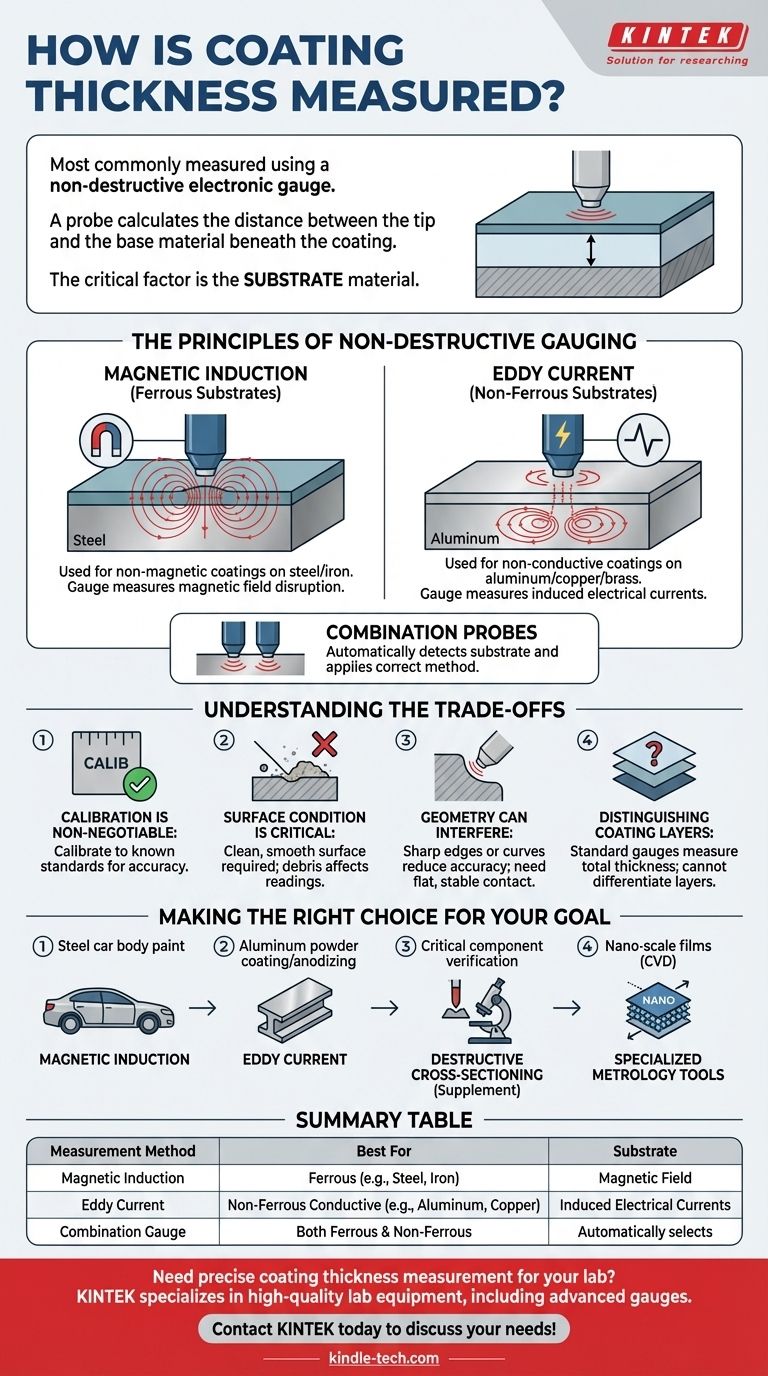
In short, coating thickness is most commonly measured using a non-destructive electronic gauge. This device uses a probe that, when placed on the surface, calculates the distance between the probe tip and the base material underneath the coating. The specific technology used depends entirely on the type of material being measured.
The critical factor in choosing a measurement method is the material of the substrate—the surface beneath the coating. One type of gauge is used for magnetic metals like steel, while another is required for non-magnetic metals like aluminum.

The Principles of Non-Destructive Gauging
Modern electronic thickness gauges are fast, accurate, and reliable, but they operate on distinct physical principles. Understanding which one to use is essential for getting an accurate measurement.
Magnetic Induction (For Ferrous Substrates)
This method is used to measure non-magnetic coatings over ferrous substrates like steel or iron.
The gauge's probe generates a constant magnetic field. When placed on the coated surface, the thickness of the coating layer alters this field. The gauge precisely measures this alteration and converts it into a thickness reading.
Eddy Current (For Non-Ferrous Substrates)
This technique is used for measuring non-conductive coatings over non-ferrous, conductive substrates like aluminum, copper, or brass.
The probe generates an alternating high-frequency electrical signal, which induces swirling electrical currents (eddy currents) in the metallic substrate. The distance between the probe and the substrate (i.e., the coating thickness) directly impacts the magnitude of these currents. The gauge measures this effect to calculate the thickness.
Combination Probes
Many modern gauges are "combo" units equipped with probes that can use both magnetic induction and eddy current principles. The device automatically detects the substrate type and applies the correct measurement method.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While electronic gauges are powerful, their accuracy depends on proper use and an awareness of their limitations.
Calibration is Non-Negotiable
A gauge's reading is only as good as its calibration. For reliable results, the device must be calibrated to known thickness standards (shims) on the specific, uncoated substrate you plan to measure. This accounts for the material's unique magnetic or conductive properties.
Surface Condition is Critical
The surface being measured must be clean and relatively smooth. Debris, dust, and significant surface roughness can lift the probe, leading to inaccurately high readings.
Geometry Can Interfere
Measurements taken on sharp edges or significant curves can be less accurate than those on a flat surface. The probe needs full, stable contact with the part to function correctly.
Distinguishing Coating Layers
Standard gauges measure the total coating thickness from the probe to the base metal. They cannot differentiate between individual layers, such as a primer, base coat, and clear coat. For that, more advanced methods are required.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct approach depends entirely on the materials involved and the level of precision required.
- If your primary focus is measuring paint on a steel car body: You need a gauge that uses the magnetic induction principle.
- If your primary focus is measuring powder coating or anodizing on an aluminum part: You must use a gauge based on the eddy current principle.
- If you need to verify a critical coating on a high-value component: Supplement electronic gauge readings with destructive cross-sectioning, where a sample is cut, polished, and measured under a microscope for ultimate accuracy.
- If you are working with nano-scale films from processes like CVD: You will require specialized metrology tools, as standard electronic gauges are not designed for these extremely thin layers.
Ultimately, matching the measurement technology to your specific coating and substrate is the key to achieving accurate and repeatable results.
Summary Table:
| Measurement Method | Best For Substrate | Principle |
|---|---|---|
| Magnetic Induction | Ferrous (e.g., Steel, Iron) | Measures disruption of a magnetic field by non-magnetic coatings. |
| Eddy Current | Non-Ferrous Conductive (e.g., Aluminum, Copper) | Measures effect of coating thickness on induced electrical currents. |
| Combination Gauge | Both Ferrous & Non-Ferrous | Automatically selects the correct method (Magnetic Induction or Eddy Current). |
Need precise coating thickness measurement for your lab?
Accurate measurements are critical for quality control, research, and development. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment, including advanced coating thickness gauges, to ensure your results are reliable and repeatable.
Our experts can help you select the perfect instrument for your specific substrate and coating materials.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your laboratory's coating measurement needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Lab Electrochemical Workstation Potentiostat for Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- KF ISO Stainless Steel Vacuum Flange Blind Plate for High Vacuum Systems
- Shaking Incubators for Diverse Laboratory Applications
People Also Ask
- Why use a vibratory sieve shaker for PET powder? Achieve Precise Particle Size Control for Chemical Research
- Why is powder classification using standard sieves essential for SHS reactions? Unlock Superior Nitriding Results
- What are the disadvantages of sieve machine? Key Limitations in Particle Size Analysis
- What function does a sieving system perform during HPS powder pretreatment? Ensure Uniform Particle Size Distribution
- Why is a precision vibratory sieving system important for Pt/Pd alloy analysis? Ensure Data Integrity & XRD Accuracy



















