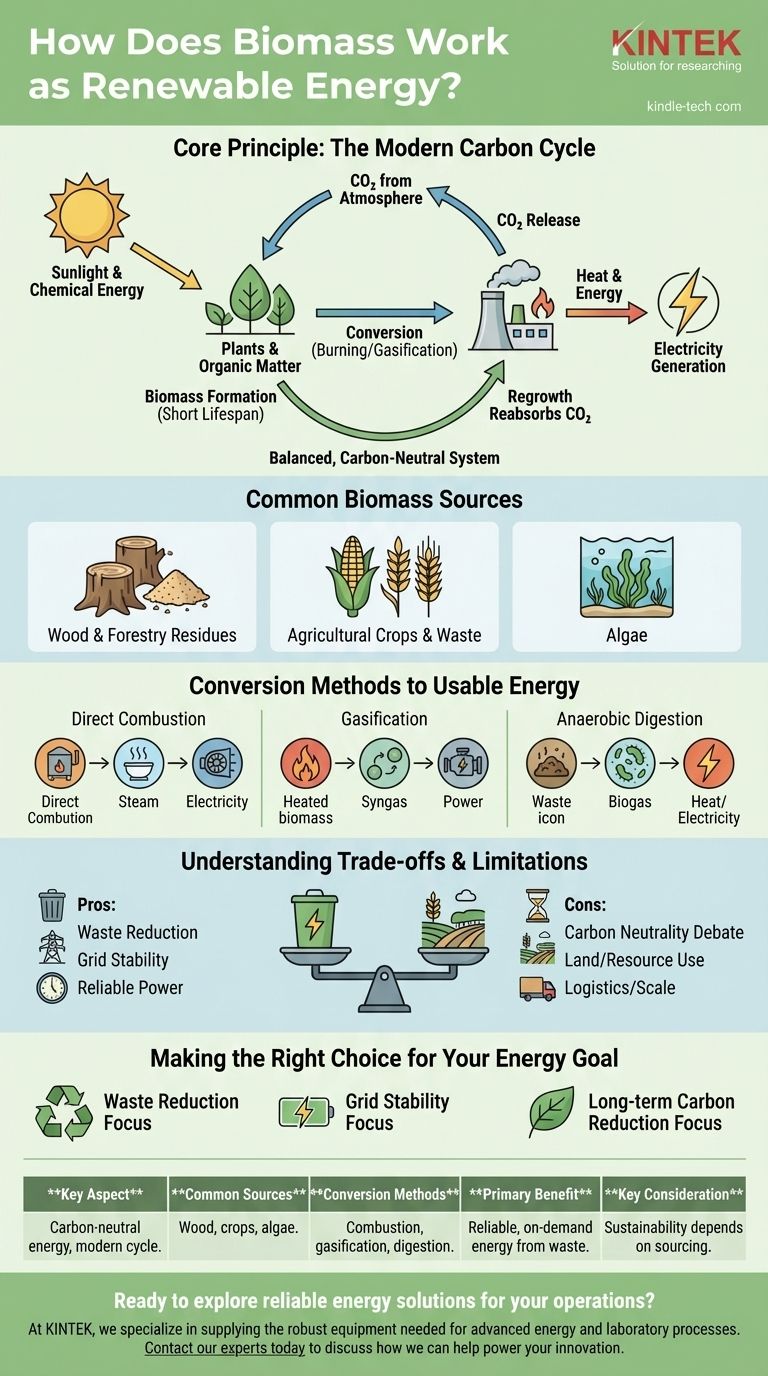
Biomass works as a renewable energy source by converting organic matter into usable energy. This organic material, which includes everything from wood and agricultural waste to dedicated energy crops, contains stored chemical energy from the sun. When this material is converted—often through burning or gasification—it releases this energy as heat, which can then be used to generate electricity.
The core principle that makes biomass a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels is its role in the modern carbon cycle. Unlike fossil fuels, which release ancient carbon into the atmosphere, biomass releases carbon that was only recently absorbed by plants, creating a theoretically balanced, or carbon-neutral, system.

The Fundamental Principle: A Balanced Carbon Cycle
The claim that biomass is "carbon-neutral" is central to its value as a renewable resource. This concept is rooted in the natural process of photosynthesis.
Releasing Recently Captured Carbon
When biomass is burned or converted, it releases carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere. This is the same basic chemical reaction that occurs when burning fossil fuels like coal or natural gas.
The Role of Plant Regrowth
The critical difference is the source of the carbon. The carbon in biomass was absorbed from the atmosphere by the plant during its relatively short lifespan.
As new plants, trees, or crops are grown to replace the biomass that was used, they pull an equivalent amount of CO2 back out of the atmosphere. This creates a closed loop, preventing a net increase in atmospheric CO2 over time.
The Contrast with Fossil Fuels
Fossil fuels, on the other hand, release vast quantities of carbon that were trapped underground for millions of years. This adds new carbon to the active atmosphere and is the primary driver of climate change.
Common Sources of Biomass Energy
Biomass is not a single fuel but a broad category of organic materials. The main sources are widely available and can be sustainably managed.
Wood and Forestry Residues
This is the most traditional form of biomass and includes everything from whole trees and lumber mill scraps to sawdust and forest debris from land clearing.
Agricultural Crops and Waste
Many agricultural processes produce valuable biomass waste, such as corn stalks, wheat straw, and sugarcane residue. Additionally, certain energy crops, like switchgrass, are grown specifically for fuel production.
Algae
Often considered a next-generation biomass source, algae can be cultivated rapidly in various water environments and have a very high energy content, making them a promising area of research.
How Biomass is Converted into Usable Energy
Several established technologies exist to transform raw organic matter into electricity, heat, or biofuels.
Direct Combustion
This is the most straightforward method. Biomass is burned in a boiler to produce high-pressure steam. This steam then drives a turbine connected to a generator, producing electricity.
Gasification
In this process, biomass is heated with a limited amount of oxygen. This doesn't burn the material but instead converts it into a flammable gas mixture known as syngas, which can then be used to power a gas engine or turbine.
Anaerobic Digestion
This biological process uses microorganisms to break down wet organic waste (like manure or sewage) in an oxygen-free environment. It produces a methane-rich biogas that can be burned for heat or electricity.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While biomass has significant potential, a truly objective assessment requires acknowledging its challenges. It is not a perfect solution.
The "Carbon Neutrality" Debate
The idea of perfect carbon neutrality is debated. The timeline matters—it can take decades for a forest to regrow and reabsorb the carbon released from burning trees. Furthermore, the energy used to harvest, process, and transport the biomass creates its own carbon footprint.
Land and Resource Use
Growing dedicated energy crops on a massive scale raises concerns about competition with food production for arable land and water resources. Sustainable biomass must prioritize waste streams or land unsuitable for traditional agriculture.
Scale and Logistics
Biomass is less energy-dense than fossil fuels, meaning a larger volume of material is required to produce the same amount of energy. This presents significant logistical challenges for collection, storage, and transportation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Energy Goal
The value of biomass depends entirely on the strategic goal it is meant to achieve within a broader energy portfolio.
- If your primary focus is waste reduction: Biomass is an excellent solution for converting agricultural, forestry, and municipal organic waste streams into a valuable energy resource.
- If your primary focus is grid stability: Biomass provides a reliable, dispatchable power source that can generate electricity on demand, perfectly complementing intermittent renewables like solar and wind.
- If your primary focus is long-term carbon reduction: Prioritize biomass sourced from genuine waste materials or non-food energy crops grown on marginal land to ensure the most sustainable and positive climate impact.
Ultimately, leveraging biomass effectively is a key component of building a diverse and resilient renewable energy system.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Carbon-neutral energy from the modern carbon cycle. |
| Common Sources | Wood waste, agricultural residues, energy crops, algae. |
| Conversion Methods | Direct combustion, gasification, anaerobic digestion. |
| Primary Benefit | Transforms waste into reliable, on-demand energy. |
| Key Consideration | Sustainability depends on sourcing and logistics. |
Ready to explore reliable energy solutions for your operations?
At KINTEK, we specialize in supplying the robust equipment needed for advanced energy and laboratory processes. Whether you're researching biomass conversion or scaling up production, our expertise and high-quality lab equipment and consumables can support your goals for efficiency and sustainability.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help power your innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Glassy Carbon Sheet RVC for Electrochemical Experiments
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- High Energy Vibratory Laboratory Ball Mill Grinding Mill Single Tank Type
People Also Ask
- What are the typical physical specifications for glassy carbon sheets? Unlock Superior Performance for Your Lab
- Why is a glassy carbon disc electrode an indispensable consumable? Ensure Reliable Catalyst Evaluation Today
- What are the functions of a glassy carbon electrode in CV testing of antioxidants? Enhance Your Redox Analysis Accuracy
- What is an RVC glassy carbon sheet? A High-Performance Material for Demanding Applications
- What are the fundamental characteristics of glassy carbon? Discover its Unique Synergy of Properties



