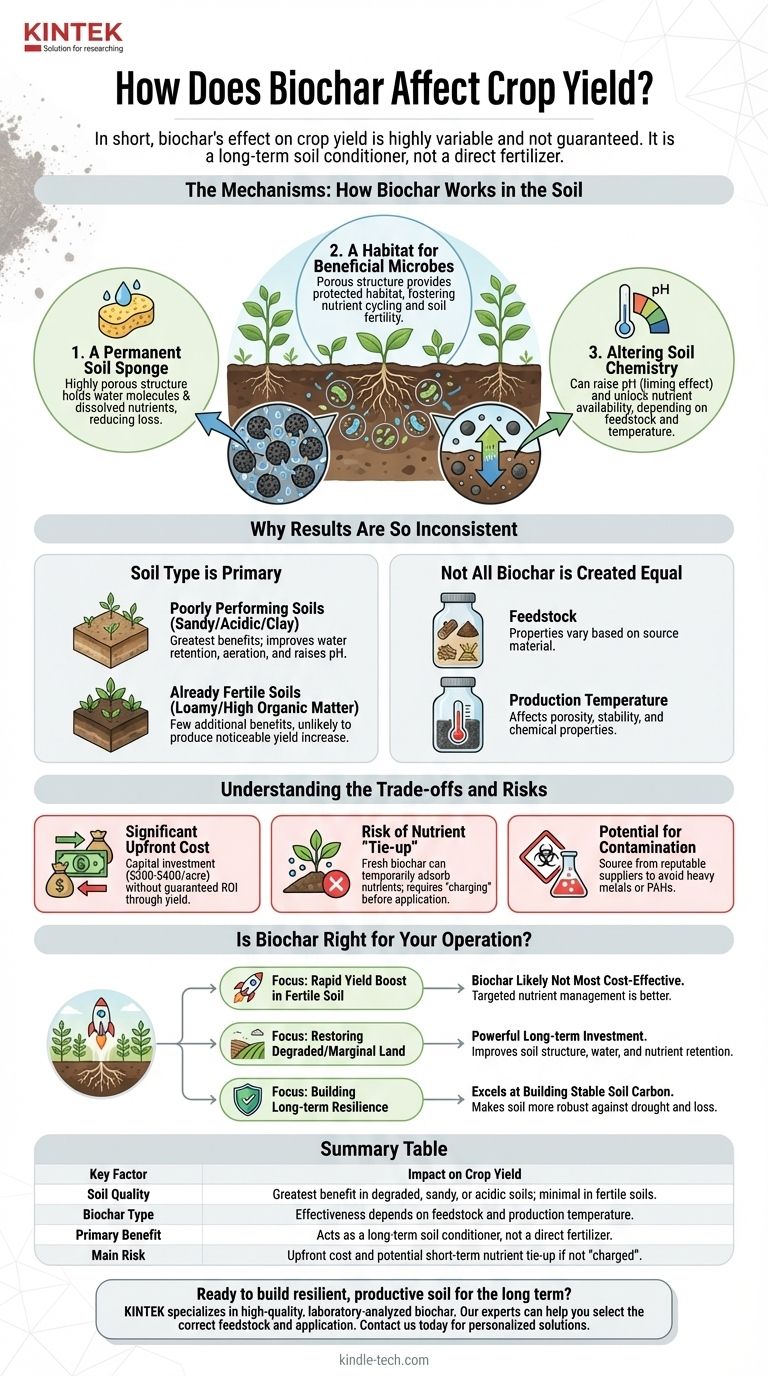
In short, biochar’s effect on crop yield is highly variable and not guaranteed. Its impact depends fundamentally on your existing soil quality, the type of biochar used, and your climate. While it is not a silver bullet for increasing yields, it can act as a powerful, long-term soil amendment that indirectly improves plant growth, especially in degraded or low-fertility soils.
Biochar is best understood as a soil conditioner, not a fertilizer. Its primary function is to improve soil structure, water retention, and microbial habitat. Any resulting yield increase is a secondary effect of this improved soil health, not a direct result of nutrient addition.
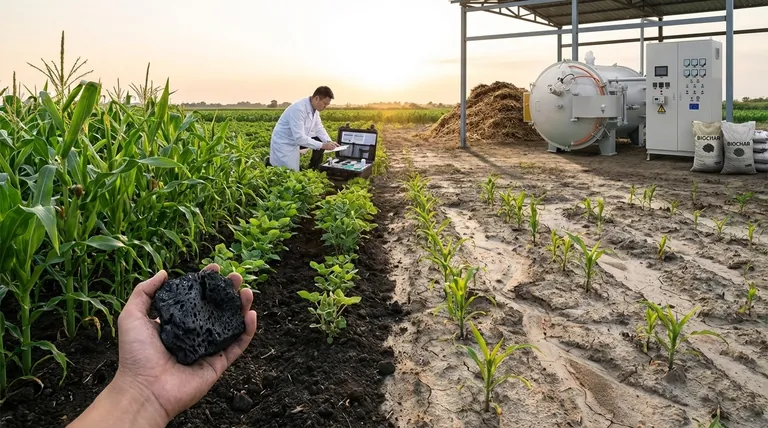

The Mechanisms: How Biochar Works in the Soil
To understand why biochar's impact varies, you must first understand how it functions. It does not act like a conventional NPK fertilizer that provides an immediate nutrient boost.
A Permanent Soil Sponge
The defining characteristic of biochar is its highly porous structure and large surface area, created during its production process (pyrolysis).
Think of it as a permanent, microscopic sponge integrated into your soil. This structure allows it to physically hold onto both water molecules and dissolved nutrients, reducing the amount lost to evaporation or leaching.
A Habitat for Beneficial Microbes
This same porous structure provides a protected habitat for beneficial soil microorganisms. These microbes are essential for nutrient cycling, a process where they convert organic matter and soil minerals into forms that plants can actually absorb.
By providing a safe refuge, biochar can help sustain a healthier and more active soil microbial community, which is foundational to long-term soil fertility.
Altering Soil Chemistry
Depending on the material it was made from (its feedstock) and the temperature it was produced at, biochar can also alter soil chemistry.
Most commonly, biochar has a liming effect, meaning it can raise the pH of acidic soils. This can unlock the availability of certain nutrients and create a more favorable environment for many crops.
Why Results Are So Inconsistent
The scientific literature shows a wide range of outcomes, from significant yield increases to no effect at all. This is not because the science is flawed, but because biochar's performance is context-dependent.
Soil Type is the Primary Factor
Biochar delivers the most significant benefits in poorly performing soils. In coarse, sandy soils, its ability to hold water and nutrients is a game-changer. In acidic, clay soils, its liming effect and ability to improve aeration are highly valuable.
Conversely, in already fertile, loamy soils with good structure and high organic matter, biochar offers few additional benefits and is unlikely to produce a noticeable yield increase.
Not All Biochar is Created Equal
The properties of biochar vary dramatically based on two factors:
- Feedstock: Biochar made from wood is different from that made from manure or straw.
- Production Temperature: Lower temperatures yield biochar with more volatile compounds, while higher temperatures create a more porous, stable carbon structure.
These variables affect its pH, porosity, and ash content, meaning one type of biochar may be effective in a certain soil while another is not.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
While biochar holds promise, it is not without risks and costs. An objective evaluation requires acknowledging these drawbacks.
The Significant Upfront Cost
Applying biochar is a capital investment. As noted, costs can run between $200 to $400 per acre. This is a major financial consideration, especially when the return on investment through yield is not guaranteed.
The Risk of Nutrient "Tie-up"
When first applied, fresh biochar can temporarily adsorb nutrients from the surrounding soil, making them unavailable to the crop in the short term. This is why experts often recommend "charging" or co-composting biochar with compost or manure before application.
Potential for Contamination
If not produced correctly or sourced from contaminated feedstock, biochar can contain heavy metals or harmful organic compounds (like polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, or PAHs). It is critical to source biochar from a reputable supplier who can provide a lab analysis of its properties and safety.
Is Biochar Right for Your Operation?
Instead of asking if biochar will increase your yield, the better question is what you want to achieve for your soil.
- If your primary focus is a rapid yield boost in fertile soil: Biochar is likely not your most cost-effective tool. Targeted nutrient management will deliver more predictable results.
- If your primary focus is restoring degraded or marginal land: Biochar can be a powerful long-term investment to improve soil structure, water-holding capacity, and nutrient retention.
- If your primary focus is building long-term resilience: Biochar excels at building stable soil carbon and making your soil more robust against drought and nutrient loss.
Ultimately, using biochar is a strategic decision about investing in the fundamental health and structure of your soil.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Impact on Crop Yield |
|---|---|
| Soil Quality | Greatest benefit in degraded, sandy, or acidic soils; minimal effect in fertile soils. |
| Biochar Type | Effectiveness depends on feedstock (wood, manure) and production temperature. |
| Primary Benefit | Acts as a long-term soil conditioner, not a direct fertilizer. |
| Main Risk | Upfront cost and potential short-term nutrient tie-up if not 'charged' properly. |
Ready to build resilient, productive soil for the long term?
Biochar is a strategic investment in your soil's health, but its success depends on using the right product for your specific conditions. KINTEK specializes in high-quality, laboratory-analyzed biochar and soil amendment solutions tailored for agricultural and research applications.
Our experts can help you select the correct biochar feedstock and provide guidance on proper application to avoid nutrient tie-up and maximize benefits like water retention and microbial activity.
Contact us today to discuss how KINTEK's reliable lab equipment and consumables can support your soil health goals. Let's build a more productive future for your land, together.
Get a Personalized Consultation
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What happens to graphite at high temperatures? Unlock its Extreme Heat Resistance
- How much temperature can graphite withstand? Unlock its true potential up to 3000°C
- What is the temperature resistance of graphite? Unlocking Its High-Temp Potential in Your Lab
- How does graphite react to heat? Unlocking Its Unique High-Temperature Strengths
- Is graphite good for high temperature? Unlock Its Full Potential in Controlled Atmospheres



















