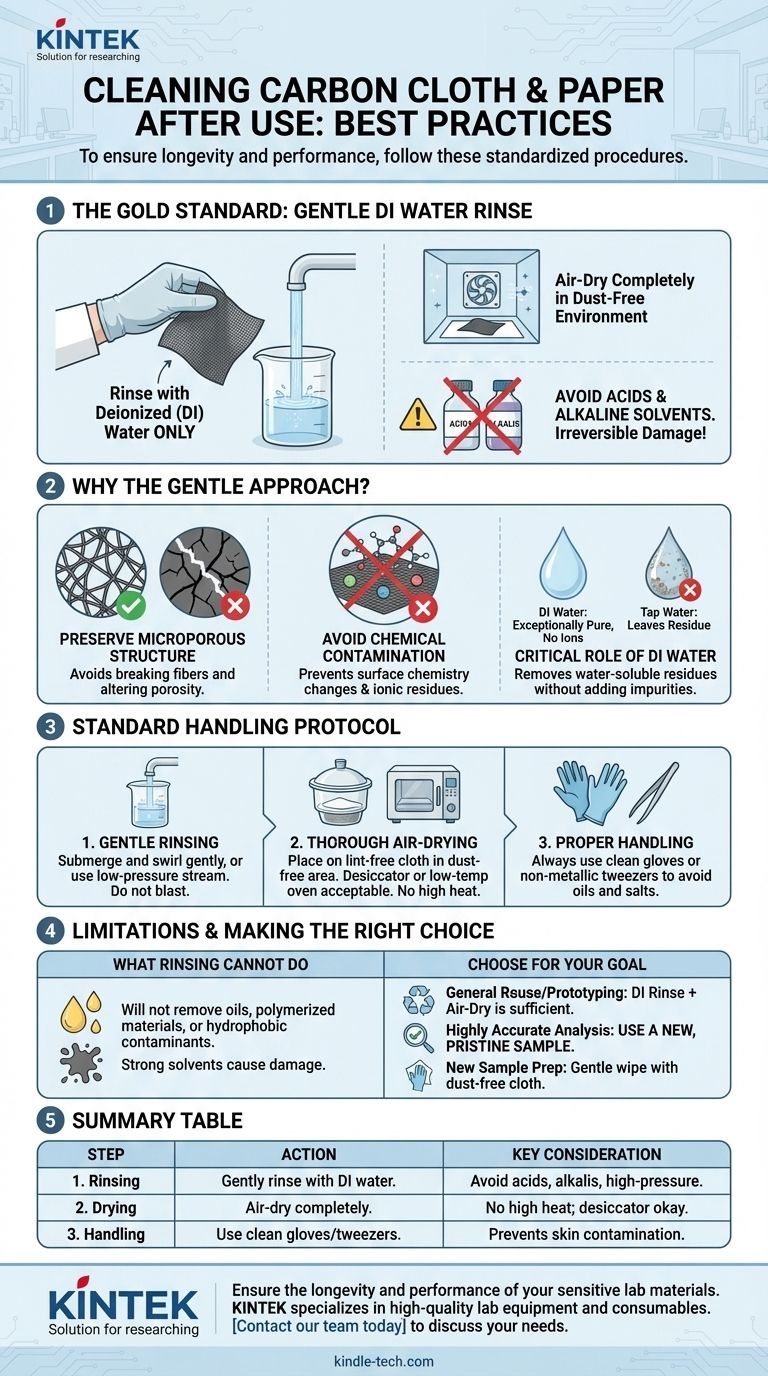
To properly clean used carbon cloth or carbon paper, the standard and safest method is to rinse the material with deionized (DI) water and allow it to air-dry completely in a dust-free environment. It is critical to avoid the use of any acidic or alkaline solvents, as these can cause irreversible damage to the material's structure and performance characteristics.
The goal of cleaning these materials is not just to remove surface residue, but to do so without altering their delicate microporous structure or introducing chemical contaminants. Therefore, a gentle rinse with deionized water is the universally accepted method to preserve the material's integrity for reuse or analysis.

The Rationale Behind Gentle Cleaning
Understanding why a specific cleaning method is required is crucial for handling these sensitive materials. The cleaning protocol is designed to protect the very properties that make carbon cloth and paper effective.
Preserving the Microporous Structure
Carbon cloth and paper are not simple flat sheets. They are engineered materials composed of a complex, non-woven network of carbon fibers, creating a high surface area and specific porosity that is essential for their function in applications like fuel cells or batteries. Aggressive cleaning, scrubbing, or high-pressure sprays can break these delicate fibers, altering the material's diffusion and conductive properties.
Avoiding Chemical Contamination
The surfaces of carbon materials are chemically active. The references explicitly warn against using acids or alkalis because they can react with the carbon, changing its surface chemistry. This can affect its hydrophobicity (water-repelling properties) and leave behind ionic residues that will interfere with future electrochemical processes, leading to unreliable experimental results.
The Critical Role of Deionized Water
Deionized (DI) water is the solvent of choice because it is exceptionally pure. It contains virtually no dissolved ions. Using tap water would deposit minerals and salts onto the carbon fibers as the water evaporates, contaminating the material. DI water effectively washes away water-soluble residues without leaving any impurities behind.
Standard Cleaning and Handling Protocols
Following a consistent procedure ensures your materials are treated correctly every time.
Step 1: Gentle Rinsing
Submerge the carbon material in a beaker of fresh deionized water and swirl it gently. Alternatively, you can hold the material with clean, non-metallic tweezers and rinse it under a gentle, low-pressure stream of DI water. The goal is to flush the surface and pores, not to blast them.
Step 2: Thorough Air-Drying
After rinsing, place the carbon material on a clean, lint-free cloth in a dust-free area to air-dry. You can also place it in a desiccator or a very low-temperature vacuum oven. Avoid using heat guns or high-temperature ovens, as excessive heat can oxidize the carbon and damage any polymeric binders or hydrophobic coatings.
Handling Before and After
Always handle carbon cloth and paper with clean gloves or tweezers to avoid transferring oils and salts from your skin. Before initial use, it is good practice to gently wipe the surface with a dust-free cloth to remove any superficial dust from storage and handling.
Understanding the Limitations
While DI water rinsing is the standard, it's important to recognize its limitations.
What Simple Rinsing Cannot Do
A water rinse is primarily effective for removing water-soluble salts or residues. It will not remove strongly adsorbed chemical species, polymerized materials, or hydrophobic contaminants like oils and certain catalyst binders. Attempting to remove these with stronger solvents often causes more harm than good.
The Risk of Altering Properties
Any cleaning process, no matter how gentle, carries a small risk of altering the material. For highly sensitive electrochemical measurements where absolute purity is paramount, using a fresh, new piece of carbon material is always the most reliable option. Reusing cleaned materials is best reserved for less critical applications or comparative studies.
Why Solvents Are Strictly Avoided
Many carbon papers and cloths are treated with materials like PTFE (Teflon) to control water management. Aggressive organic solvents, acids, or bases can strip away these vital coatings, degrade the binders holding the fibers together, and permanently damage the material's performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your cleaning strategy should align with the objective of your work.
- If your primary focus is general reuse in prototyping or less sensitive tests: A thorough rinse with deionized water followed by careful air-drying is the correct and sufficient procedure.
- If your primary focus is highly accurate analytical measurement: It is strongly recommended to use a new, pristine sample to ensure your results are not influenced by contaminants or cleaning artifacts.
- If your primary focus is preparing a new sample for its first use: Gently wipe it with a clean, dust-free cloth to remove any superficial particles from storage and handling.
By adhering to these principles, you can confidently maintain the structural and chemical integrity of your carbon materials for more reliable and repeatable work.
Summary Table:
| Step | Action | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Rinsing | Gently rinse with deionized (DI) water. | Avoid acids, alkalis, and high-pressure sprays to prevent structural damage. |
| 2. Drying | Air-dry completely in a dust-free environment. | Do not use high heat; a desiccator or low-temperature oven is acceptable. |
| 3. Handling | Use clean gloves or non-metallic tweezers. | Prevents contamination from skin oils and salts. |
Ensure the longevity and performance of your sensitive lab materials. Proper handling and cleaning are crucial for accurate results. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including materials like carbon cloth and paper. Our experts can help you select the right products and provide guidance on best practices for your specific laboratory needs.
Contact our team today to discuss how we can support your research and ensure reliable, repeatable outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Hydrophilic Carbon Paper TGPH060 for Battery Lab Applications
- Glassy Carbon Sheet RVC for Electrochemical Experiments
- Conductive Carbon Fiber Brush for Static Removal and Cleaning
- Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer Quartz Plate JGS1 JGS2 JGS3
- E Beam Crucibles Electron Gun Beam Crucible for Evaporation
People Also Ask
- What role does hydrophilic carbon fiber paper play as an electrode material? Enhancing Flow Cell Efficiency
- What is an RVC glassy carbon sheet? A High-Performance Material for Demanding Applications
- How can the lifespan of carbon paper be extended? Reinforce Edges with Epoxy for Maximum Durability
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the major components of biomass? Unlocking the Building Blocks of Renewable Energy


















