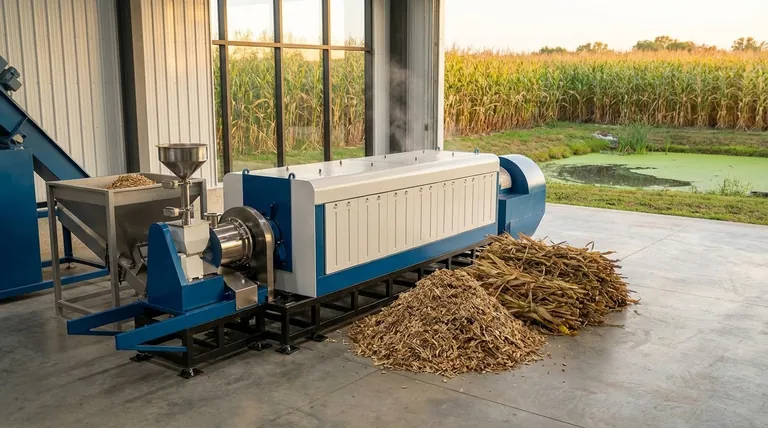
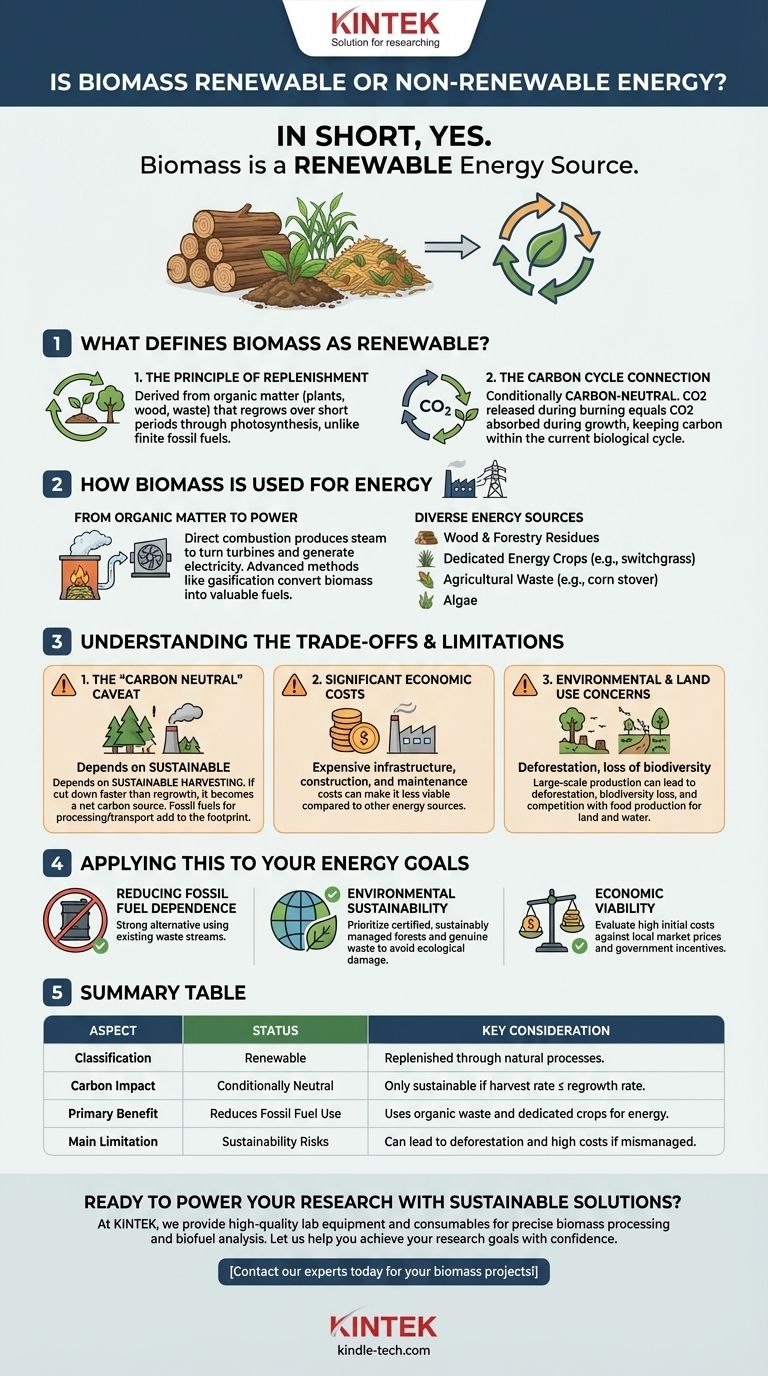
In short, yes. Biomass is classified as a renewable energy source. It is derived from organic matter—such as plants, wood, and agricultural waste—which can be replenished over a relatively short period through natural processes like photosynthesis. This stands in direct contrast to non-renewable fossil fuels, which were formed over millions of years and exist in finite quantities.
While biomass is technically a renewable resource, its true sustainability is not guaranteed. Its environmental benefit hinges entirely on responsible sourcing and ensuring that the rate of consumption does not exceed the rate of replenishment.

What Defines Biomass as Renewable?
The classification of biomass as "renewable" is rooted in its relationship with the planet's natural cycles, particularly the carbon cycle.
The Principle of Replenishment
Unlike coal, oil, or natural gas, the sources of biomass energy can be regrown. Sources include dedicated energy crops, agricultural and forestry waste, and even algae. Because these organic materials are part of a constantly regenerating system, they are not considered a finite resource in the same way as fossil fuels.
The Carbon Cycle Connection
Biomass is often considered carbon-neutral. The carbon dioxide (CO2) released when biomass is burned for energy is approximately equal to the amount of CO2 the plants absorbed from the atmosphere during their growth. This process keeps carbon within the current biological cycle, rather than releasing ancient, long-sequestered carbon from fossil fuels and adding it to the atmosphere.
How Biomass is Used for Energy
Biomass conversion is the process of transforming this raw organic material into usable energy, offering a sustainable alternative to conventional fuels.
From Organic Matter to Power
The most common method of conversion is direct combustion, where biomass is burned to produce steam that turns a turbine and generates electricity. Other advanced methods like gasification can convert biomass into valuable fuels and products with greater efficiency.
Diverse Energy Sources
The term "biomass" covers a wide range of materials. This diversity allows for flexibility in sourcing and can turn waste products into valuable energy assets. Common sources include:
- Wood and forestry residues
- Dedicated energy crops like switchgrass
- Agricultural waste like corn stover
- Algae
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Calling biomass renewable does not mean it is without significant challenges and environmental impacts. Its sustainability is conditional.
The "Carbon Neutral" Caveat
The carbon-neutral claim depends entirely on sustainable harvesting practices. If forests are cut down faster than they are replanted and regrown, biomass energy becomes a net source of carbon emissions. Furthermore, the energy used to harvest, process, and transport the biomass often comes from fossil fuels, adding to its overall carbon footprint.
Significant Economic Costs
The infrastructure required for biomass energy is expensive. High costs for construction, production, and ongoing maintenance can make it a less economically viable option compared to other energy sources in some regions.
Environmental and Land Use Concerns
Large-scale biomass production can have serious environmental consequences. It can lead to deforestation, loss of biodiversity, and soil degradation if not managed properly. Growing dedicated energy crops can also compete with food production for valuable agricultural land and water resources.
Applying This to Your Energy Goals
Choosing an energy source requires weighing its benefits against its drawbacks based on your specific priorities.
- If your primary focus is reducing fossil fuel dependence: Biomass is a strong alternative, especially when it utilizes existing waste streams from agriculture and forestry.
- If your primary focus is environmental sustainability: Prioritize biomass sourced from genuine waste products or certified, sustainably managed forests to avoid the ecological damage of large-scale land conversion.
- If your primary focus is economic viability: The high initial investment and operational costs of biomass must be carefully evaluated against local energy markets and the availability of government incentives.
Understanding biomass as a renewable but conditional resource is the first step toward integrating it wisely into a truly sustainable energy portfolio.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Status | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Classification | Renewable | Can be replenished through natural processes (e.g., plant growth). |
| Carbon Impact | Conditionally Neutral | Only sustainable if harvest rate ≤ regrowth rate. |
| Primary Benefit | Reduces Fossil Fuel Use | Uses organic waste and dedicated crops for energy. |
| Main Limitation | Sustainability Risks | Can lead to deforestation and high costs if mismanaged. |
Ready to power your research with sustainable solutions?
At KINTEK, we understand that navigating energy sources like biomass requires precision and reliable equipment. Whether you're processing biomass samples or analyzing biofuel outputs, our high-quality lab equipment and consumables are designed for accuracy and durability.
We serve laboratories focused on developing sustainable energy solutions. Let us help you achieve your research goals with confidence.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect equipment for your biomass and energy projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
People Also Ask
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output






