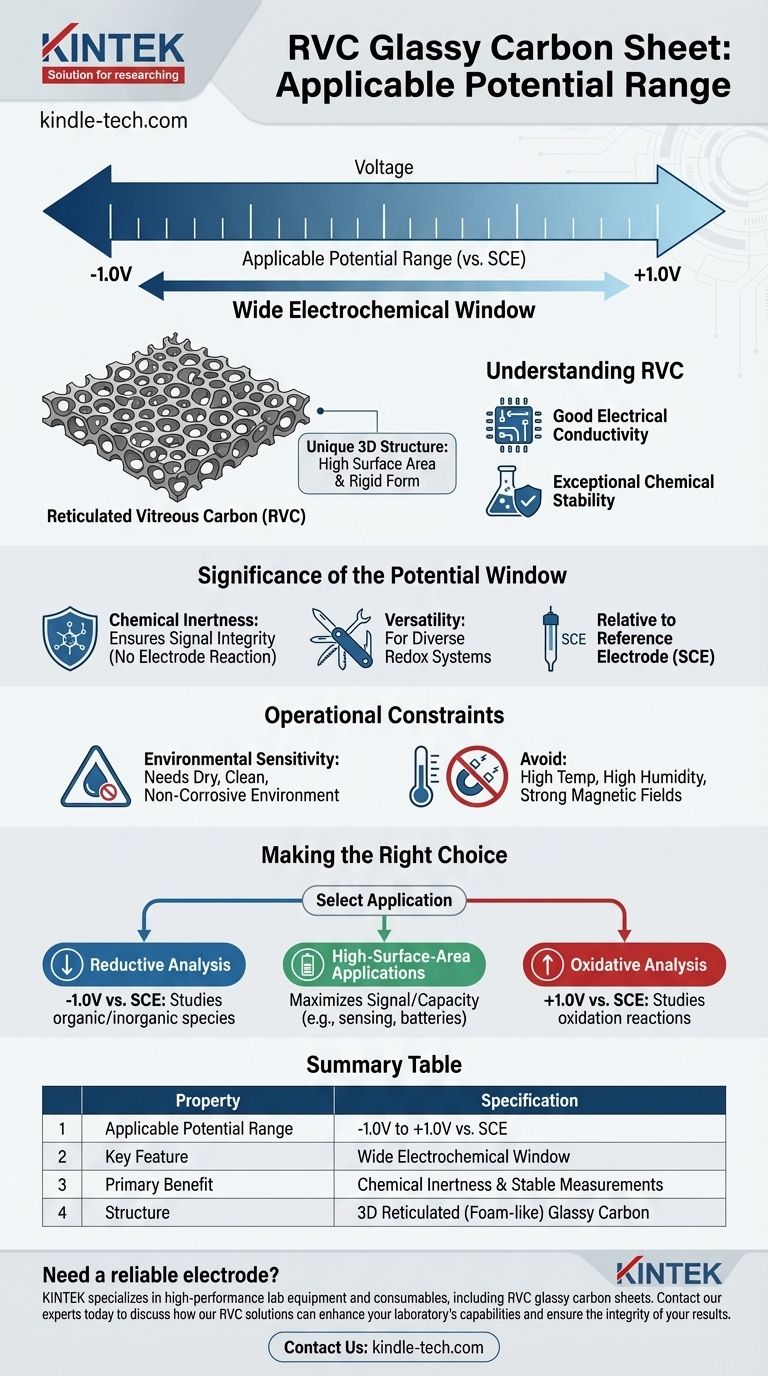
The applicable potential range for an RVC glassy carbon sheet is approximately -1.0V to +1.0V when measured against a saturated calomel electrode (SCE). This wide electrochemical window is a key feature that makes it a highly versatile and reliable working electrode for a broad array of electrochemical experiments.
The wide potential window of Reticulated Vitreous Carbon (RVC) is a direct result of its inherent chemical inertness and stable structure. This allows the material to function effectively as an electrode without undergoing oxidation or reduction itself, ensuring the integrity of your electrochemical measurements.

Understanding RVC Glassy Carbon
A Unique Three-Dimensional Structure
Reticulated Vitreous Carbon (RVC) is not a simple flat sheet. It is a three-dimensional, foam-like material produced by the high-temperature carbonization of a polymer foam.
This process creates an open-pore, "reticulated" network of glassy carbon that combines high surface area with a rigid structure.
Core Material Properties
The performance of RVC stems from its fundamental characteristics. It possesses good electrical conductivity and exceptional chemical stability across a wide range of environments.
Furthermore, its unique microscopic structure provides a very large specific surface area, which is highly advantageous for many electrochemical applications.
The Significance of the -1V to +1V Potential Window
Why Chemical Inertness Matters
The primary reason for RVC's wide potential range is its chemical stability. The material itself does not easily oxidize or reduce within this -1V to +1V window.
This inertness is critical because it ensures that the electrical current measured during an experiment comes from the chemical reaction you are studying, not from a reaction involving the electrode itself.
Versatility in Electrochemical Studies
This stable potential window accommodates the requirements of many different redox systems.
Whether you are studying reductive processes at negative potentials or oxidative processes at positive potentials, the RVC electrode provides a stable background for your measurements.
The Importance of the Reference Electrode
It is crucial to note that this potential range is defined relative to a specific reference electrode, in this case, the Saturated Calomel Electrode (SCE).
Electrochemical potentials are always measured as a difference, so the stated range of your working electrode (RVC) is only meaningful when the reference is known.
Operational Constraints to Consider
Environmental Sensitivity
To maintain its optimal performance, an RVC glassy carbon sheet should be used and stored in a dry, clean, and non-corrosive gas environment.
Contamination or corrosion can alter the surface chemistry and compromise the integrity of your results.
Avoiding Performance Degradation
You must avoid using the material in conditions of high temperature, high humidity, or strong magnetic fields.
These factors can adversely affect the material's structural and electrical properties, potentially narrowing its effective potential range or leading to inaccurate measurements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Experiment
- If your primary focus is reductive analysis: The negative potential limit of -1.0V vs. SCE provides ample range for studying many organic and inorganic species without interference from the electrode.
- If your primary focus is oxidative analysis: The positive potential limit of +1.0V vs. SCE allows for the stable investigation of various oxidation reactions without electrode degradation.
- If your primary focus is high-surface-area applications (e.g., sensing or batteries): The combination of a wide potential window and the unique reticulated structure makes RVC an excellent choice for maximizing signal or capacity.
By understanding both its capabilities and its limitations, you can effectively leverage RVC glassy carbon to achieve reliable and accurate electrochemical results.
Summary Table:
| Property | Specification |
|---|---|
| Applicable Potential Range | -1.0V to +1.0V vs. SCE |
| Key Feature | Wide Electrochemical Window |
| Primary Benefit | Chemical Inertness & Stable Measurements |
| Structure | 3D Reticulated (Foam-like) Glassy Carbon |
Need a reliable electrode for your specific electrochemical application?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including RVC glassy carbon sheets. Our electrodes provide the stable potential window and high surface area you need for accurate analysis in sensing, battery research, and more.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our RVC solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and ensure the integrity of your results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Glassy Carbon Sheet RVC for Electrochemical Experiments
- Glassy Carbon Electrochemical Electrode
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- RRDE rotating disk (ring disk) electrode / compatible with PINE, Japanese ALS, Swiss Metrohm glassy carbon platinum
- Graphite Disc Rod and Sheet Electrode Electrochemical Graphite Electrode
People Also Ask
- What is an RVC glassy carbon sheet? A High-Performance Material for Demanding Applications
- What actions and conditions are strictly prohibited when working with a glassy carbon sheet? Protect Your Investment and Data Integrity
- What are the fundamental characteristics of glassy carbon? Discover its Unique Synergy of Properties
- What are the typical physical specifications for glassy carbon sheets? Unlock Superior Performance for Your Lab
- What is the porosity of an RVC glassy carbon sheet? Understanding the Critical Difference Between PPI and Porosity



















