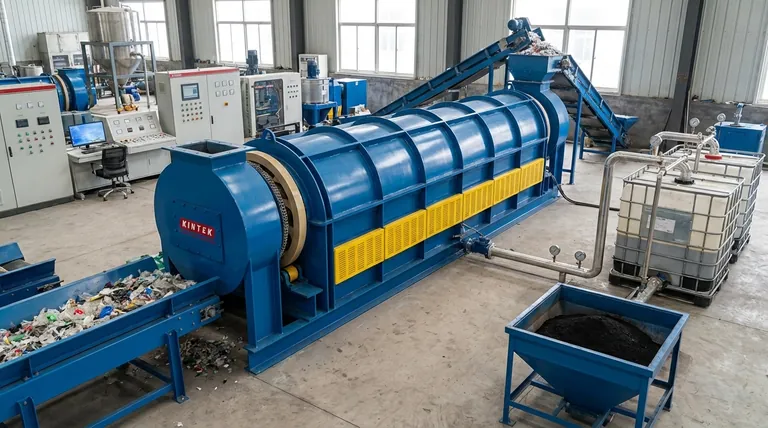
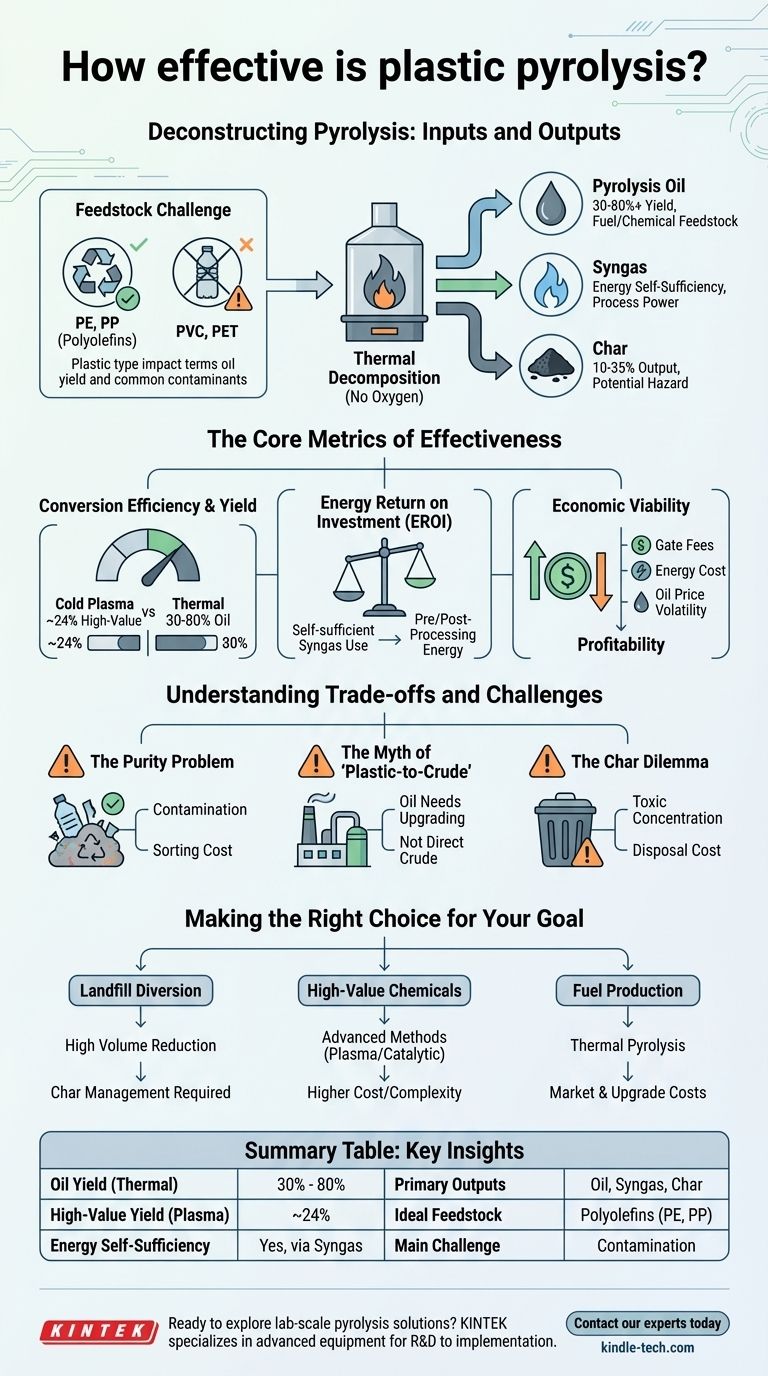
The effectiveness of plastic pyrolysis is highly variable, depending on the specific technology used and the type of plastic being processed. While advanced methods like cold plasma pyrolysis can convert around 24% of plastic into high-value products, traditional thermal pyrolysis often focuses on producing pyrolysis oil, with yields that can range from 30% to over 80% by weight.
Plastic pyrolysis is a promising technology for managing plastic waste, but its effectiveness is not a single number. It is a complex trade-off between the volume of waste processed, the quality of the resulting products, the energy required to run the process, and significant operational challenges.

Deconstructing Pyrolysis: Inputs and Outputs
Plastic pyrolysis is a form of thermal decomposition, breaking down long polymer chains into smaller, simpler molecules in the absence of oxygen. Understanding what goes in and what comes out is the first step in evaluating its effectiveness.
The Feedstock Challenge
The process is highly sensitive to the type of plastic used. Polyolefins (like PE and PP, found in packaging and containers) are ideal and yield the most oil.
However, plastics like PVC release chlorine, which can create corrosive hydrochloric acid and toxic dioxins. PET (from water bottles) contains oxygen, which ends up in the pyrolysis oil, lowering its quality and requiring extra processing steps.
The Three Primary Outputs
Pyrolysis doesn't make plastic disappear; it transforms it. The primary outputs are a liquid oil, a synthetic gas (syngas), and a solid residue (char).
- Pyrolysis Oil: This is often the main target product. It's a complex hydrocarbon mixture that can be refined into fuels or chemical feedstocks. Its quality and energy content vary widely.
- Syngas: A mixture of flammable gases (like hydrogen and methane). A portion of this gas is almost always used to power the pyrolysis process itself, making it partially self-sustaining.
- Char: A solid, carbon-rich residue. Depending on the feedstock's contamination, this char can contain heavy metals and other toxic substances, requiring careful disposal.
The Core Metrics of Effectiveness
True effectiveness goes beyond just the yield of one product. It must be measured across several interconnected factors.
Conversion Efficiency and Product Yield
This is the most common metric. As noted, cold plasma pyrolysis can convert 24% of plastic into valuable gases and solids for a circular economy.
More conventional thermal pyrolysis of ideal mixed plastics can yield 50% liquid oil, 30% gas, and 20% char by weight. The goal is often to maximize the oil fraction.
Energy Return on Investment (EROI)
An effective process should not consume more energy than it produces. Most modern pyrolysis plants are designed to be energy self-sufficient by using the syngas they produce as fuel for the reaction.
However, the energy required for pre-processing the plastic (shredding, cleaning, drying) and post-processing the oil can significantly impact the net energy balance.
Economic Viability
Effectiveness is ultimately determined by whether a facility can operate profitably. This depends on "gate fees" (payment received for taking waste), the cost of energy, and the market price for the pyrolysis oil and char.
The unstable price of crude oil directly impacts the value of pyrolysis oil, creating significant market risk for operators.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
Pyrolysis is not a perfect solution. An objective assessment requires acknowledging its significant operational hurdles.
The Purity Problem
Real-world plastic waste is messy. It's a mix of different polymer types, labels, food residue, and other contaminants.
This contamination is the single biggest challenge. It can poison catalysts, degrade the quality of the oil, and create toxic byproducts in the char and emissions, requiring expensive sorting and cleaning infrastructure.
The Myth of "Plastic-to-Crude"
Pyrolysis oil is not synthetic crude oil. It is often acidic, unstable, and contains contaminants that must be removed through significant, costly upgrading before it can be used in a traditional refinery.
This crucial post-processing step is often overlooked when discussing the technology's effectiveness.
The Char Dilemma
The solid char byproduct can account for 10-35% of the output. While it has potential uses as a solid fuel or activated carbon, it can also concentrate heavy metals and toxic chemicals from the original waste stream.
If deemed hazardous, this char must be disposed of in a specialized landfill, adding cost and environmental burden to the overall process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Evaluating pyrolysis requires aligning the technology's capabilities with a specific objective.
- If your primary focus is landfill diversion: Pyrolysis can be highly effective at reducing the volume of non-recyclable plastic waste, but it requires robust systems to manage the char and emissions safely.
- If your primary focus is creating high-value chemicals: Advanced methods like catalytic or plasma pyrolysis are necessary, which have higher costs and complexity but produce more refined and valuable outputs.
- If your primary focus is producing fuel: Thermal pyrolysis is the most mature and common approach, but its economic success is heavily tied to the volatile energy market and the cost of upgrading the raw oil.
Ultimately, plastic pyrolysis is a powerful tool with specific applications, not a universal remedy for the plastic waste crisis.
Summary Table:
| Metric | Key Insight |
|---|---|
| Oil Yield (Thermal Pyrolysis) | 30% - 80% by weight, depending on plastic type and process. |
| High-Value Product Yield (Cold Plasma) | ~24% conversion to valuable gases and solids. |
| Energy Self-Sufficiency | Modern plants can be self-powered by produced syngas. |
| Primary Outputs | Pyrolysis oil, syngas, and solid char. |
| Ideal Feedstock | Polyolefins (PE, PP); PVC and PET are problematic. |
| Main Challenge | Contamination from mixed, real-world plastic waste. |
Ready to explore lab-scale pyrolysis solutions for your research or waste management project? KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment, including pyrolysis systems, to help you accurately test feedstocks, optimize yields, and validate processes. Our expertise supports your journey from R&D to effective implementation. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and how we can help you achieve your goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- High Performance Laboratory Freeze Dryer
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- High Performance Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Research and Development
People Also Ask
- What equipment is used in pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Products
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products



















