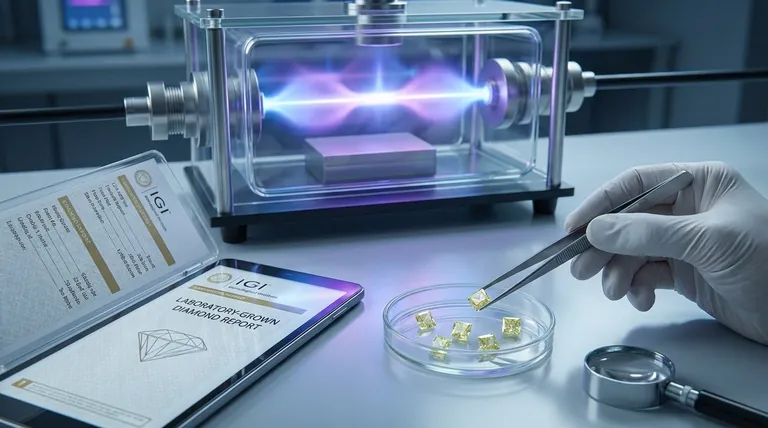
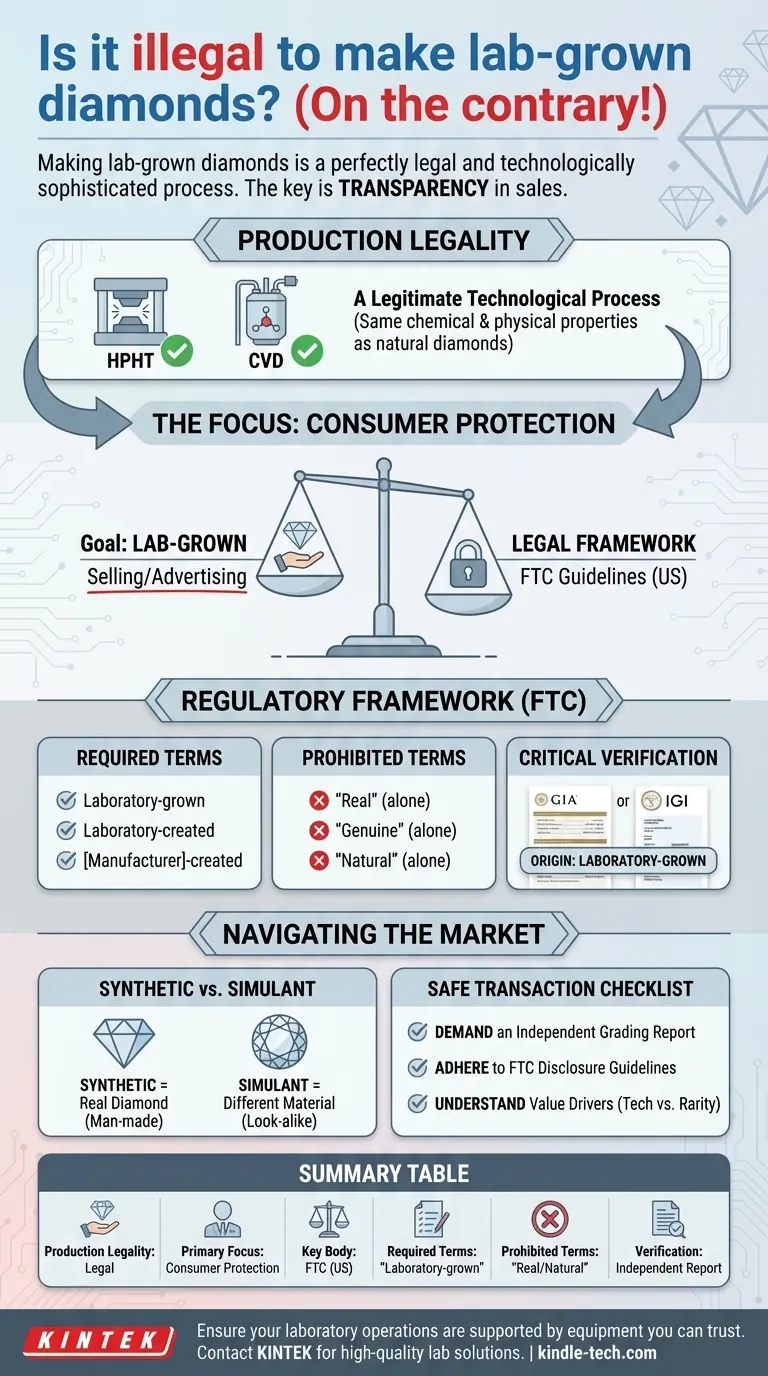
On the contrary, making lab-grown diamonds is a perfectly legal and technologically sophisticated process. The legality is not in question; the critical legal and ethical requirement revolves around ensuring absolute transparency when these diamonds are sold to consumers, to distinguish them clearly from mined diamonds.
The creation of lab-grown diamonds is entirely legal. The focus of all laws and regulations in this industry is to prevent misrepresentation and protect consumers by mandating clear, unambiguous disclosure of a diamond's origin.

The Legality of Creation vs. The Regulation of Sale
The core of this issue is not about banning a technology. It is about maintaining integrity and trust in the jewelry market.
A Legitimate Technological Process
Lab-grown diamonds are real diamonds, possessing the same chemical composition, crystal structure, and physical properties as their natural counterparts.
They are primarily created through two established scientific methods. The High Pressure, High Temperature (HPHT) method mimics the natural diamond-forming process, while Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) involves growing a diamond crystal from a hydrocarbon gas mixture.
These are not illegal industrial secrets but rather well-understood manufacturing techniques used to produce a legitimate product.
The Focus of Regulation: Consumer Protection
Legal frameworks are not concerned with the production of lab-grown diamonds. Instead, they are focused entirely on how these diamonds are advertised and sold.
The goal of regulation is to ensure that a consumer knows exactly what they are buying. This prevents sellers from passing off a lab-created diamond as a more expensive natural, mined diamond, which would be fraudulent.
The Regulatory Framework: Ensuring Transparency
To protect consumers, government bodies and industry organizations have established strict rules for how lab-grown diamonds must be described.
The Role of the FTC
In the United States, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) is the primary regulatory body. Its "Jewelry Guides" provide a legal framework for the industry.
The FTC mandates that any diamond produced in a laboratory must be clearly described using terms such as "laboratory-grown," "laboratory-created," or "[manufacturer name]-created."
Prohibited and Restricted Terms
Under FTC guidelines, it is considered deceptive to use the word "diamond" alone to describe a lab-grown product. Likewise, terms like "real," "genuine," or "natural" cannot be used to describe a lab-grown diamond, as they imply a mined origin.
The Importance of Grading Reports
Reputable gemological laboratories, such as the Gemological Institute of America (GIA) and the International Gemological Institute (IGI), provide grading reports for lab-grown diamonds.
These reports are distinct from those for natural diamonds and will always clearly state the diamond's origin as "Laboratory-Grown." This serves as a critical, third-party verification for consumers.
Understanding the Key Distinctions
Navigating the market requires understanding the terminology and the potential for confusion. Being informed is your best protection against misrepresentation.
The Risk is in the Selling, Not the Making
The legal danger in the diamond industry is not for the manufacturer creating the diamond. The risk falls squarely on the retailer or individual who attempts to sell a lab-grown diamond without proper disclosure. This act constitutes fraud.
"Synthetic" vs. "Simulant"
This is a crucial distinction. A lab-grown diamond is a synthetic diamond, meaning it is chemically a real diamond created by humans.
A simulant, like cubic zirconia or moissanite, is a different material entirely that only looks like a diamond. Lab-grown diamonds are not simulants; they are physically and chemically diamonds.
How to Navigate the Diamond Market Safely
Your goal determines how you should apply this information to ensure a safe and transparent transaction.
- If your primary focus is buying a diamond: Always demand a grading report from a reputable, independent laboratory that explicitly states the diamond's origin as either "Natural" or "Laboratory-Grown."
- If your primary focus is selling jewelry: Adhere strictly to FTC guidelines for disclosure. Using clear, approved terminology builds customer trust and protects you from serious legal liability.
- If your primary focus is understanding the industry: Recognize that the value of lab-grown diamonds is driven by technology and production costs, while the value of natural diamonds is tied to market-controlled rarity and geology.
By understanding that the debate is about transparency, not legality, you can confidently navigate the modern diamond market.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Status/Requirement |
|---|---|
| Production Legality | Legal and technologically advanced |
| Primary Regulation Focus | Consumer protection and transparent selling |
| Key Regulatory Body (US) | Federal Trade Commission (FTC) |
| Required Disclosure Terms | "Laboratory-grown," "laboratory-created" |
| Prohibited Terms | "Real," "genuine," "natural" (when used alone) |
| Critical Verification | Independent grading report (e.g., GIA, IGI) |
Ensure your laboratory operations are supported by equipment you can trust.
Whether you are involved in research, quality control, or material synthesis, having reliable and precise tools is fundamental. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to meet the rigorous demands of modern laboratories.
Let us help you achieve precision and efficiency in your work. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can support your specific projects and enhance your lab's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the fluorescence of a CVD diamond? A Guide to Its Unique Glow and Purpose
- What is the future value of lab grown diamond? Understanding Its Depreciating Financial Worth
- What are the common sources of contamination during CVD diamond growth? Improve Purity and Quality Control
- What is the difference between CVD and original diamond? Choose the Right Diamond for Your Needs
- What is the main difference between CVD and natural diamond? Origin, Purity, and Value Explained



















