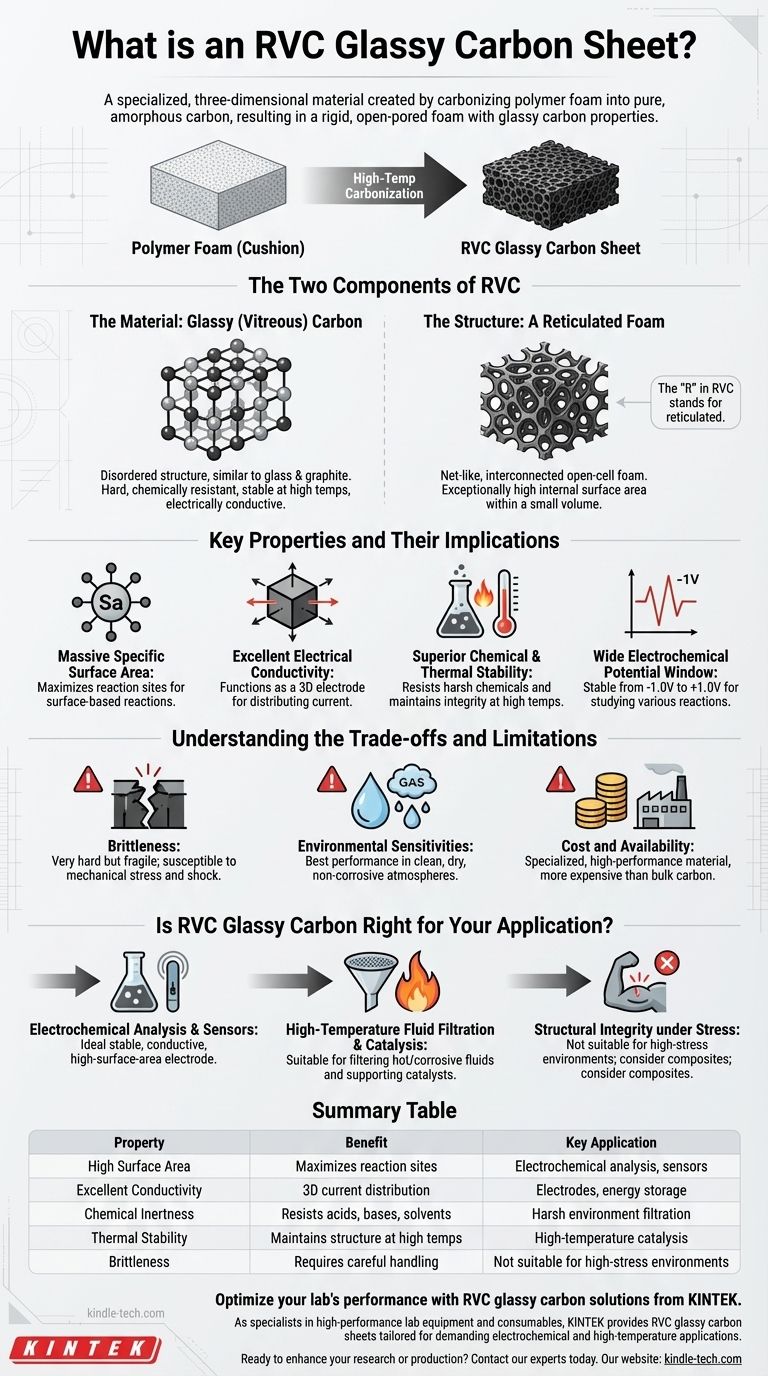
At its core, an RVC glassy carbon sheet is a specialized material with a unique, three-dimensional structure. It is created by taking a polymer foam, like the kind you might find in a cushion, and converting it into pure, amorphous carbon through a high-temperature process called carbonization. This results in a material that is both a rigid, open-pored foam and a sheet of glassy carbon.
The true value of RVC glassy carbon lies in its dual nature: it combines the exceptional chemical inertness and electrical conductivity of glassy carbon with the massive surface area of a reticulated (foam-like) structure. This unique combination makes it highly effective for specific electrochemical and high-temperature applications.
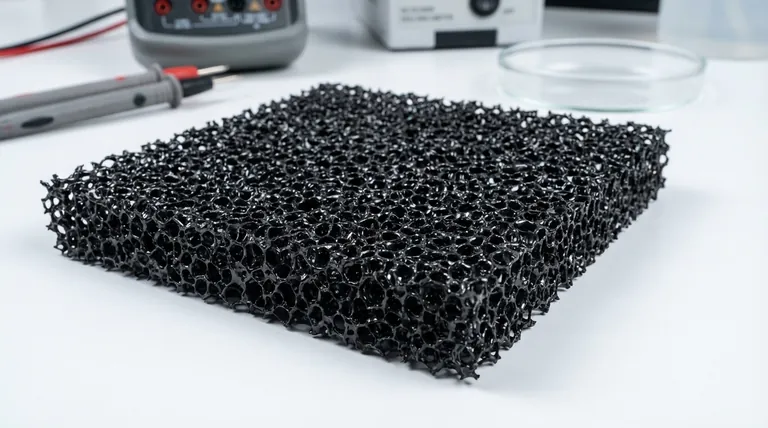

The Two Components of RVC
To understand RVC, you must first understand its two distinct parts: the material it's made from and the structure it takes.
The Material: Glassy (Vitreous) Carbon
Glassy carbon, sometimes called vitreous carbon, is a non-graphitizing, amorphous form of the element. Unlike graphite, its atoms are not arranged in neat, orderly layers.
This disordered structure gives it a combination of properties similar to both glass and graphite. It is very hard, highly resistant to chemical attack, and stable at extreme temperatures. It is also a good conductor of electricity.
The Structure: A Reticulated Foam
The "R" in RVC stands for reticulated, which describes a net-like, interconnected structure. The material is not a solid, flat plate but a porous, open-cell foam.
Think of a rigid kitchen sponge. Now, imagine that entire sponge structure is made not of polymer, but of pure glassy carbon. This network of interconnected struts and pores creates an exceptionally high internal surface area within a small volume.
Key Properties and Their Implications
The fusion of glassy carbon's properties with a foam structure results in a material optimized for performance in demanding environments.
Massive Specific Surface Area
The open-pored foam structure is the most significant feature. This high surface area is critical for applications where reactions occur on the material's surface, as it provides far more active sites than a flat sheet of the same size.
Excellent Electrical Conductivity
Because it is made of carbon, RVC is electrically conductive. This allows it to function effectively as a three-dimensional electrode, distributing electrical current throughout its entire volume.
Superior Chemical and Thermal Stability
Glassy carbon is famously inert. It does not react with most acids, bases, or organic solvents, making it a reliable material in harsh chemical environments. It also maintains its structural integrity at very high temperatures.
Wide Electrochemical Potential Window
In electrochemical setups, RVC offers a wide potential range (approximately -1.0V to +1.0V) where it remains stable without reacting itself. This versatility allows it to be used for studying a broad spectrum of chemical reactions.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is perfect. Acknowledging the trade-offs of RVC is crucial for successful implementation.
Brittleness and Mechanical Fragility
Like glass, glassy carbon is very hard but also brittle. The thin struts of the foam structure can be fragile and may fracture if subjected to shock, vibration, or mechanical stress. Careful handling is essential.
Environmental Sensitivities
For optimal and repeatable performance, especially in sensitive electrochemical measurements, RVC should be used in a clean, dry, and non-corrosive atmosphere. High humidity or exposure to certain gases can affect its surface and, consequently, its performance.
Cost and Availability
The multi-step, high-temperature manufacturing process makes RVC glassy carbon significantly more expensive than other carbon forms like graphite rods or carbon felt. It is a specialized, high-performance material, not a bulk commodity.
Is RVC Glassy Carbon Right for Your Application?
Choosing this material depends entirely on whether its unique advantages align with your primary technical goals.
- If your primary focus is electrochemical analysis or sensor development: RVC is an exceptional choice for a working electrode, offering a stable, conductive, and high-surface-area platform for reactions.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature fluid filtration or catalysis: Its thermal stability and porous structure make it ideal for filtering hot, corrosive fluids or for supporting a catalyst material.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity under mechanical stress: Its inherent brittleness means you should consider more robust alternatives like carbon-carbon composites or flexible materials like carbon felt.
Ultimately, RVC glassy carbon is a problem-solving material designed for environments where performance cannot be compromised.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit | Key Application |
|---|---|---|
| High Surface Area | Maximizes reaction sites | Electrochemical analysis, sensors |
| Excellent Conductivity | 3D current distribution | Electrodes, energy storage |
| Chemical Inertness | Resists acids, bases, solvents | Harsh environment filtration |
| Thermal Stability | Maintains structure at high temps | High-temperature catalysis |
| Brittleness | Requires careful handling | Not suitable for high-stress environments |
Optimize your lab's performance with RVC glassy carbon solutions from KINTEK.
As specialists in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, KINTEK provides RVC glassy carbon sheets tailored for demanding electrochemical and high-temperature applications. Our materials ensure superior conductivity, chemical resistance, and thermal stability for your most critical processes.
Ready to enhance your research or production? Contact our experts today to discuss how RVC glassy carbon can solve your specific challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Glassy Carbon Sheet RVC for Electrochemical Experiments
- Glassy Carbon Electrochemical Electrode
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Hydrophilic Carbon Paper TGPH060 for Battery Lab Applications
- Optical Ultra-Clear Glass Sheet for Laboratory K9 B270 BK7
People Also Ask
- What actions and conditions are strictly prohibited when working with a glassy carbon sheet? Protect Your Investment and Data Integrity
- What are the functions of a glassy carbon electrode in CV testing of antioxidants? Enhance Your Redox Analysis Accuracy
- What is the porosity of an RVC glassy carbon sheet? Understanding the Critical Difference Between PPI and Porosity
- What are the fundamental characteristics of glassy carbon? Discover its Unique Synergy of Properties
- What is the ideal operating environment for a glassy carbon sheet? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity



















