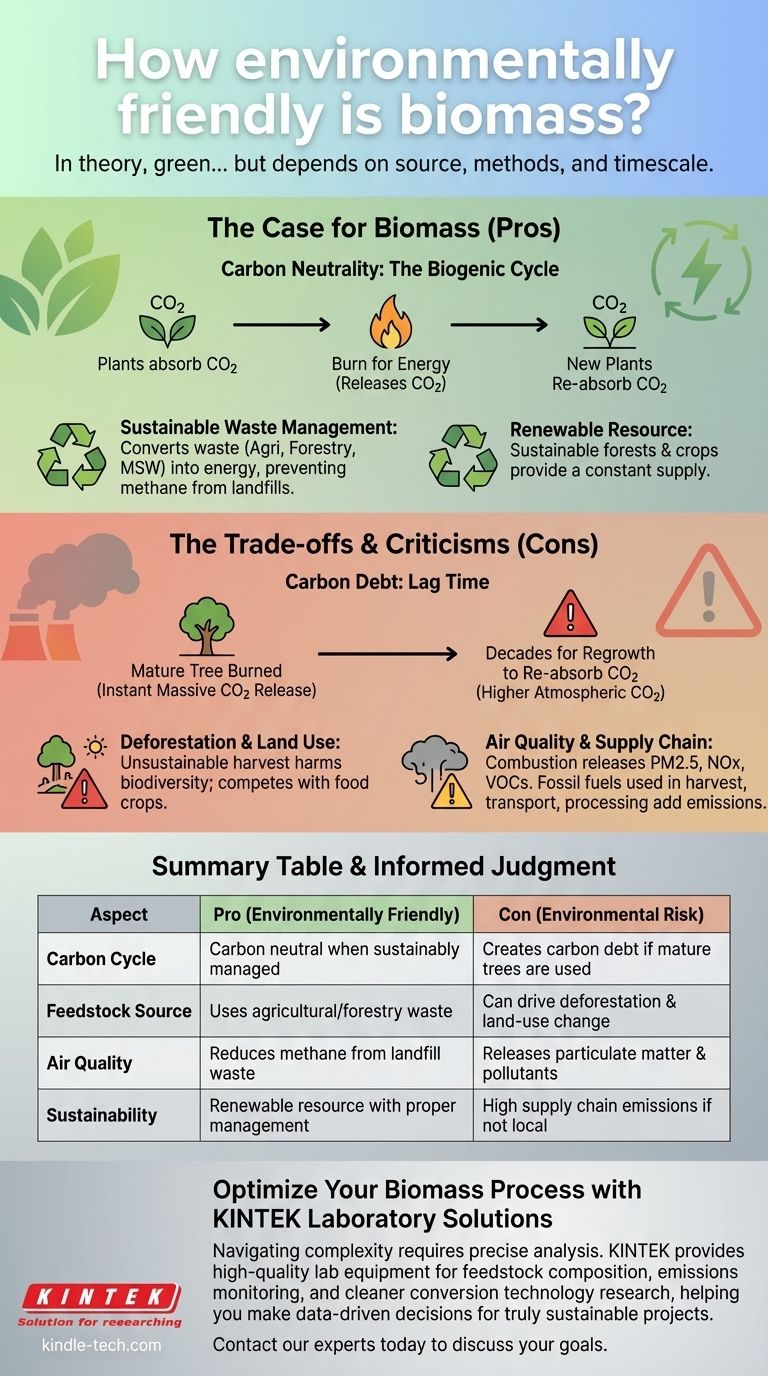
In theory, biomass is presented as an environmentally friendly energy source. It is considered renewable because it utilizes organic material, and its proponents argue that it reduces greenhouse gas emissions by making use of waste that would otherwise decompose. The carbon dioxide released during combustion is part of the existing biogenic carbon cycle, which is absorbed by new plant growth.
The environmental friendliness of biomass is not a given; it is entirely dependent on the source of the material (the "feedstock"), the methods of harvesting and conversion, and the timescale over which its carbon impact is measured.

The Case for Biomass as a Green Energy Source
To understand the potential of biomass, it's important to recognize the principles that make it an attractive alternative to fossil fuels.
The Principle of Carbon Neutrality
Biomass energy operates on the biogenic carbon cycle. Plants absorb CO2 from the atmosphere, and when they are burned for energy, that same amount of CO2 is released back.
As long as new plants are grown to replace what was harvested, the process is considered carbon neutral. This is a stark contrast to fossil fuels, which release vast quantities of ancient, sequestered carbon into the atmosphere.
Sustainable Waste Management
A key benefit of biomass is its ability to convert waste into energy.
This includes agricultural residues (like corn stalks), forestry byproducts (like wood chips and sawdust), and certain components of municipal solid waste. Using these materials prevents them from decomposing in landfills, where they would release methane—a greenhouse gas far more potent than CO2.
A Constant, Renewable Resource
Unlike finite resources like coal or natural gas, biomass is fundamentally renewable.
As long as forests are managed sustainably and crops continue to be grown, a consistent supply of feedstock is available. This makes it a potential source of reliable, baseload power that can complement intermittent renewables like wind and solar.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Criticisms
The idealized vision of biomass often clashes with real-world implementation. The environmental credentials of biomass are subject to intense debate and depend heavily on practical factors.
The Problem of "Carbon Debt"
The most significant criticism revolves around the concept of carbon debt.
When a mature tree is cut down and burned, decades of stored carbon are released into the atmosphere instantly. It can take an equivalent number of decades for a newly planted tree to grow and re-absorb that same amount of carbon.
During this lag time, the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere is higher than it would have been, potentially worsening climate change in the critical short-to-medium term.
Deforestation and Land Use Impacts
The demand for biomass can create perverse incentives, leading to the unsustainable harvesting of forests.
If demand outstrips the supply of genuine waste, it can drive deforestation and harm biodiversity. Furthermore, growing dedicated energy crops can compete with land needed for food production, impacting global food security and ecosystems.
Air Quality Concerns
Burning biomass, particularly solid wood, is not clean.
Combustion releases harmful air pollutants like particulate matter (PM2.5), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). These pollutants are linked to respiratory illnesses, cardiovascular problems, and other serious public health issues, especially near the power plants.
Supply Chain Emissions
The journey from forest or farm to power plant has its own carbon footprint.
Fossil fuels are used in the machinery that harvests, collects, processes (e.g., drying and pelletizing), and transports biomass, often across oceans. These "lifecycle emissions" must be accounted for and can erode the net climate benefit.
Making an Informed Judgment on Biomass
To assess whether a specific biomass project is environmentally sound, the central question must always be: "Where is the feedstock coming from?"
- If your primary focus is rapid decarbonization: Be highly cautious, as the carbon debt from burning whole trees can increase emissions over critical decades.
- If your primary focus is sustainable waste management: Biomass is an excellent solution when feedstock is strictly limited to genuine agricultural, forestry, or municipal waste streams.
- If your primary focus is air quality and public health: The technology used for combustion is critical; advanced filtration and gasification systems are necessary to minimize harmful pollutants.
Ultimately, the environmental impact of biomass is determined not by what it is, but by how it is sourced, processed, and managed.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Pro (Environmentally Friendly) | Con (Environmental Risk) |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Cycle | Carbon neutral when sustainably managed | Creates carbon debt if mature trees are used |
| Feedstock Source | Uses agricultural/forestry waste | Can drive deforestation & land-use change |
| Air Quality | Reduces methane from landfill waste | Releases particulate matter & pollutants |
| Sustainability | Renewable resource with proper management | High supply chain emissions if not local |
Optimize Your Biomass Process with KINTEK Laboratory Solutions
Navigating the complexities of biomass sustainability requires precise analysis and reliable equipment. Whether you're researching feedstock composition, monitoring emissions, or developing cleaner conversion technologies, KINTEK provides the high-quality lab equipment and consumables you need for accurate, reproducible results.
We serve laboratories and research facilities focused on renewable energy, helping you make data-driven decisions for truly sustainable biomass projects.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can support your environmental and energy goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy



