At its core, a sieve test is a straightforward method for sorting particles by size. A sample of granular material is placed on a screen with a specific mesh opening size and then agitated. This shaking motion allows particles smaller than the mesh openings to fall through, while larger particles are retained on the screen's surface.
The true purpose of a sieve test is not simply to separate particles, but to precisely quantify the distribution of different sizes within a sample. This provides a critical "fingerprint" used to predict material behavior and ensure quality control.
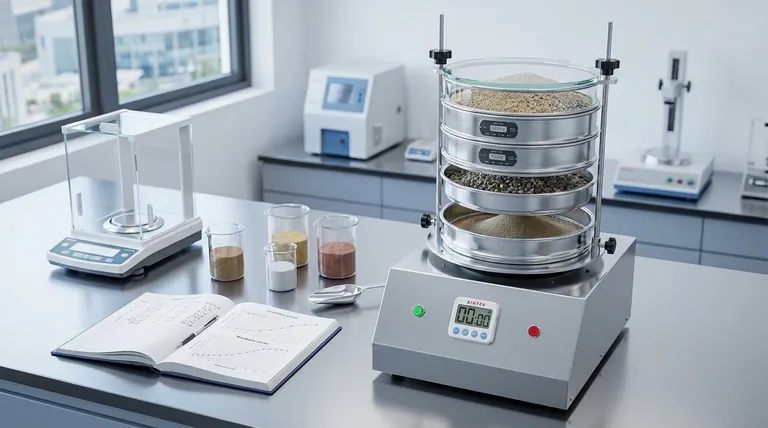

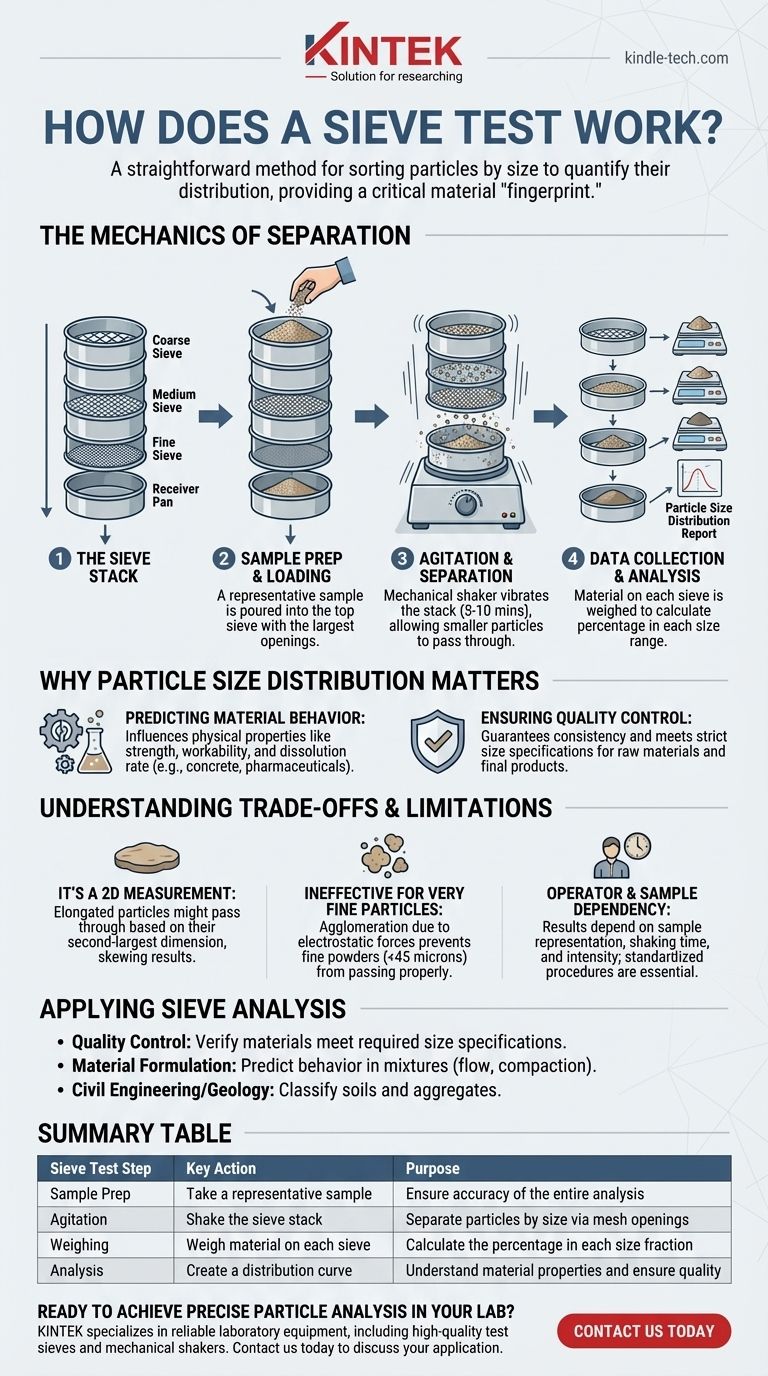
The Mechanics of Separation: A Step-by-Step View
To understand the data a sieve test provides, you must first understand the physical process. It is a methodical procedure designed for repeatable, accurate results.
The Sieve Stack
A professional sieve analysis rarely uses a single sieve. Instead, it employs a sieve stack: a column of sieves with progressively smaller mesh openings from top to bottom.
At the very bottom of the stack is a solid pan, known as the receiver, which collects the finest particles that pass through all the screens.
Sample Preparation and Loading
The process begins with a carefully measured sample that is representative of the entire batch of material. This sample is poured into the top sieve, which has the largest openings.
Agitation and Separation
The entire stack is placed in a mechanical shaker. The shaker vibrates or taps the stack for a set duration, typically 5 to 10 minutes.
This agitation gives each particle multiple opportunities to pass through the mesh openings until it is retained on a sieve that is too small for it to pass. Gravity and motion work together to sort the material down through the stack.
Data Collection and Analysis
Once the shaking is complete, the stack is disassembled. The material retained on each individual sieve (and in the bottom pan) is carefully collected and weighed.
By dividing the weight of material on each sieve by the total initial weight of the sample, you can calculate the percentage of material falling within each specific size range. This data is then used to create a particle size distribution report, often visualized as a gradation curve.
Why Particle Size Distribution Matters
The raw data from a sieve test is the key to unlocking critical insights about a material's potential performance and consistency.
Predicting Material Behavior
Particle size directly influences a material's physical properties. For example, in construction, the distribution of sand and gravel aggregates determines the strength and workability of concrete. In pharmaceuticals, particle size affects how quickly a drug dissolves and is absorbed by the body.
Ensuring Quality Control
Industries rely on sieve analysis to guarantee consistency. A supplier of sand for glass manufacturing, for instance, must provide material within a very tight size specification. A sieve test is a fast and reliable way to verify that a batch of raw material or a final product meets these established standards.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, sieve analysis is not a perfect solution for every scenario. Understanding its limitations is crucial for accurate interpretation.
It's a 2D Measurement
A sieve measures a particle based on its second-largest dimension. An elongated or needle-shaped particle might pass through a mesh opening end-first, even if its length or volume is much larger than the opening would suggest. This can skew the results for non-spherical materials.
Ineffective for Very Fine Particles
For extremely fine powders (typically smaller than about 45 microns), particles tend to clump together due to electrostatic forces. This agglomeration prevents them from passing through the fine mesh screens properly, leading to inaccurate results. For these materials, methods like laser diffraction or sedimentation are more appropriate.
Operator and Sample Dependency
The results are highly dependent on the initial sample being a true representation of the entire batch. Furthermore, variations in shaking time, intensity, and sample overloading can introduce errors, making standardized procedures essential.
Applying Sieve Analysis to Your Goal
Use this framework to decide how to apply the results of a sieve analysis to your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is quality control: Use sieve analysis to verify that incoming materials and outgoing products consistently fall within your required size specifications.
- If your primary focus is material formulation: Use the particle size distribution data to predict how a component will behave in a mixture, affecting properties like flow, compaction, or reaction rate.
- If your primary focus is civil engineering or geology: Use the gradation curve to classify soils and aggregates, determining their suitability for applications like road bases, foundations, and filters.
By understanding both the method and its meaning, you can transform simple particle separation into powerful material insight.
Summary Table:
| Sieve Test Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Sample Prep | Take a representative sample | Ensure accuracy of the entire analysis |
| Agitation | Shake the sieve stack | Separate particles by size via mesh openings |
| Weighing | Weigh material on each sieve | Calculate the percentage in each size fraction |
| Analysis | Create a distribution curve | Understand material properties and ensure quality |
Ready to achieve precise particle analysis in your lab?
Accurate sieve testing is fundamental to quality control and material performance. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable laboratory equipment, including high-quality test sieves and mechanical shakers, to ensure your particle size analysis is consistent and trustworthy.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss your specific application. Our experts will help you select the ideal equipment to meet your quality control and R&D goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
People Also Ask
- Why is sieve analysis important? Ensure Consistent Quality and Performance of Your Materials
- What is the primary function of a mechanical sieve shaker for biomass analysis? Optimize Particle Size Distribution
- What is the function of sieving equipment in CuAlMn alloys? Master Pore Size Precision
- What are the specifications for test sieves? A Guide to ASTM & ISO Standards for Accurate Particle Analysis
- What is the role of standard sieves in gold scrap leaching kinetic studies? Ensure Precision in Particle Classification



















