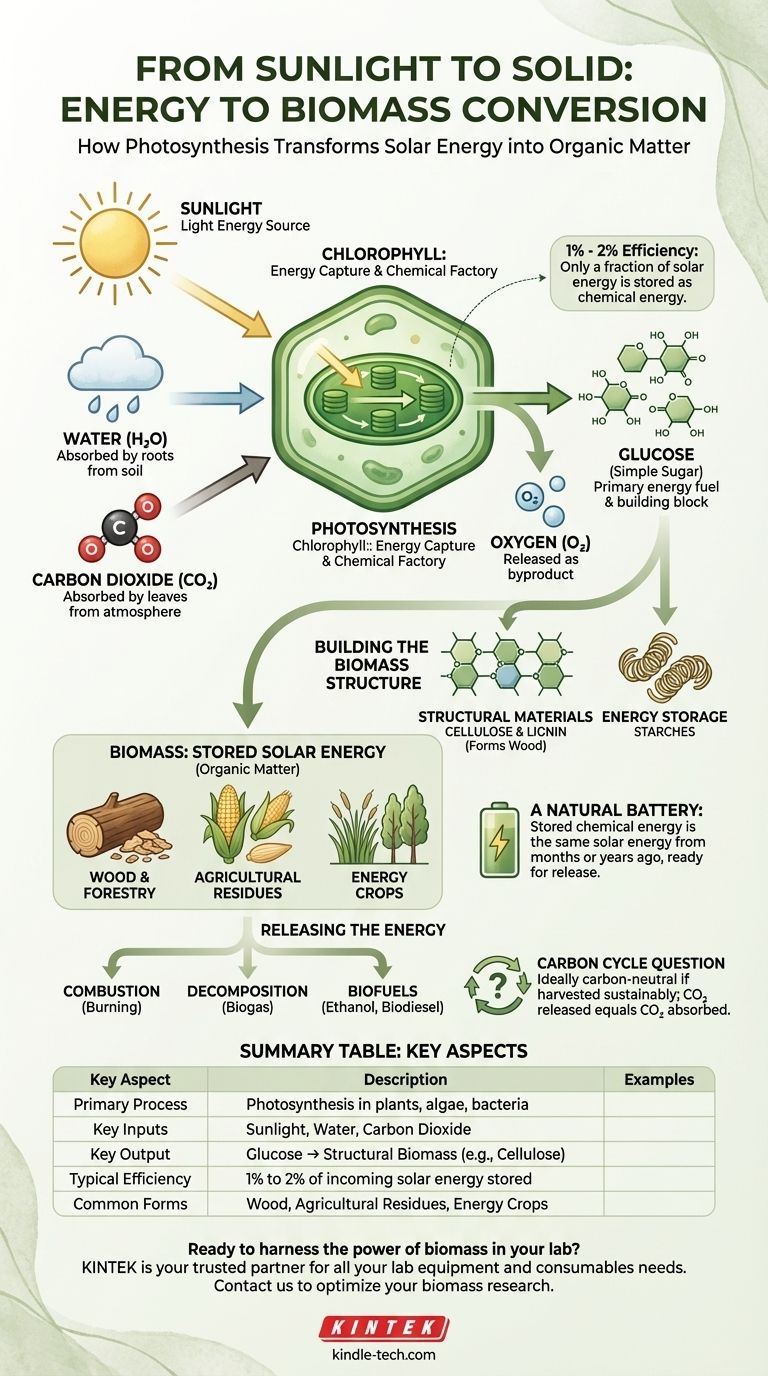
At its core, the conversion of energy into biomass is accomplished through photosynthesis. Plants, algae, and some bacteria act as natural converters, using the sun's light energy to transform simple inorganic molecules like carbon dioxide and water into complex, energy-rich organic compounds. This organic matter is what we call biomass.
The creation of physical mass from sunlight is not magic, but a fundamental chemical process. Plants capture solar energy and store it as chemical energy within their own structure, effectively turning light into a solid, usable resource.

The Engine of Conversion: Photosynthesis Explained
To understand how energy becomes mass, you must first understand the mechanism of photosynthesis. It is the single most important process for life on Earth, providing the energy foundation for nearly all ecosystems.
The Key Ingredients
The process begins with three simple inputs from the environment:
- Sunlight: The primary energy source.
- Water (H₂O): Typically absorbed from the soil through roots.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO₂): Absorbed from the atmosphere through small pores in leaves.
The Chemical Factory
Inside the plant's cells, a green pigment called chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight. This captured energy drives a chemical reaction that rearranges the atoms of water and carbon dioxide.
The process essentially uses light energy to split water molecules and combine them with carbon dioxide to create glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆), a simple sugar. Oxygen (O₂) is released as a byproduct.
From Sugar to Structure
This newly created glucose serves two purposes for the plant. It's an immediate fuel source for the plant's own metabolic needs, but more importantly, it's the fundamental building block for growth.
Plants link these simple sugar molecules together into long, complex chains to create structural materials like cellulose and lignin (which form wood) and energy storage molecules like starches. This physical material—the leaves, stems, roots, and wood—is the biomass.
What Constitutes Biomass?
Biomass is simply a term for organic matter derived from living, or recently living, organisms. It is a physical repository of solar energy.
A Form of Stored Solar Energy
Think of a log of wood as a natural battery. The energy stored in its chemical bonds is the same energy that originated from the sun months or years ago. When you burn that log, you are releasing that stored solar energy as heat and light.
Common Forms of Biomass
This energy-storing organic matter comes in many forms, including:
- Wood: From forests, sawmills, and dedicated forestry plantations.
- Agricultural Residues: Stalks, leaves, and husks left over after a crop is harvested, like corn stover or wheat straw.
- Energy Crops: Fast-growing, non-food plants like switchgrass or poplar trees, grown specifically for energy production.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Realities
While the conversion process is natural, its efficiency and application are subject to practical limitations. Understanding these is key to evaluating biomass as a resource.
The Efficiency of Photosynthesis
The process is not perfectly efficient. Of all the solar energy that strikes a plant's leaf, only a small fraction—typically 1% to 2%—is successfully converted and stored as chemical energy in biomass.
Releasing the Stored Energy
To be useful as an energy source for humans, the stored chemical energy in biomass must be released. This is typically done through combustion (burning), decomposition (which produces biogas), or conversion into biofuels like ethanol and biodiesel.
The Carbon Cycle Question
When biomass is burned, it releases the same amount of CO₂ that the plant originally absorbed from the atmosphere. In theory, this makes it a carbon-neutral energy source.
However, this neutrality depends heavily on sustainable practices. If biomass is harvested faster than it can regrow, or if significant fossil fuel energy is used in its cultivation and transport, the net carbon benefit is reduced or eliminated.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding this energy conversion is fundamental for work in multiple fields. How you apply this knowledge depends on your objective.
- If your primary focus is renewable energy: Recognize biomass as a method for storing and transporting solar energy, providing a dispatchable power source that wind and direct solar cannot offer alone.
- If your primary focus is agriculture or forestry: View your management practices as optimizing a natural energy conversion system, where crop and tree growth directly equates to captured and stored energy.
- If your primary focus is environmental science: Use this process as the baseline for evaluating the carbon cycle, land use impacts, and the true lifecycle sustainability of different bioenergy solutions.
By grasping how simple sunlight is transformed into solid matter, you can better harness one of the planet's most foundational renewable resources.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Process | Photosynthesis in plants, algae, and some bacteria |
| Key Inputs | Sunlight, Water (H₂O), Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) |
| Key Output | Glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆), which forms structural biomass (e.g., cellulose, lignin) |
| Typical Efficiency | 1% to 2% of incoming solar energy is stored as chemical energy |
| Common Biomass Forms | Wood, agricultural residues (e.g., corn stover), dedicated energy crops (e.g., switchgrass) |
Ready to harness the power of biomass in your lab?
Understanding the conversion of energy into biomass is just the first step. Applying this knowledge requires precise and reliable laboratory equipment for analysis, processing, and testing.
KINTEK is your trusted partner for all your lab equipment and consumables needs. Whether you are developing new biofuels, analyzing crop yields, or conducting environmental lifecycle assessments, we provide the tools for success.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can optimize your biomass research and development workflow.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- High Energy Vibratory Ball Mill for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output















