelerating a natural process, enabling discovery and production across countless scientific and industrial fields.
Summary Table:
| Key Centrifuge Parameter | Description | Common Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| RCF (g-force) | Relative Centrifugal Force; the actual separating power. | Standardized, reproducible separation. |
| RPM | Revolutions Per Minute; the rotor's speed. | Machine setting, but RCF is more accurate. |
| Microcentrifuge | High speed for small volumes (<2 mL). | Molecular biology (e.g., DNA precipitation). |
| High-Speed Centrifuge | Medium to high RCF (10,000 - 25,000 x g), often refrigerated. | Isolating organelles, harvesting cells. |
| Ultracentrifuge | Extremely high RCF (>100,000 x g). | Separating proteins, viruses, macromolecules. |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities? Choosing the right centrifuge is critical for efficient sample preparation, whether for cell culture, clinical diagnostics, or chemical purification. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the ideal centrifuge for your specific application, ensuring safety, performance, and reproducibility. Contact us today to find the perfect solution for your separation goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Centrifuge Tubes
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
- Carbon Graphite Boat -Laboratory Tube Furnace with Cover
- Laboratory Hybrid Tissue Grinding Mill
People Also Ask
- What are alloys in simple words? Unlock the Power of Engineered Materials
- What is the primary function of an Alumina (Al2O3) tube in LLZTO sintering? Optimize Your Thermal Processing
- Why are quartz reaction tubes preferred for fixed-bed reactors? Ensure Data Integrity in Methane Reforming
- What are the advantages of using a centrifuge? Achieve Rapid, High-Resolution Sample Separation
- What are the benefits of using nickel-based alloys for reaction tubes? Ensure Purity in Supercritical Esterification



















