In essence, zirconia is sintered by subjecting it to a precise, high-temperature thermal cycle that fuses its ceramic particles into a solid, dense mass without melting it. This critical process involves three distinct phases—heating, holding, and cooling—which collectively reduce porosity, cause significant shrinkage, and dramatically increase the material's final strength and integrity.
Sintering is not merely a heating process; it is the fundamental transformation that converts a soft, porous zirconia "green state" into a hard, high-performance ceramic by systematically eliminating internal voids.
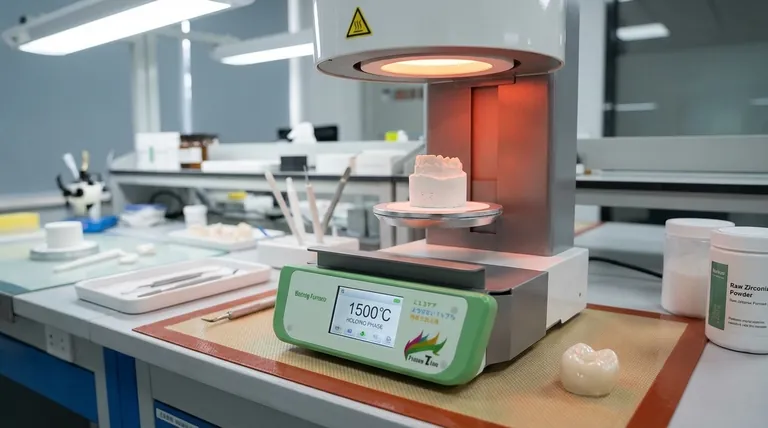

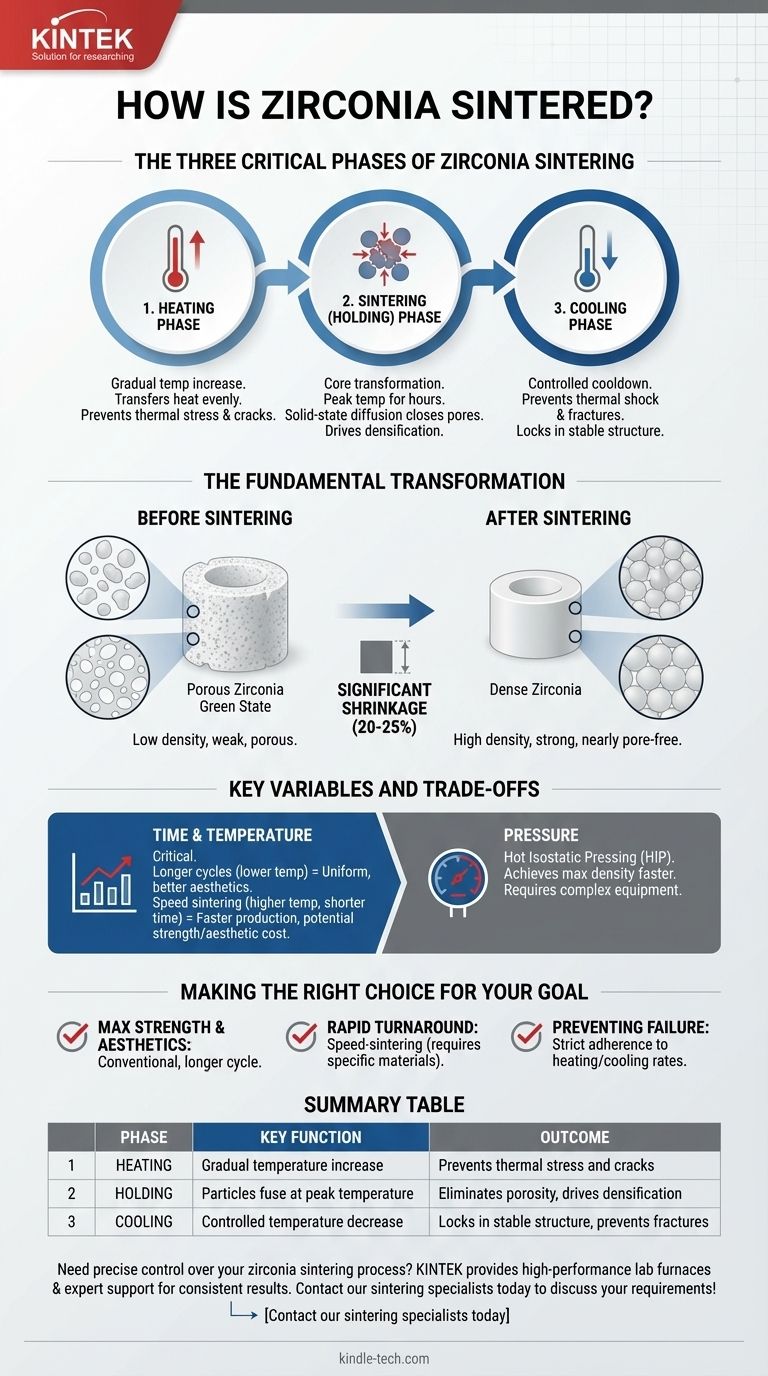
The Three Critical Phases of Zirconia Sintering
The entire sintering process is a carefully controlled thermal journey. Each phase serves a specific purpose in developing the final properties of the material, and any deviation can compromise the outcome.
The Heating Phase
The process begins with a controlled, gradual increase in temperature. This ramp-up must be slow enough to ensure the heat transfers evenly from the surface to the core of the zirconia component. Heating too quickly can create thermal stress, leading to cracks and structural failure.
The Sintering (Holding) Phase
This is the core of the process where the actual transformation occurs. The zirconia is held at a peak temperature, often for several hours. At this high temperature, the individual ceramic particles bond and fuse together, a process known as solid-state diffusion.
This fusion systematically closes the microscopic pores between the particles, which is the primary driver of densification.
The Cooling Phase
After the holding phase, the zirconia must be cooled in a controlled manner. A slow, managed cooldown is essential to prevent thermal shock, which could reintroduce stress or cause fractures in the newly densified material. This final phase locks in the strong, stable crystalline structure.
The Fundamental Transformation: Why Sintering Matters
Understanding the physical changes that occur during sintering is key to appreciating its importance. The process is designed to fundamentally re-engineer the material's internal structure.
From Porous to Dense
Before sintering, a milled zirconia component is in a porous, chalk-like state. It has low density and very little strength. The sintering process eliminates these voids, pulling the ceramic particles tightly together and dramatically increasing the material's density.
The Impact of Shrinkage
The most noticeable outcome of sintering is significant shrinkage. This is not a defect but a direct and predictable consequence of densification. As the pores between particles are eliminated, the overall volume of the component must decrease, often by 20-25%.
This shrinkage must be precisely calculated and accounted for during the initial design and milling stage, where the component is made intentionally oversized.
Achieving Final Strength
The ultimate goal of sintering is to achieve the material's renowned mechanical strength and fracture resistance. By creating a dense, nearly pore-free structure, the process removes the internal weak points where cracks could begin, resulting in a highly robust and durable final product.
Key Variables and Trade-offs
The success of sintering depends on a delicate balance of variables. Adjusting these parameters affects the final properties of the zirconia, creating a series of important trade-offs.
Time and Temperature
The most critical variables are the peak temperature and the duration of the holding phase. Longer cycles at slightly lower temperatures can produce a more uniform grain structure, often enhancing aesthetic properties like translucency.
Conversely, "speed sintering" cycles use higher temperatures for shorter times to reduce production time, but this can sometimes come at the cost of optimal strength or aesthetics.
The Role of Pressure
While most conventional sintering relies solely on heat, some advanced industrial processes also apply external pressure. This technique, known as Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP), can help achieve maximum density more efficiently, but it requires specialized and more complex equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific sintering protocol must be aligned with the intended application of the final zirconia part.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and aesthetics: A conventional, longer sintering cycle is the standard, as it ensures complete densification and a fine-grained microstructure.
- If your primary focus is rapid turnaround time: Speed-sintering cycles are effective, but you must use zirconia materials specifically formulated for this process to avoid compromising structural integrity.
- If your primary focus is preventing component failure: Strict adherence to the manufacturer's recommended heating and cooling rates is non-negotiable to avoid thermal shock and internal stress.
Controlling the sintering process is about transforming a raw material into a final component with predictable and exceptional performance.
Summary Table:
| Phase | Key Function | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Heating | Gradual temperature increase | Prevents thermal stress and cracks |
| Holding | Particles fuse at peak temperature | Eliminates porosity, drives densification |
| Cooling | Controlled temperature decrease | Locks in stable structure, prevents fractures |
Need precise control over your zirconia sintering process? KINTEK provides the high-performance lab furnaces and expert support you need to achieve consistent, reliable results. Whether you're working with conventional or speed-sintering cycles, our equipment ensures the exact temperature control critical for strong, dense zirconia components. Contact our sintering specialists today to discuss your laboratory's requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the sintering time for zirconia? A Guide to Precise Firing for Optimal Results
- What is the sintering temperature of zirconium? A Guide to the 1400°C-1600°C Range for Dental Labs
- What is the effect of zirconia sintering temperature? Master the Key to Strength and Stability
- What is the temperature of sintering zirconia? Mastering the Protocol for Perfect Dental Restorations
- What are the white spots on zirconia after sintering? A Guide to Diagnosing and Preventing Defects



















