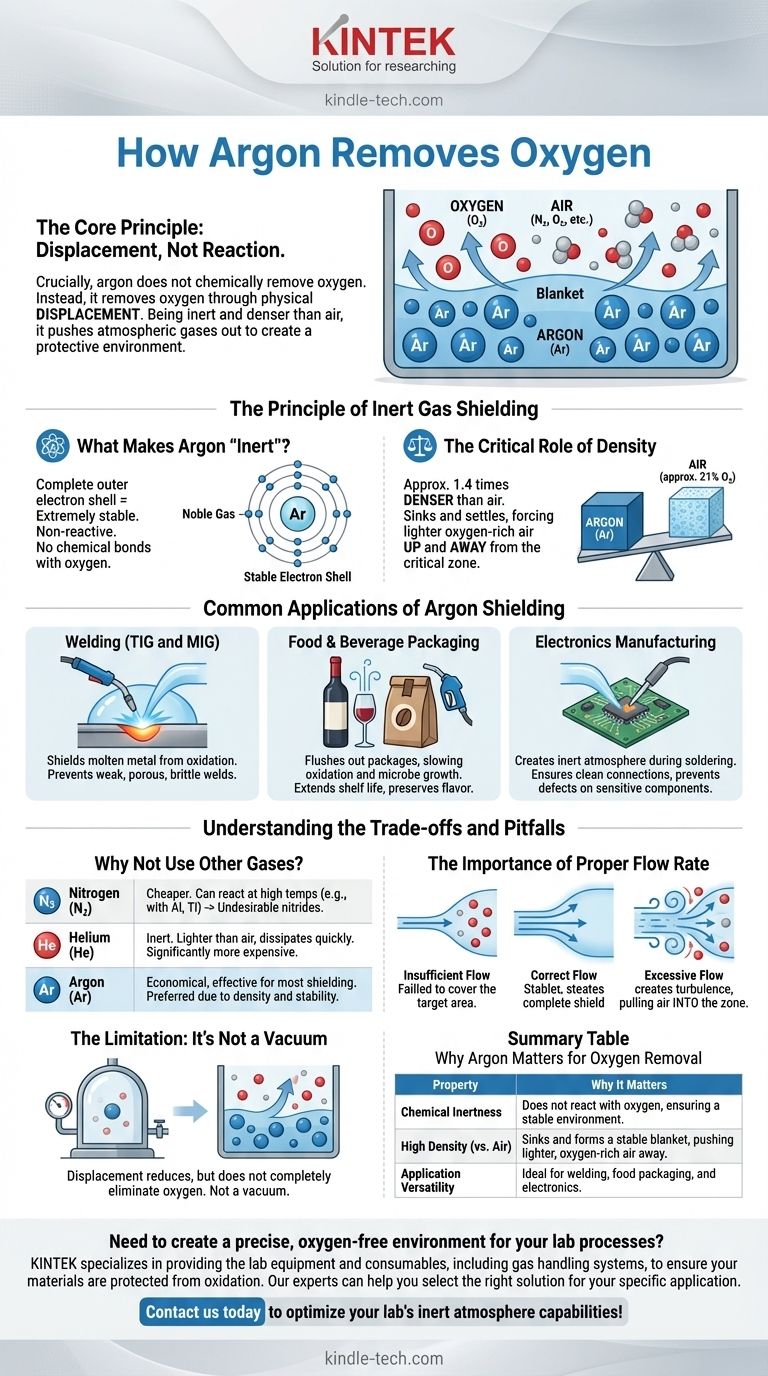
Crucially, argon does not chemically remove oxygen. Instead, argon removes oxygen from a specific area through a physical process called displacement. Because it is an inert gas and denser than air, it can effectively push oxygen and other atmospheric gases out of a workspace to create a protective, non-reactive environment.
The core principle is not a chemical reaction, but a physical takeover. Argon, being chemically non-reactive and heavier than air, sinks into a space and physically forces the lighter oxygen-containing air up and away, creating an oxygen-free zone.

The Principle of Inert Gas Shielding
To understand how argon works, you must first understand its fundamental properties. Its effectiveness comes from a combination of chemical stability and physical density, a method often called inert gas shielding.
What Makes Argon 'Inert'
Argon is a noble gas. This means its outermost electron shell is completely full, making it extremely stable and non-reactive.
It has virtually no tendency to share, gain, or lose electrons to form chemical bonds with other elements, including highly reactive ones like oxygen. This chemical indifference is the definition of inert.
The Key Mechanism: Displacement, Not Reaction
Since argon will not react with oxygen, it must rely on a physical mechanism. When you introduce argon gas into an environment, it physically occupies that space.
Because two gases cannot occupy the same space at the same time, the incoming argon pushes out the existing atmosphere. This is the simple, powerful principle of displacement.
The Critical Role of Density
The effectiveness of this displacement is greatly enhanced by argon's density. Argon gas is approximately 1.4 times denser than air.
This causes it to settle and form a stable, protective "blanket" over a designated area, such as a molten weld pool or the surface of a liquid in a container. The lighter air, which contains about 21% oxygen, is forced upward and away from the critical zone.
Common Applications of Argon Shielding
This principle of displacement is vital in numerous industrial and scientific processes where oxygen would be destructive.
Welding (TIG and MIG)
In processes like TIG and MIG welding, a continuous flow of argon is directed at the weld point. This shields the molten metal from atmospheric oxygen and nitrogen.
Without this argon shield, the molten metal would rapidly oxidize, resulting in a weak, porous, and brittle weld.
Food and Beverage Packaging
Argon is often used to flush out packages before sealing, particularly for products like wine, coffee, and snack foods.
By displacing the oxygen, it dramatically slows down oxidation and the growth of aerobic microbes, significantly extending the product's shelf life and preserving its flavor.
Electronics Manufacturing
During the soldering of circuit boards or the manufacturing of semiconductors, even minimal oxidation can compromise a component's integrity.
Argon is used to create an inert atmosphere, ensuring clean connections and preventing defects on sensitive electronic parts.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
While highly effective, using argon for inerting requires understanding its limitations and proper application.
Why Not Use Other Gases?
Argon is often preferred over other gases like nitrogen or helium. Nitrogen, while cheaper, can react with certain metals (like aluminum and titanium) at high temperatures to form undesirable nitrides.
Helium, another inert gas, is much lighter than air and dissipates more quickly. It is also significantly more expensive, making argon the more economical and effective choice for most shielding applications.
The Importance of Proper Flow Rate
Simply using argon is not enough; it must be used correctly. An insufficient flow rate will fail to displace all the atmospheric oxygen, leaving the area unprotected.
Conversely, an excessively high flow rate can create turbulence. This turbulence can actually pull surrounding air into the shielded zone, defeating the purpose and contaminating the area with oxygen.
The Limitation: It's Not a Vacuum
It's important to remember that displacement does not create a perfect vacuum. While it dramatically reduces oxygen levels, trace amounts may remain. For applications requiring near-total oxygen removal, a vacuum chamber is necessary.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right inerting strategy depends entirely on your material and objective.
- If your primary focus is high-quality welding on most metals: Argon's density, inertness, and excellent arc stability make it the definitive industry standard.
- If your primary focus is preserving sensitive products like food or wine: Argon is a superior choice for displacing oxygen in packaging to prevent spoilage and maintain quality.
- If your primary focus is general inerting on a tight budget: Nitrogen may be a viable option, but only if you can confirm it will not react negatively with your specific materials.
Understanding that argon works by physical displacement empowers you to control your atmosphere with precision.
Summary Table:
| Property | Why It Matters for Oxygen Removal |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Does not react with oxygen or other elements, ensuring a stable environment. |
| High Density (vs. Air) | Sinks and forms a stable blanket, effectively pushing lighter, oxygen-rich air away. |
| Application Versatility | Ideal for welding, food packaging, and electronics manufacturing. |
Need to create a precise, oxygen-free environment for your lab processes? KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and consumables, including gas handling systems, to ensure your materials are protected from oxidation. Our experts can help you select the right solution for your specific application. Contact us today to optimize your lab's inert atmosphere capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- 30L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- 20L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- Aluminum Foil Current Collector for Lithium Battery
- 10L Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath
People Also Ask
- Why is a controlled atmosphere tube furnace required for HPS catalysts? Ensure Optimal Metal Site Activation
- What are the advantages of using multi-stage split tube furnaces for heating methane pyrolysis reactors? Boost Efficiency
- What function does a high-temperature tube furnace serve in alkali fusion hydroxide recovery? Precision Thermal Control
- How does a three-zone high-temperature split tube furnace ensure data accuracy in creep experiments? Achieve Thermal Precision
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of SPAN? Optimize Your Li-S Battery Research Today

















