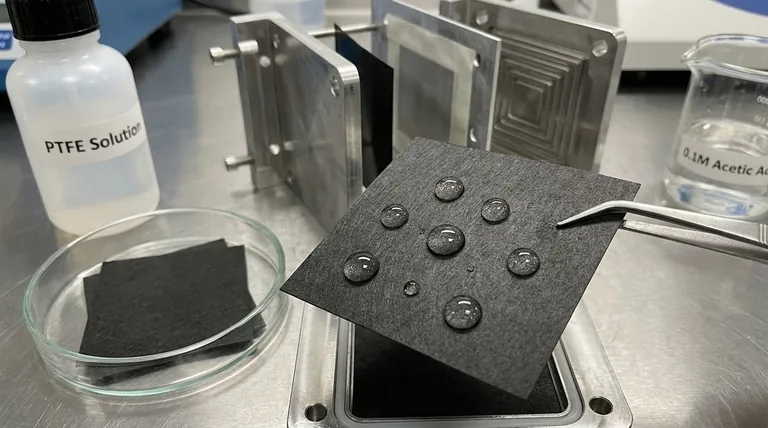
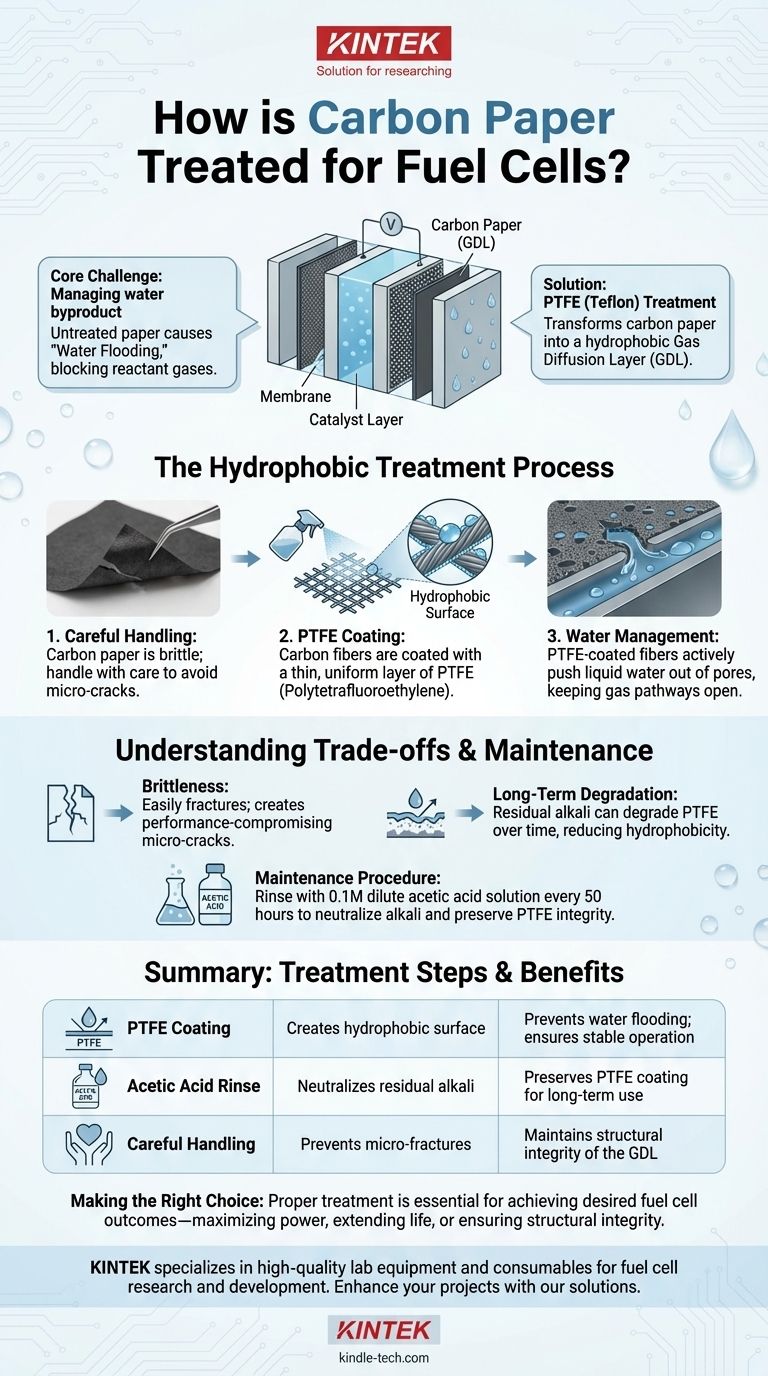
To prepare carbon paper for use in a fuel cell, it is treated with a coating of PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene). This treatment is critical because it makes the porous paper hydrophobic, or water-repellent. This property is essential for preventing a condition known as "water flooding," where excess water blocks the flow of reactant gases, thereby ensuring the fuel cell can operate efficiently.
The core challenge in a fuel cell is not just generating power, but managing the water it produces. Treating carbon paper with PTFE transforms it from a simple electrical conductor into a sophisticated Gas Diffusion Layer (GDL) designed to expel liquid water while allowing reactant gases to reach the catalyst.
The Role of Carbon Paper as a Gas Diffusion Layer
The Dual Nature of Water in a Fuel Cell
In a polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM) fuel cell, water is a necessary component for proton conductivity through the membrane. However, water is also a byproduct of the electrochemical reaction.
If this product water is not effectively removed, it can accumulate in the pores of the carbon paper, physically blocking the path for reactant gases (hydrogen and oxygen) to reach the catalyst layer.
Preventing "Water Flooding"
This blockage is known as water flooding. It essentially starves the fuel cell of its fuel, causing a dramatic drop in performance and potentially stopping its operation altogether. The primary goal of carbon paper treatment is to prevent this.
The Hydrophobic Treatment Process
Coating with PTFE
The key treatment is coating the carbon paper with a thin, uniform layer of PTFE, a polymer well-known for its non-stick and water-repellent properties (e.g., Teflon).
This coating does not completely seal the paper. Instead, it coats the carbon fibers within the porous structure, changing their surface properties from water-attracting (hydrophilic) to water-repelling (hydrophobic).
How it Manages Water
When water droplets form on the PTFE-coated fibers, they are actively pushed out of the pores and into the flow channels, where they can be removed from the cell. This keeps the gas pathways open and maintains stable fuel cell operation.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Practical Challenges
Physical Handling and Brittleness
Before any chemical treatment, it's important to recognize that carbon paper is inherently brittle and can easily fracture. It must be handled with care and cut slowly with a very sharp blade to avoid creating micro-cracks that would compromise its performance as a GDL.
Long-Term Coating Degradation
The PTFE coating is not indestructible. During long-term operation, certain conditions, such as the presence of residual alkali, can degrade the coating.
This degradation reduces the paper's hydrophobicity, making the cell increasingly susceptible to water flooding over time.
The Need for Maintenance
To counteract this degradation, a maintenance procedure may be necessary. Rinsing the carbon paper with a 0.1M dilute acetic acid solution after extended periods of operation (e.g., every 50 hours) helps neutralize any harmful residual alkali and preserve the integrity of the PTFE coating.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Properly preparing and maintaining your carbon paper is essential for achieving desired fuel cell outcomes.
- If your primary focus is maximizing power output: Ensure your PTFE treatment is uniform and sufficient to prevent water flooding, as this is the most common cause of sudden performance loss.
- If your primary focus is extending operational life: You must account for the degradation of the PTFE coating by implementing a maintenance schedule, such as an acetic acid rinse, to preserve hydrophobicity.
- If you are in the cell assembly phase: Your first priority is careful physical handling to prevent fractures, as a structurally compromised GDL cannot function correctly regardless of its chemical treatment.
Ultimately, treating the carbon paper correctly is what transforms it from a passive component into an active manager of the fuel cell's internal environment.
Summary Table:
| Treatment Step | Purpose | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| PTFE Coating | Creates a hydrophobic surface | Prevents water flooding by repelling liquid water |
| Acetic Acid Rinse | Neutralizes residual alkali | Preserves PTFE coating integrity for long-term use |
| Careful Handling | Prevents micro-fractures | Maintains structural integrity of the Gas Diffusion Layer |
Achieve optimal fuel cell performance with reliable GDL materials. The proper treatment of carbon paper is critical for managing water and ensuring stable power output. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for fuel cell research and development. Our products support precise material preparation and long-term experimental success. Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your fuel cell projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Hydrophilic Carbon Paper TGPH060 for Battery Lab Applications
- Glassy Carbon Sheet RVC for Electrochemical Experiments
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Ultra-High Vacuum Flange Aviation Plug Glass Sintered Airtight Circular Connector for KF ISO CF
- Tungsten Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
People Also Ask
- What is an RVC glassy carbon sheet? A High-Performance Material for Demanding Applications
- What are the major components of biomass? Unlocking the Building Blocks of Renewable Energy
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the key properties of carbon felt? Unlocking High-Temperature & Electrochemical Performance
- How is carbon paper constructed? The Engineered Porous Scaffold for High-Performance Applications






