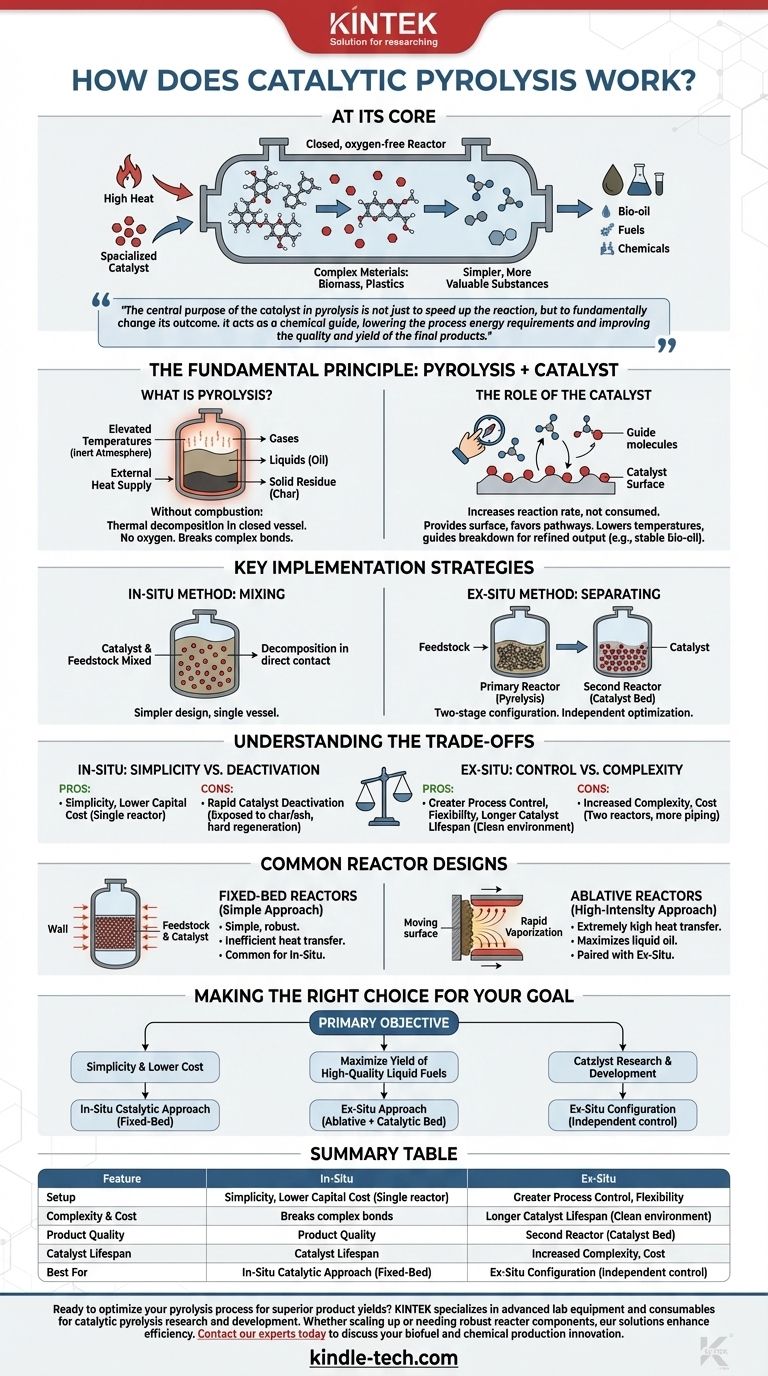
At its core, catalytic pyrolysis is a thermochemical process that uses a combination of high heat and a specialized catalyst to break down complex materials, like biomass or plastics, into simpler, more valuable substances. The process occurs in a closed, oxygen-free reactor, where the catalyst acts to lower the required temperature and selectively steer the chemical reactions toward desired products such as bio-oil, fuels, or other chemicals.
The central purpose of the catalyst in pyrolysis is not just to speed up the reaction, but to fundamentally change its outcome. It acts as a chemical guide, lowering the process energy requirements and improving the quality and yield of the final products.

The Fundamental Principle: Pyrolysis + Catalyst
To understand catalytic pyrolysis, we must first separate its two core components: the thermal process (pyrolysis) and the chemical guide (the catalyst).
What is Pyrolysis?
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of materials at elevated temperatures in an inert atmosphere. Think of it as high-temperature cooking in a closed vessel without any oxygen.
Because it operates as a closed system with an external heat supply, the material doesn't combust. Instead, the intense heat breaks the long, complex chemical bonds of the feedstock, turning solids into a mixture of gases, liquids (oil), and solid residue (char).
The Role of the Catalyst
Adding a catalyst to the process introduces a new level of control. A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed by it.
In catalytic pyrolysis, the catalyst provides a surface that favors certain chemical pathways. This allows the decomposition to happen at lower temperatures than traditional pyrolysis and, more importantly, it guides the breakdown of molecules to produce a more refined output—for example, a bio-oil with less oxygen, which is more stable and closer to conventional crude oil.
Key Implementation Strategies
Catalytic pyrolysis is not a single method but a strategy that can be implemented in two primary ways: in-situ or ex-situ. The choice between them is a foundational design decision.
The In-Situ Method: Mixing Catalyst and Feedstock
In this approach, the catalyst and the raw feedstock (e.g., wood chips, plastic waste) are mixed together inside the pyrolysis reactor.
As heat is applied, the feedstock decomposes while in direct contact with the catalyst. This is a simpler design from an equipment standpoint, as the entire process occurs within a single vessel.
The Ex-Situ Method: Separating the Process
This method uses a two-stage configuration. First, the feedstock undergoes pyrolysis in a primary reactor. The resulting hot gases and vapors are then immediately routed into a second, separate reactor containing the catalyst bed.
This separation allows for independent optimization. The pyrolysis step can be tuned for maximum vapor yield, while the catalytic upgrading step can be tailored for specific chemical conversions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither method is universally superior. The optimal choice depends entirely on the project's goals, balancing process complexity against product quality.
In-Situ: Simplicity vs. Catalyst Deactivation
The primary advantage of the in-situ method is its simplicity and lower capital cost. Using a single reactor vessel streamlines the design and operation.
However, the major drawback is rapid catalyst deactivation. The catalyst is physically mixed with the feedstock, exposing it to char and inorganic ash, which block its active sites. This makes regenerating and reusing the catalyst difficult and costly.
Ex-Situ: Control vs. Complexity
The ex-situ approach offers far greater process control and flexibility. By separating pyrolysis from catalytic upgrading, you can maintain the catalyst in a clean environment, which significantly extends its lifespan and simplifies regeneration. This also allows for fine-tuning the final product composition.
The trade-off is increased complexity and cost. An ex-situ system requires two separate reactors and associated piping, leading to a more expensive and operationally complex plant.
Common Reactor Designs
The choice of reactor technology is closely tied to the pyrolysis strategy. Different designs manage heat transfer in fundamentally different ways.
Fixed-Bed Reactors: The Simple Approach
A fixed-bed reactor is a simple vessel where the feedstock (and catalyst, if in-situ) forms a stationary "bed." Heat is transferred slowly from the reactor walls inward.
This design is mechanically simple and robust but suffers from inefficient heat transfer, which can lead to lower yields of the desired liquid product. It is most commonly associated with in-situ catalytic pyrolysis due to its simple configuration.
Ablative Reactors: The High-Intensity Approach
An ablative reactor works by pressing the feedstock against a very hot moving surface. The intense, direct contact causes the material to rapidly "melt" and vaporize, a process known as ablation.
This method achieves extremely high rates of heat transfer, maximizing the production of liquid oil. Due to the mechanics involved, ablative pyrolysis is almost always paired with an ex-situ catalytic reactor to upgrade the resulting vapors.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct catalytic pyrolysis architecture requires a clear understanding of your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is process simplicity and lower initial cost: An in-situ catalytic approach in a simple fixed-bed reactor is the most direct path, despite challenges with catalyst lifespan.
- If your primary focus is maximizing the yield of high-quality liquid fuels: An ex-situ approach, pairing a fast pyrolysis reactor (like an ablative one) with a separate catalytic bed, offers superior control and product quality.
- If your primary focus is catalyst research and development: An ex-situ configuration is essential, as it provides the independent control needed to effectively test and optimize catalyst performance without interference from char and ash.
Understanding these core principles and trade-offs empowers you to select the right pyrolysis strategy to meet your specific technical and economic objectives.
Summary Table:
| Feature | In-Situ Catalytic Pyrolysis | Ex-Situ Catalytic Pyrolysis |
|---|---|---|
| Setup | Single reactor, catalyst mixed with feedstock | Two-stage: separate pyrolysis & catalytic reactors |
| Complexity & Cost | Lower capital cost, simpler design | Higher capital cost, more complex operation |
| Product Quality | Moderate, catalyst deactivation is rapid | High, optimized for specific chemical output |
| Catalyst Lifespan | Short, due to contamination by char/ash | Long, as catalyst is protected in a clean bed |
| Best For | Simpler, lower-cost setups | Maximizing liquid fuel yield and catalyst R&D |
Ready to optimize your pyrolysis process for superior product yields? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for catalytic pyrolysis research and development. Whether you're scaling up from in-situ to ex-situ systems or need robust reactor components, our solutions are designed to enhance your efficiency and results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's innovation in biofuel and chemical production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
People Also Ask
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions



















