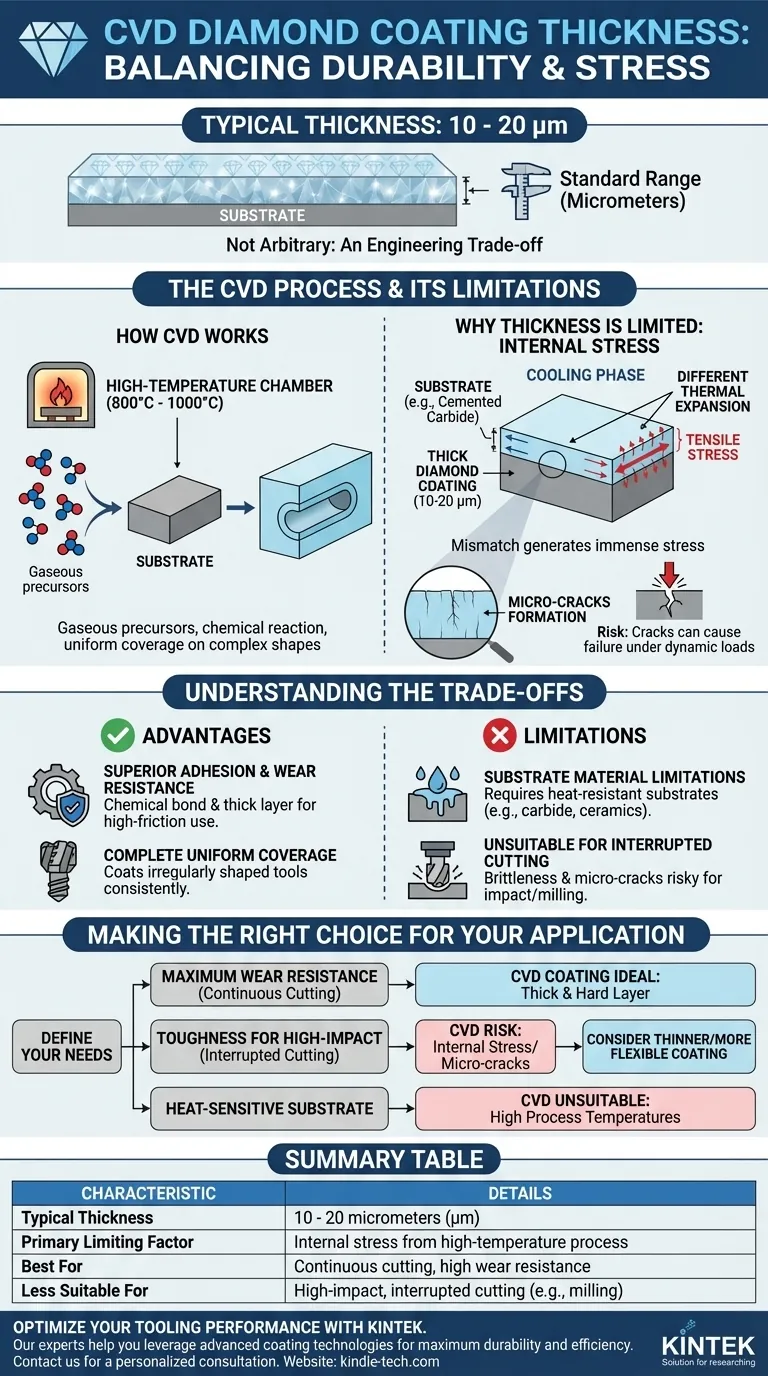
A standard CVD diamond coating is typically between 10 to 20 micrometers (μm) thick. This thickness is not an arbitrary choice; it is a direct consequence of the chemical vapor deposition (CVD) process itself, representing a critical balance between achieving maximum durability and managing the inherent internal stresses that form during the coating's application.
The thickness of a CVD coating is a fundamental engineering trade-off. While the process creates a thick, highly durable layer, exceeding a certain thickness introduces internal stress that can lead to micro-cracks and coating failure, especially under dynamic loads.

The Fundamentals of the CVD Process
To understand why CVD diamond coatings have their specific thickness, we must first understand the process that creates them. It is the nature of this process that dictates the final properties of the film.
How CVD Works
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a process where a thin film is grown on a substrate through a chemical reaction. Gaseous precursor molecules are introduced into a high-temperature, vacuum-sealed chamber. The heat causes these gases to react or decompose on the surface of the part, creating a new, solid layer that is chemically bonded to the substrate.
Key Characteristics
Unlike line-of-sight processes like PVD, the gaseous nature of CVD allows it to coat all surfaces of a complex part uniformly. This includes internal bores, threads, and blind holes, ensuring complete and even coverage. This comprehensive coverage is one of the primary advantages of the CVD method.
Why Thickness is Limited: The Role of Internal Stress
The primary factor limiting the thickness of a CVD coating is not the capability of the process, but the physics of the materials involved. The significant heat required is the root cause of this limitation.
The Impact of High Temperatures
The CVD process for hard coatings like diamond and titanium carbide operates at very high temperatures, often between 800°C and 1000°C. This extreme heat is necessary to drive the chemical reactions that form the hard, dense coating layer.
Stress from Cooling
After the coating is deposited, the part must cool down from this extreme temperature. The substrate material (often cemented carbide) and the new diamond coating have different rates of thermal expansion. As they cool, this mismatch generates immense tensile stress within the thick (10-20μm) coating.
The Risk of Micro-Cracks
This internal stress can be so significant that it leads to the formation of fine, microscopic cracks in the coating layer. While not always visible, these cracks become points of weakness. Under external impact or vibration, these cracks can propagate and cause the coating to chip or peel away from the substrate.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a CVD diamond coating requires acknowledging its distinct advantages and limitations, which are directly tied to its thickness and high-temperature application process.
Pro: Superior Adhesion and Wear Resistance
The chemical bond formed during the CVD process results in exceptional adhesion to the substrate. This, combined with a relatively thick and hard layer, provides outstanding resistance to abrasion and wear in stable, high-friction applications.
Pro: Complete and Uniform Coverage
For irregularly shaped tools, such as end mills or drill bits, the ability of CVD to coat every surface uniformly is a major advantage. This ensures consistent protection and performance across the entire tool.
Con: Substrate Material Limitations
The high processing temperatures mean that CVD can only be applied to materials that can withstand the heat without deforming or losing their structural integrity. This largely restricts its use to substrates like cemented carbide and certain high-temperature ceramics.
Con: Unsuitability for Interrupted Cutting
The internal stress and potential for micro-cracks make thick CVD coatings less ideal for applications with high-impact forces or non-uniform cutting. In processes like milling, where the cutting edge repeatedly enters and exits the material, the constant impact can exploit these micro-cracks and lead to premature coating failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The optimal coating is always defined by the specific demands of its environment. The thickness of a CVD diamond coating is a feature that makes it perfect for some tasks and unsuitable for others.
- If your primary focus is maximum wear resistance in a continuous cutting or forming operation: The thickness and hardness of a CVD coating provide the superior durability you need.
- If your primary focus is toughness for high-impact or interrupted cutting (e.g., milling): The inherent brittleness from the internal stress of a thick CVD coating is a significant risk; a thinner, more flexible coating may be more appropriate.
- If your primary focus is coating a heat-sensitive substrate material: The high-temperature nature of the CVD process makes it an unsuitable choice.
Ultimately, understanding the relationship between thickness, stress, and application is key to leveraging the powerful advantages of CVD diamond coatings.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Details |
|---|---|
| Typical Thickness | 10 - 20 micrometers (μm) |
| Primary Limiting Factor | Internal stress from high-temperature process |
| Best For | Continuous cutting, high wear resistance |
| Less Suitable For | High-impact, interrupted cutting (e.g., milling) |
Optimize your tooling performance with the right coating solution.
The specific thickness of a CVD diamond coating is a critical engineering decision that directly impacts tool life and performance. Choosing the correct coating requires expert knowledge of your application's unique demands for wear resistance, impact tolerance, and substrate material.
At KINTEK, we specialize in lab equipment and consumables, including advanced coating technologies. Our experts can help you determine if a CVD diamond coating is the right choice for your laboratory or manufacturing needs, ensuring you achieve maximum durability and efficiency.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how our solutions can enhance your operational results.
Get a personalized consultation →
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- CVD Diamond Dressing Tools for Precision Applications
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
People Also Ask
- What is the process of CVD diamond coating? Grow a Superior, Chemically-Bonded Diamond Layer
- What is diamond coating film? A Thin Layer of Diamond for Extreme Performance
- How are tools coated with diamond? Achieve Superior Hardness and Low Friction for Your Tools
- Is diamond coating worth it? Maximize Component Life and Performance
- What are the three types of coating? A Guide to Architectural, Industrial, and Special Purpose



















