In short, synthesizing a high-quality, gem-grade diamond typically takes several weeks to over a month. The exact duration depends heavily on the desired size and quality of the stone, with larger and more flawless diamonds requiring significantly longer growth periods using methods like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
The time it takes to grow a diamond in a lab is not a fixed number; it is a direct function of the desired outcome. The core principle is a trade-off: accelerating the process almost always compromises the final quality of the diamond.
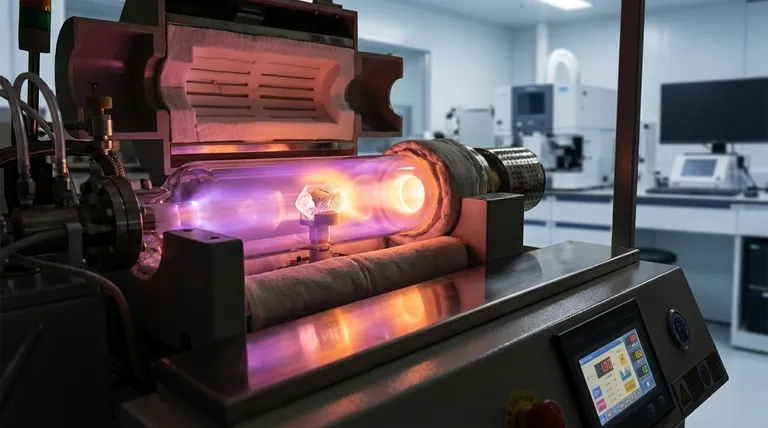

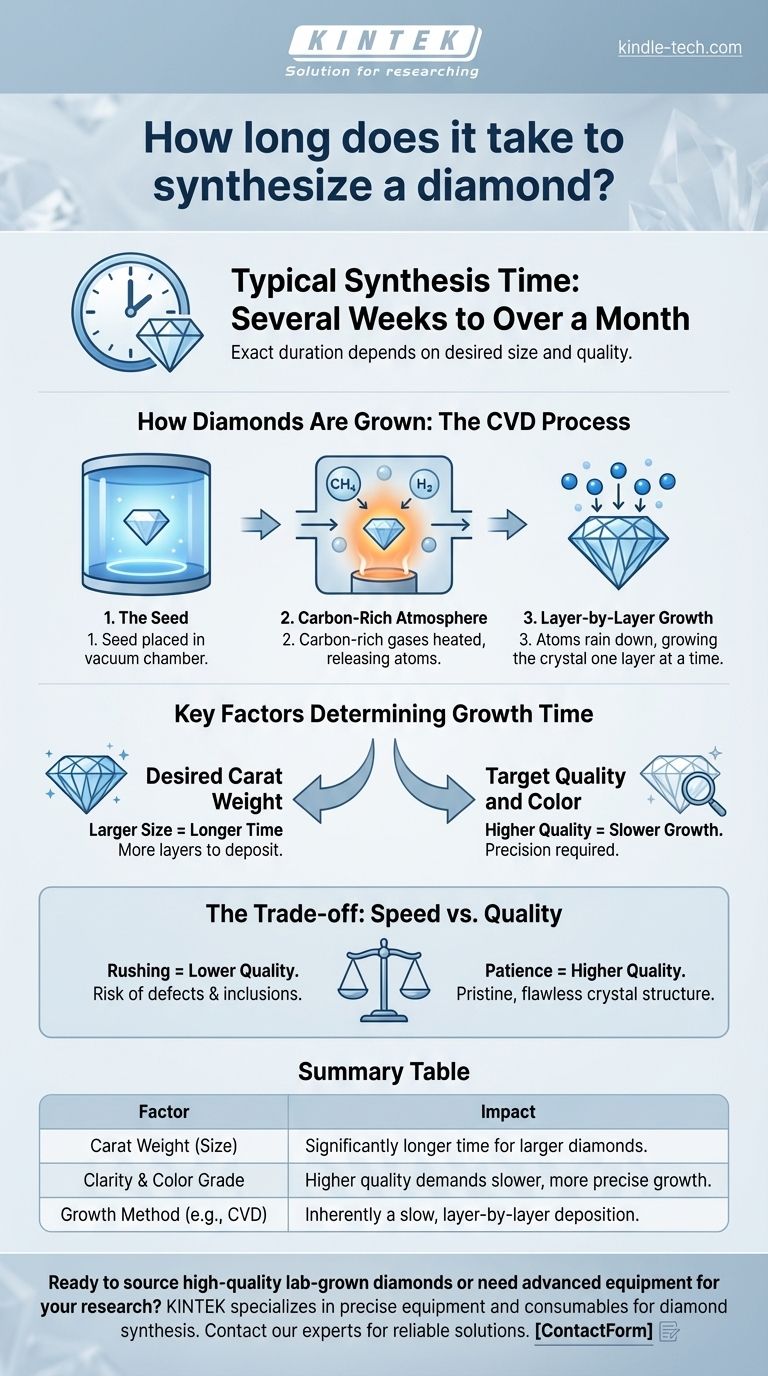
How Diamonds Are Grown: The CVD Process
The most advanced and common method for creating gem-quality lab diamonds is Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). This process mimics the way diamonds form in interstellar gas clouds, but on a vastly accelerated timeline compared to nature's billion-year process.
The Seed of Creation
The process begins with a "seed"—a tiny, high-quality sliver of a previously grown diamond. This seed is placed inside a sealed vacuum chamber.
A Carbon-Rich Atmosphere
The chamber is then filled with carbon-rich gases, typically methane and hydrogen. These gases are heated to extremely high temperatures, often exceeding several thousand degrees Celsius.
Layer-by-Layer Growth
At these temperatures, the gas molecules break apart, freeing carbon atoms. These atoms then rain down and deposit onto the diamond seed, building upon its crystal structure one layer at a time. This meticulous, atom-by-atom growth is why the process takes time.
Key Factors That Determine Growth Time
The "several weeks to a month" estimate is a general range. Two primary factors dictate the precise schedule for growing a specific diamond.
Desired Carat Weight
The most significant factor is the final size of the diamond. A larger carat weight requires more layers of carbon to be deposited, directly translating to more time in the growth chamber. Growing a 2-carat diamond will take considerably longer than a 1-carat diamond under the same conditions.
Target Quality and Color
Achieving high clarity (fewer inclusions) and a colorless grade requires a very slow, stable, and controlled growth rate. If the process is rushed, defects can form in the crystal lattice, resulting in a lower-quality stone with visible imperfections or a yellowish tint.
Understanding the Trade-off: Speed vs. Quality
The central challenge in diamond synthesis is balancing the speed of growth with the final quality of the gem.
The Risk of Rushing
Attempting to grow a diamond too quickly introduces instability. This can lead to internal fractures, cloudy inclusions, or a less desirable color, all of which dramatically reduce the diamond's value.
The Patience for Perfection
Producers of top-tier, colorless, and flawless lab diamonds intentionally use slower, more deliberate growth rates. This ensures each layer of carbon atoms has the time to align perfectly, resulting in a pristine and structurally sound crystal. This commitment to quality is the main reason larger, high-grade diamonds can take well over a month to synthesize.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the growth process empowers you to evaluate the characteristics of any lab-grown diamond.
- If your primary focus is the largest possible size for your budget: Be prepared to encounter diamonds with slightly lower clarity or color grades, as these may have been grown on a faster timeline.
- If your primary focus is exceptional quality (high clarity and color): Recognize that the time and precision required to grow these stones contribute significantly to their value.
Ultimately, the synthesis time is a direct reflection of the diamond's journey from a simple carbon seed to a complex and beautiful gemstone.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Synthesis Time |
|---|---|
| Carat Weight (Size) | Larger diamonds require significantly more time to grow. |
| Clarity & Color Grade | Higher quality (flawless, colorless) demands slower, more precise growth. |
| Growth Method (e.g., CVD) | The standard process is inherently a slow, layer-by-layer deposition. |
Ready to source high-quality lab-grown diamonds or need advanced equipment for your research? KINTEK specializes in providing the precise laboratory equipment and consumables needed for consistent, high-quality diamond synthesis. Our expertise supports laboratories in achieving their specific goals, whether for research, industrial applications, or gem production. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your project with reliable, high-performance solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the industrial uses of synthetic diamonds? Unlock High-Performance Solutions for Your Tech Needs
- Can a diamond tester tell the difference between lab grown and natural diamonds? The Surprising Truth
- How does chemical vapor deposition work for diamonds? Grow Lab-Created Diamonds Layer by Layer
- Can CVD diamonds change color? No, their color is permanent and stable.
- What is a microwave plasma reactor? Unlock Precision Synthesis of High-Performance Materials
- What is the microwave plasma method? A Guide to High-Purity Material Synthesis
- Can you chemically make diamonds? Yes, CVD & HPHT Create Real Diamonds
- How do you test a diamond CVD? Verify Authenticity with Grading Reports & Laser Inscription



















