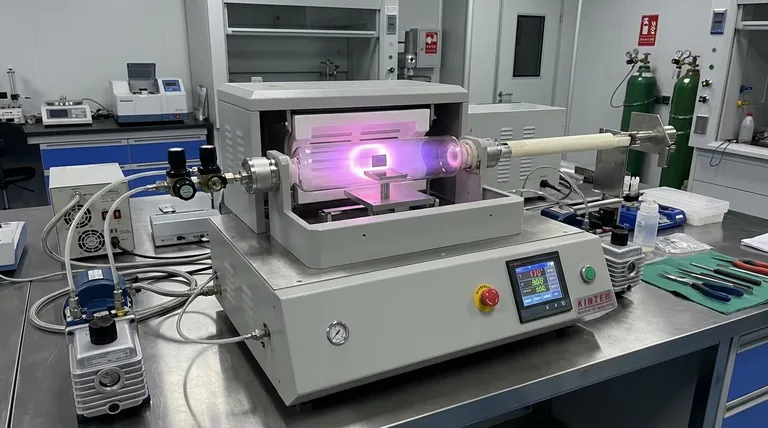
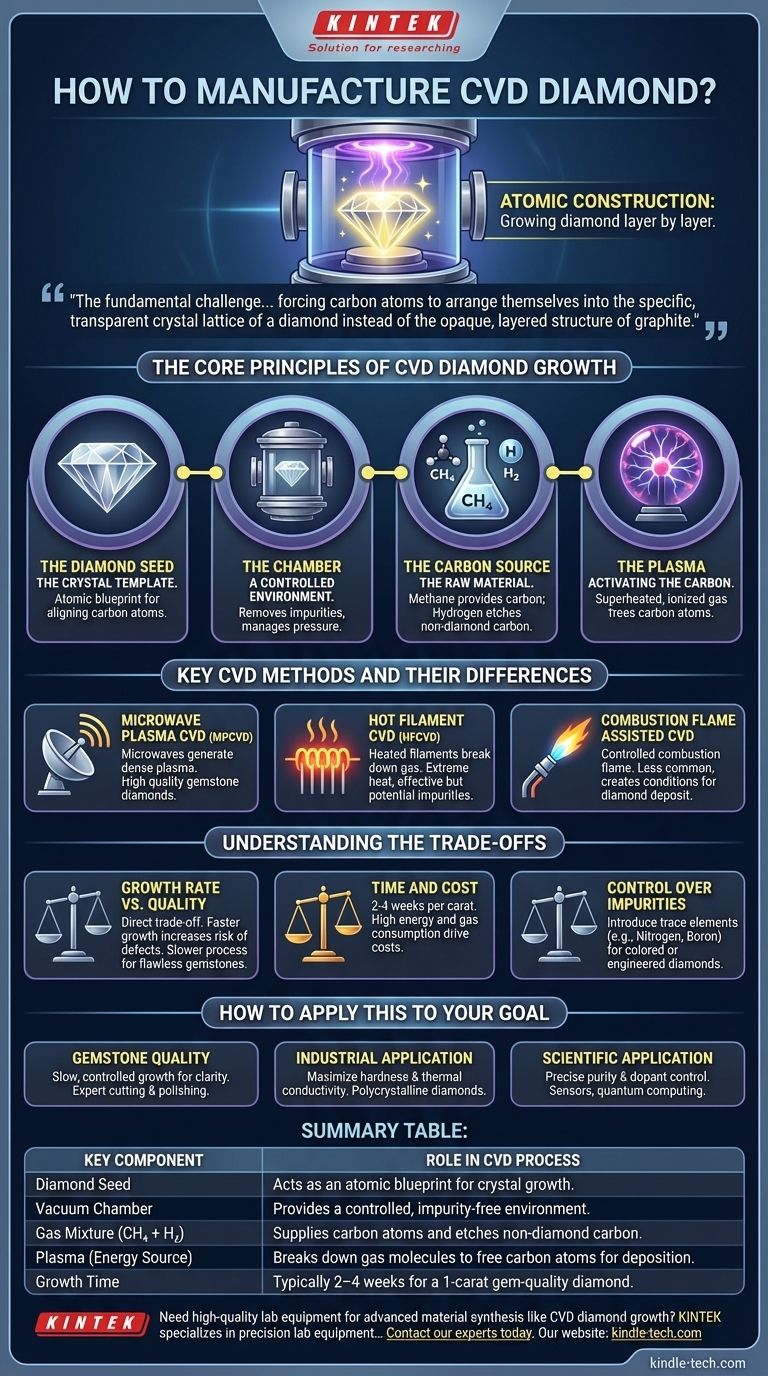
At its core, manufacturing a diamond with the Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) method is a process of atomic construction. A small, flat "seed" of a previously grown diamond is placed inside a vacuum chamber. The chamber is heated to extreme temperatures and filled with a carbon-rich gas, which is then energized into a plasma, causing carbon atoms to rain down and attach to the seed, growing a new diamond layer by layer over several weeks.
The fundamental challenge in creating a diamond is not just sourcing carbon, but forcing those carbon atoms to arrange themselves into the specific, transparent crystal lattice of a diamond instead of the opaque, layered structure of graphite. The CVD process achieves this by creating a highly controlled environment where the diamond structure is the most stable one that can form.

The Core Principles of CVD Diamond Growth
To understand how a CVD diamond is made, it's best to break the process down into its four critical components: the seed, the chamber, the gas, and the energy source.
The Diamond Seed: The Crystal Template
A thin slice of a high-quality existing diamond, often produced by a previous CVD run, serves as the foundation, or seed. This is not merely a surface to grow on; it is the atomic blueprint. The carbon atoms depositing from the gas phase align with the seed's crystal lattice, ensuring the new material grows with the exact same diamond structure.
The Chamber: A Controlled Environment
The entire process takes place within a sealed vacuum chamber. This serves two purposes. First, it allows for the removal of all other atmospheric gases, like nitrogen and oxygen, which would introduce defects and impurities into the diamond. Second, it enables precise control over the pressure, which is kept at sub-atmospheric levels to manage the chemical reactions.
The Carbon Source: The Raw Material
A carefully prepared mixture of gases is introduced into the chamber. The primary ingredient is a carbon-rich gas, typically methane (CH₄), which provides the carbon atoms for the diamond. This is almost always mixed with a large amount of hydrogen gas. Hydrogen plays a crucial role by selectively etching away any non-diamond carbon (like graphite) that might form, ensuring the purity and quality of the final crystal.
The Plasma: Activating the Carbon
The gas mixture is energized, typically with microwaves or hot filaments, to create a plasma. This is a superheated, ionized state of matter where the gas molecules are broken apart. This step is what frees individual carbon atoms from the stable methane molecules, allowing them to deposit onto the diamond seed below.
Key CVD Methods and Their Differences
While the principle remains the same, different techniques can be used to generate the necessary energy and plasma.
Microwave Plasma CVD (MPCVD)
This is the most advanced and widely used method for producing high-quality gemstone diamonds. It uses microwaves to generate a dense, stable plasma ball that sits directly above the diamond seeds. Increasing the microwave power can increase the plasma density, which in turn accelerates the diamond's growth rate.
Hot Filament CVD (HFCVD)
In this method, a series of heated filaments made of a material like tungsten or tantalum are placed above the substrate. The extreme heat from these filaments (over 2000°C) provides the energy needed to break down the carbon gas molecules. This method is effective but can sometimes introduce impurities from the filament material itself.
Combustion Flame Assisted CVD
This less common technique uses a controlled combustion flame, like an oxy-acetylene torch, in a low-pressure environment. The chemistry within the flame itself creates the right atomic species and temperature conditions for diamond to deposit onto a cooled substrate.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The CVD process is a sophisticated balancing act between several key variables. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for appreciating the technology's capabilities and limitations.
Growth Rate vs. Quality
There is a direct trade-off between the speed of growth and the final quality of the diamond. While increasing the power and gas concentration can make a diamond grow faster, it also increases the risk of inclusions or structural defects. Creating a top-tier, flawless gemstone requires a slower, more meticulously controlled process.
Time and Cost
Growing a single one-carat gem-quality diamond can take two to four weeks of continuous operation inside a reactor. The equipment is highly specialized, and the process consumes significant amounts of energy and purified gases, which are the primary drivers of the final cost.
Control Over Impurities
A major advantage of the CVD method is the ability to finely control the chemical environment. By intentionally introducing trace elements like nitrogen or boron into the gas mixture, manufacturers can create colored diamonds (yellow or blue, respectively) or engineer diamonds with specific electronic properties for advanced industrial and scientific applications.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
The right choice depends entirely on the intended application, as the definition of a "good" CVD diamond changes with the goal.
- If your primary focus is gemstone quality for jewelry: The key is a slow, controlled growth process that prioritizes clarity and avoids inclusions, followed by expert cutting and polishing.
- If your primary focus is an industrial application (e.g., cutting tools or heat sinks): The goal is maximizing hardness and thermal conductivity, where polycrystalline diamonds grown over a large area are often more cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is a scientific application (e.g., sensors or quantum computing): The critical factor is the precise control over purity and the ability to embed specific atomic-level impurities (dopants), which is a unique strength of the CVD process.
Ultimately, the CVD process transforms a simple gas into one of the hardest, most valuable materials on Earth through a remarkable feat of atomic-scale engineering.
Summary Table:
| Key Component | Role in CVD Process |
|---|---|
| Diamond Seed | Acts as an atomic blueprint for crystal growth. |
| Vacuum Chamber | Provides a controlled, impurity-free environment. |
| Gas Mixture (CH₄ + H₂) | Supplies carbon atoms and etches non-diamond carbon. |
| Plasma (Energy Source) | Breaks down gas molecules to free carbon atoms for deposition. |
| Growth Time | Typically 2–4 weeks for a 1-carat gem-quality diamond. |
Need high-quality lab equipment for advanced material synthesis like CVD diamond growth? KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables, serving research and industrial laboratories. Whether you're developing gem-grade diamonds, industrial tools, or quantum materials, our reactors and supporting systems ensure controlled, reliable results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your CVD diamond manufacturing goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the methods of producing CNT? Scalable CVD vs. High-Purity Lab Techniques
- How high of temperature do carbon nanotubes in air have the ability to sustain? Understanding the Oxidation Limit
- What is a CVD tube furnace? A Complete Guide to Thin-Film Deposition
- What role does Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) equipment play in the preparation of C/C composites? Expert Analysis
- What function does CVD equipment serve in rhodium-modified coatings? Achieve Deep Diffusion and Microstructural Precision



















