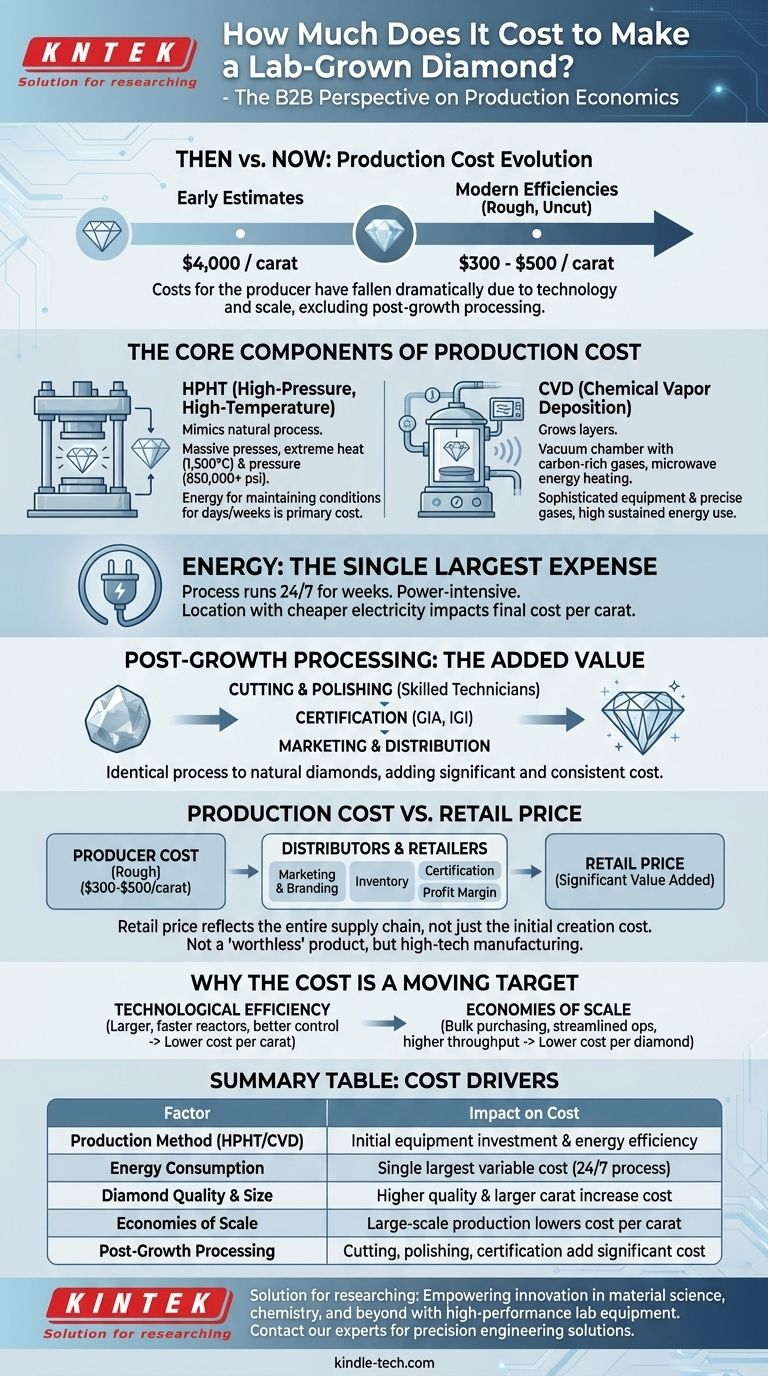
The true cost to produce a lab-grown diamond is not a single, fixed number but a complex variable that has fallen dramatically over the last decade. While early estimates placed production costs at around $4,000 per carat, modern efficiencies have driven this figure down significantly, with some industry analyses suggesting costs can now range from $300 to $500 per carat for the producer, depending on the technology, quality, and scale of the operation. This cost is for the rough, uncut stone and does not include the significant expenses of cutting, polishing, and certification.
The central takeaway is that the cost to create a lab-grown diamond is a fraction of its retail price, driven primarily by immense energy consumption and sophisticated machinery. This cost is continuously decreasing due to technological advancements, fundamentally altering the economics of the entire jewelry market.

The Core Components of Production Cost
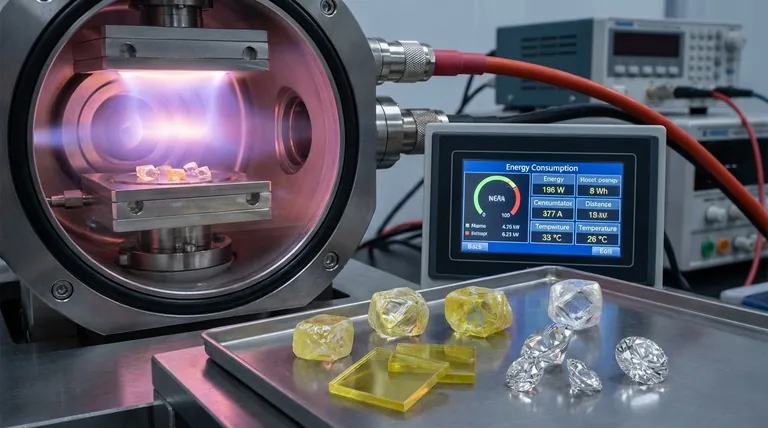
To understand the price, you must first understand the process. The cost is not in raw materials, which are abundant and cheap (like carbon), but in the extreme conditions required to transform them into a diamond.
High-Pressure, High-Temperature (HPHT)
The HPHT method mimics the natural diamond-growing process. A small diamond "seed" is placed in a cell with a carbon source, typically graphite.
This cell is then subjected to immense pressure (over 850,000 pounds per square inch) and extreme heat (around 1,500°C) inside massive, specialized presses. These machines are expensive to build and operate, and the energy required to maintain these conditions for days or weeks is the primary cost driver.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
The CVD method "grows" a diamond in layers. A diamond seed is placed in a vacuum chamber filled with carbon-rich gases like methane.
Microwave energy heats the chamber to incandescent temperatures, causing the gas to break down and carbon atoms to deposit onto the seed, growing a diamond crystal layer by layer. The main costs are the sophisticated vacuum and microwave equipment, the precise gases used, and, once again, the tremendous and sustained energy consumption.
Energy: The Single Largest Expense
Regardless of the method, energy is the most significant variable cost in producing a lab-grown diamond. The process is incredibly power-intensive, running 24/7 for weeks at a time to grow a single batch of stones.
This is why many large-scale diamond labs are established in locations with access to cheaper and more reliable electricity. The local cost of a kilowatt-hour directly impacts the final cost per carat.
Post-Growth Processing
The cost to grow the rough crystal is only part of the story. This new diamond must then be cut, faceted, and polished by skilled technicians using specialized equipment—a process that is identical for both lab-grown and natural diamonds. This final stage adds a significant and consistent cost to the finished gem.
Why the Cost is a Moving Target
The price you see today is not what it was five years ago, nor what it will be in five years. The market is defined by rapid technological evolution.
The Impact of Technological Efficiency
As the provided reference notes, production methods are constantly improving. Engineers are developing larger, more efficient reactors that can grow higher-quality diamonds faster and in larger batches.
Each incremental improvement in machine efficiency or process control reduces the energy and time required, directly lowering the cost per carat. This is the primary force driving down lab-grown diamond prices.
The Role of Economies of Scale
As production moves from smaller labs to massive, dedicated factories, economies of scale come into play. Bulk purchasing of equipment and energy, streamlined operations, and higher throughput all contribute to a lower cost for each individual diamond produced.
Understanding the Key Distinction
It is critical to separate the cost of production from the price you pay as a consumer. They are not the same thing.
Production Cost vs. Retail Price
The producer's cost of a few hundred dollars per carat is just the first step in the value chain. After the diamond is grown and cut, it goes through distributors and retailers.
Each of these steps adds costs for marketing, branding, inventory, certification (GIA, IGI), and a profit margin. The final retail price reflects this entire supply chain, not just the initial creation cost.
The Myth of "Free" Diamonds
A common misconception is that because these diamonds are "man-made," they should be nearly worthless. This ignores the reality of the process.
Creating a lab-grown diamond requires some of the most advanced material science technology in the world, housed in multi-million dollar facilities that consume vast amounts of energy. The cost reflects this high-tech, capital-intensive manufacturing process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the production economics empowers you to make a decision based on logic rather than just marketing.
- If your primary focus is budget and size: A lab-grown diamond offers fundamentally better value, as its production cost is tied to technology and efficiency, not finite supply and mining monopolies.
- If your primary focus is understanding value: Judge the gem on its merits—the 4Cs (cut, color, clarity, carat)—not its origin. The cost to create a flawless, colorless lab diamond is significant, reflecting the advanced technology required for its perfection.
- If your primary focus is the future: Recognize that the cost to produce lab-grown diamonds will likely continue to fall, which may impact long-term resale value but will also make larger, higher-quality stones more accessible.
Knowing the cost drivers shifts your perspective from seeing a lab-grown diamond as an alternative to seeing it as a distinct product of modern technological achievement.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Cost |
|---|---|
| Production Method (HPHT/CVD) | Determines initial equipment investment and energy efficiency. |
| Energy Consumption | The single largest variable cost; process runs 24/7 for weeks. |
| Diamond Quality & Size | Higher quality (color, clarity) and larger carat weights increase cost. |
| Economies of Scale | Large-scale production in dedicated factories lowers cost per carat. |
| Post-Growth Processing | Cutting, polishing, and certification add significant, consistent costs. |
Ready to explore the science behind advanced materials? The sophisticated technology used to create lab-grown diamonds is just one example of precision engineering. At KINTEK, we specialize in supplying the high-performance lab equipment and consumables that power innovation in research and development. Whether your lab is focused on material science, chemistry, or any other field, we provide the reliable tools you need to achieve precise and repeatable results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs and help you push the boundaries of what's possible.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the objective of GH3535 alloy solution treatment? Achieve Uniform Microstructure with KINTEK Furnaces
- What are the applications of thin films in semiconductors? Powering Modern Electronics from Transistors to Solar Cells
- What is physical sputtering? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What are the two heat treatment processes? Softening vs. Hardening Explained
- How does DNA storage at -20°C and -80°C compare? Ensure Long-Term Sample Integrity
- What type of plastic is usually used with compression molding and transfer molding? Master Thermosets for Superior Performance
- What are the applications of thin film technology? Powering Electronics, Energy, and Innovation
- What do jewelers use to test diamonds? Essential Tools for Accurate Diamond Verification



















