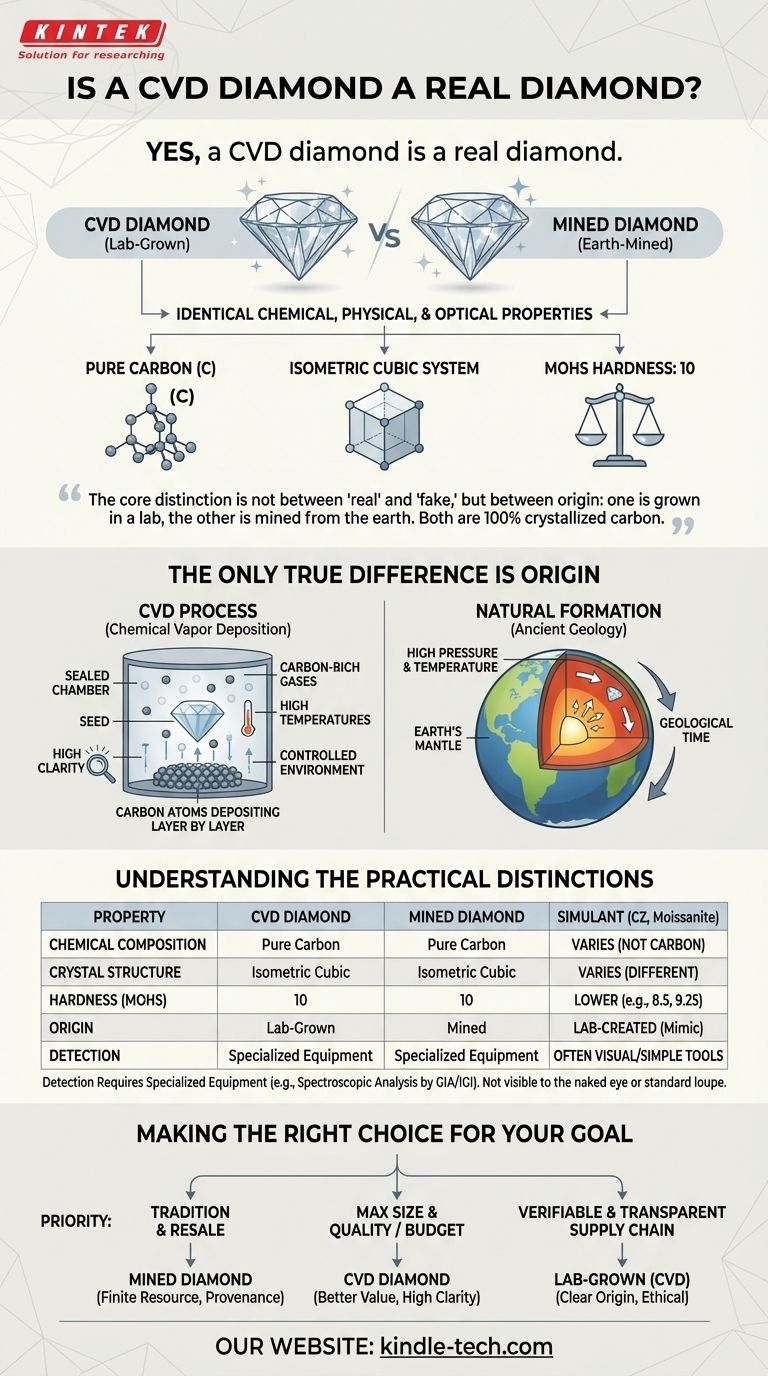
Yes, a CVD diamond is a real diamond. It possesses the exact same chemical, physical, and optical properties as a diamond mined from the earth. Both are composed of pure carbon crystallized in an isometric cubic system, making them indistinguishable to even a trained jeweler without specialized equipment.
The core distinction is not between "real" and "fake," but between origin: one is grown in a lab, the other is mined from the earth. Both are 100% crystallized carbon, just as ice from a freezer is chemically identical to ice from a glacier.

What Defines a "Real" Diamond?
To understand why a CVD diamond is considered authentic, we must first define what a diamond is at its most fundamental level. The identity of a diamond is determined by its material composition and structure, not its origin.
The Atomic Structure
A diamond is pure carbon with its atoms arranged in a specific crystal lattice. This structure is what gives a diamond its unparalleled hardness and unique ability to interact with light.
CVD diamonds are grown from a diamond "seed" and share this exact atomic structure, making them chemically identical to their mined counterparts.
Identical Physical and Optical Properties
Because the chemical makeup is the same, all other properties follow suit. A CVD diamond exhibits the same fire, brilliance, and scintillation as a natural diamond.
It also registers a 10 on the Mohs hardness scale, the highest possible rating, just like a mined diamond.
The Official Ruling
The debate over terminology was officially settled in 2018. The United States Federal Trade Commission (FTC) ruled that a diamond is a diamond, regardless of its origin.
This ruling legally affirms that lab-grown diamonds, including those made via the CVD process, are not simulants or fakes; they are simply diamonds created through a different process.
The Only True Difference Is Origin
The single factor that separates a CVD diamond from a natural one is its formation process. One is a product of modern technology, while the other is a product of ancient geology.
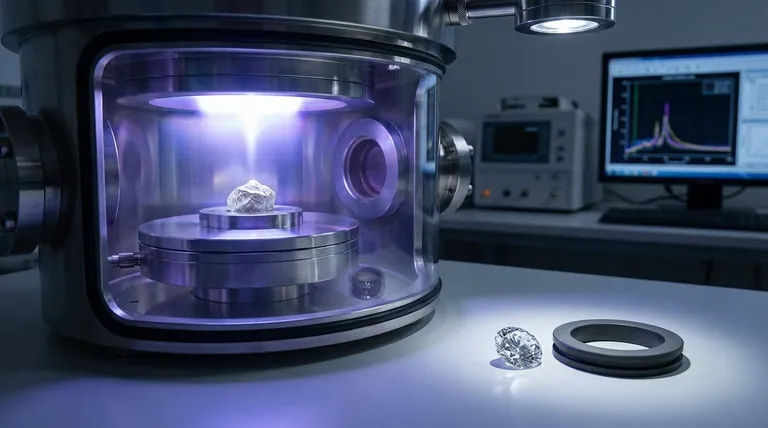
How CVD Diamonds Are Made
CVD stands for Chemical Vapor Deposition. The process begins with a thin slice of a diamond, known as a seed. This seed is placed in a sealed chamber filled with carbon-rich gases.
The chamber is heated to extreme temperatures, causing the gases to break down and allowing carbon atoms to deposit onto the diamond seed, growing the crystal layer by layer.
A Controlled Environment
Because this process occurs under highly controlled and supervised conditions, CVD diamonds often have very high clarity and fewer inclusions than many natural diamonds. This technological precision allows for the creation of stones with exceptional quality.
Understanding the Practical Distinctions
While physically identical, the different origins of mined and CVD diamonds lead to a few practical considerations for a buyer. It is crucial to distinguish them from diamond simulants, which are not real diamonds at all.
Not a Simulant (like CZ or Moissanite)
A common point of confusion is comparing lab-grown diamonds to simulants like cubic zirconia (CZ) or moissanite. These materials are not carbon; they only mimic the appearance of a diamond and have vastly different physical and chemical properties.
A CVD diamond is not a simulant; it is chemically and structurally a diamond.
Detection Requires Specialized Equipment
You cannot tell the difference between a CVD and a mined diamond with the naked eye or a standard jeweler's loupe. The distinction can only be made by a trained gemologist using advanced spectroscopic equipment.
These machines detect subtle differences in crystal growth patterns and trace elements that indicate a lab-grown origin. This is why official grading reports from labs like GIA or IGI are essential.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the choice between a CVD diamond and a mined diamond comes down to your personal priorities and values. Both are authentic, beautiful options.
- If your primary focus is tradition and potential long-term resale value: A mined diamond with a strong provenance may be your preference, as it is a finite natural resource.
- If your primary focus is maximizing size and quality for your budget: A CVD diamond is the logical choice, as it offers a significantly better value proposition.
- If your primary focus is a verifiable and transparent supply chain: A lab-grown diamond provides a clear origin story free from the uncertainties of mining.
Choosing a CVD diamond means you are selecting a real diamond created through the power of human technology rather than geology.
Summary Table:
| Property | CVD Diamond | Mined Diamond |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Pure Carbon | Pure Carbon |
| Crystal Structure | Isometric Cubic | Isometric Cubic |
| Hardness (Mohs Scale) | 10 | 10 |
| Origin | Lab-Grown | Mined |
Ready to find the perfect diamond for your needs? Whether you prioritize exceptional quality, value, or a transparent supply chain, KINTEK's expertise in advanced materials can guide you. As specialists in laboratory equipment and consumables, we understand the science behind creating flawless diamonds. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how we can support your journey with confidence and clarity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- CVD Diamond Optical Windows for Lab Applications
People Also Ask
- What are diamond coated films? Enhance Materials with Super-Hard, Transparent Layers
- How long does diamond coating last? Maximize Lifespan with the Right Coating for Your Application
- Is diamond coating permanent? The Truth About Its Long-Lasting Durability
- What are the three types of coating? A Guide to Architectural, Industrial, and Special Purpose
- Is diamond coating worth it? Maximize Component Life and Performance



















