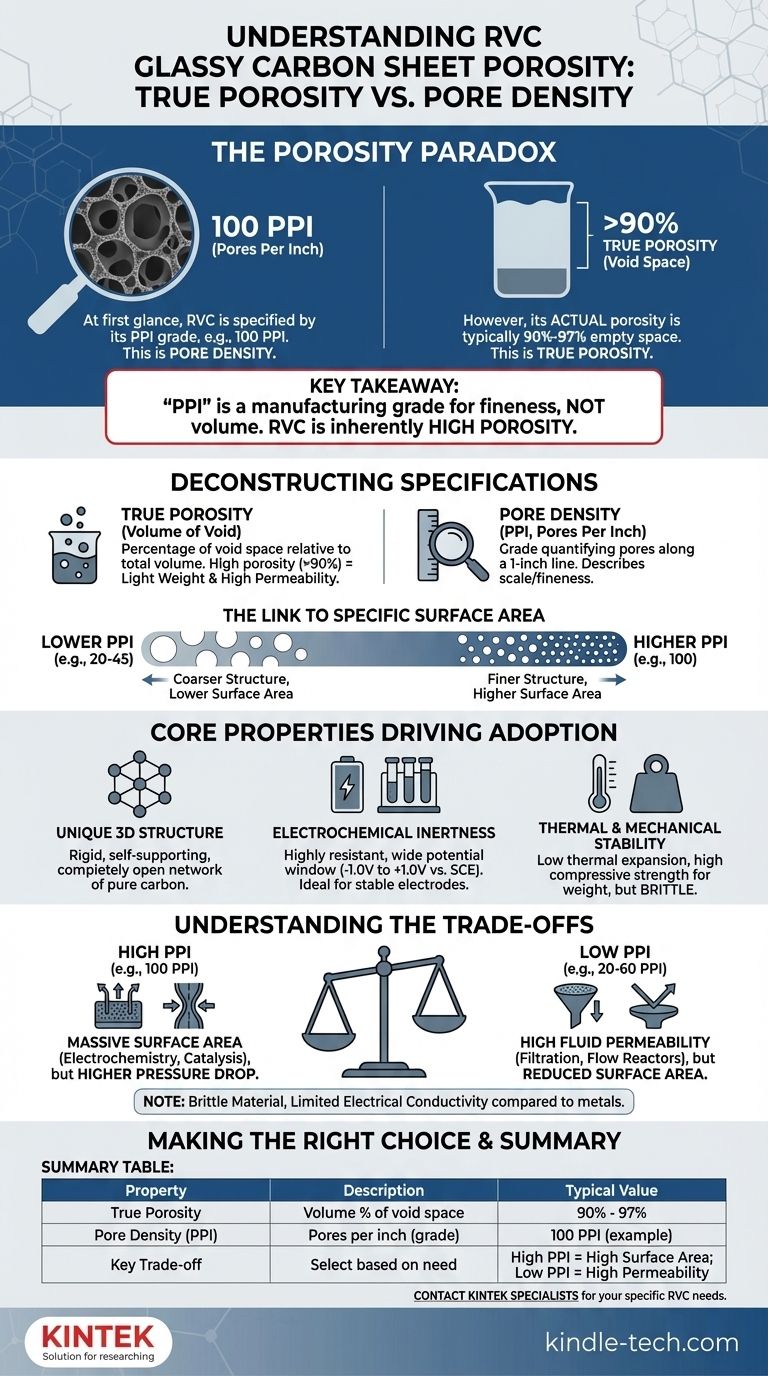
At first glance, the porosity of a standard RVC glassy carbon sheet is specified as 100 ppi (pores per inch). However, it is critical to understand that this "ppi" value describes the material's pore density, or grade, not its true porosity. The actual porosity of RVC—the percentage of empty or void space—is exceptionally high, typically between 90% and 97%.
The key takeaway is that "100 ppi" is a manufacturing grade that defines the fineness of the foam's structure, not the volume of empty space. While RVC is inherently a high-porosity material, the ppi grade determines critical performance characteristics like surface area and fluid permeability.

Deconstructing RVC Specifications: Porosity vs. Pore Density
To use RVC effectively, you must distinguish between these two fundamental properties. They describe different aspects of the material's open-foam structure and have different implications for your application.
What is True Porosity?
True porosity is a dimensionless ratio, usually expressed as a percentage, that represents the volume of void space relative to the total volume of the material.
RVC is a "reticulated" foam, meaning its structure is an open network of interconnected struts. This results in an extremely low-density material where the vast majority of the volume is empty space. This high porosity (often >90%) is responsible for its light weight and high permeability.
What is Pore Density (ppi)?
Pore density, measured in pores per inch (ppi), is a grade that quantifies how many pores exist along a one-inch line. It describes the scale or fineness of the foam's cellular structure.
A higher ppi grade, like 100 ppi, indicates smaller, more numerous pores and a finer, more intricate network of carbon struts.
A lower ppi grade (e.g., 20 or 45 ppi) indicates larger, more open pores and a coarser structure.
The Link to Specific Surface Area
The ppi grade is directly related to the specific surface area (the total surface area per unit of volume or mass).
Because a 100 ppi material has a more complex network of smaller carbon struts, its specific surface area is significantly higher than that of a lower ppi material of the same external dimensions. This is a crucial factor for electrochemical and catalytic applications.
The Core Properties Driving RVC Adoption
Understanding the structure explains why RVC is a valuable material for advanced applications. It combines the properties of a foam with the inherent stability of glassy carbon.
Unique Three-Dimensional Structure
RVC is produced by pyrolyzing (carbonizing at high temperature) an open-cell polymer foam. This process creates a rigid, self-supporting, and completely open 3D network of pure carbon.
Electrochemical Inertness
Like solid glassy carbon, RVC is highly resistant to chemical attack and offers a wide potential window for electrochemical reactions (approximately -1.0V to +1.0V vs. SCE). This makes it an ideal, stable electrode material that won't interfere with experiments.
Thermal and Mechanical Stability
RVC possesses a very low coefficient of thermal expansion, making it dimensionally stable during temperature changes. It is also hard and mechanically strong for its extremely low density, though it remains a brittle material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting an RVC material involves balancing its properties. The ppi grade is the most common variable you will choose, and it presents a primary trade-off.
High Surface Area vs. Fluid Permeability
A higher ppi grade (e.g., 100 ppi) offers a massive surface area, which is ideal for maximizing reaction sites in an electrode or a catalyst support. However, the finer pores create greater resistance to fluid flow, leading to a higher pressure drop.
A lower ppi grade (e.g., 45 ppi) allows fluids or gases to pass through with much less resistance. This is better for applications like filters, flow-through reactors, or heat exchangers, but it comes at the cost of reduced specific surface area.
Strength vs. Brittleness
While RVC has high compressive strength for its weight, it is a form of glass. It is a brittle material and will fracture under sharp impact or high tensile or bending stress. It does not deform plastically like a metal foam.
Electrical Conductivity
RVC has good electrical conductivity for a carbon foam, but it is substantially less conductive than graphite or metals. In high-current applications, the electrical resistance of the RVC structure itself can lead to significant voltage (IR) drop, which may be a limiting factor.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of RVC grade should be driven entirely by the primary requirement of your application.
- If your primary focus is maximizing active surface area (for electrochemistry, sensing, or catalysis): A high ppi grade like 100 ppi is the correct choice, as it provides the most reaction sites per unit volume.
- If your primary focus is high flow-rate with low pressure drop (for filtration, diffusers, or heat exchangers): A lower ppi grade (e.g., 20-60 ppi) is necessary to ensure efficient fluid transport through the material.
- If your primary focus is a lightweight, rigid structural material: Any ppi grade will provide high porosity and low density; the choice then depends on the desired visual texture or interaction with other components.
By understanding the distinction between pore density and true porosity, you can select the precise RVC material that meets your project's performance requirements.
Summary Table:
| Property | Description | Typical Value for RVC |
|---|---|---|
| True Porosity | Volume percentage of void space | 90% - 97% |
| Pore Density (PPI) | Pores per inch (defines grade/fineness) | 100 PPI (example grade) |
| Key Trade-off | High PPI = High Surface Area, Low PPI = High Permeability | Select based on application need |
Ready to select the perfect RVC glassy carbon sheet for your project?
Understanding the nuances between pore density (PPI) and true porosity is critical for application success. Whether you need the massive surface area of a 100 PPI electrode for electrochemistry or the high permeability of a lower PPI grade for filtration, KINTEK is here to help.
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including RVC glassy carbon. Our experts can guide you to the ideal material grade to maximize your results in catalysis, sensing, flow-through reactors, and more.
Contact our specialists today to discuss your specific requirements and ensure you get the right RVC for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Glassy Carbon Sheet RVC for Electrochemical Experiments
- Copper Foam
- Hydrophilic Carbon Paper TGPH060 for Battery Lab Applications
- Copper Nickel Foam Metal Sheet
- Optical Ultra-Clear Glass Sheet for Laboratory K9 B270 BK7
People Also Ask
- What is the ideal operating environment for a glassy carbon sheet? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What are the typical physical specifications for glassy carbon sheets? Unlock Superior Performance for Your Lab
- What is an RVC glassy carbon sheet? A High-Performance Material for Demanding Applications
- Why is a glassy carbon disc electrode an indispensable consumable? Ensure Reliable Catalyst Evaluation Today
- What are the fundamental characteristics of glassy carbon? Discover its Unique Synergy of Properties



















