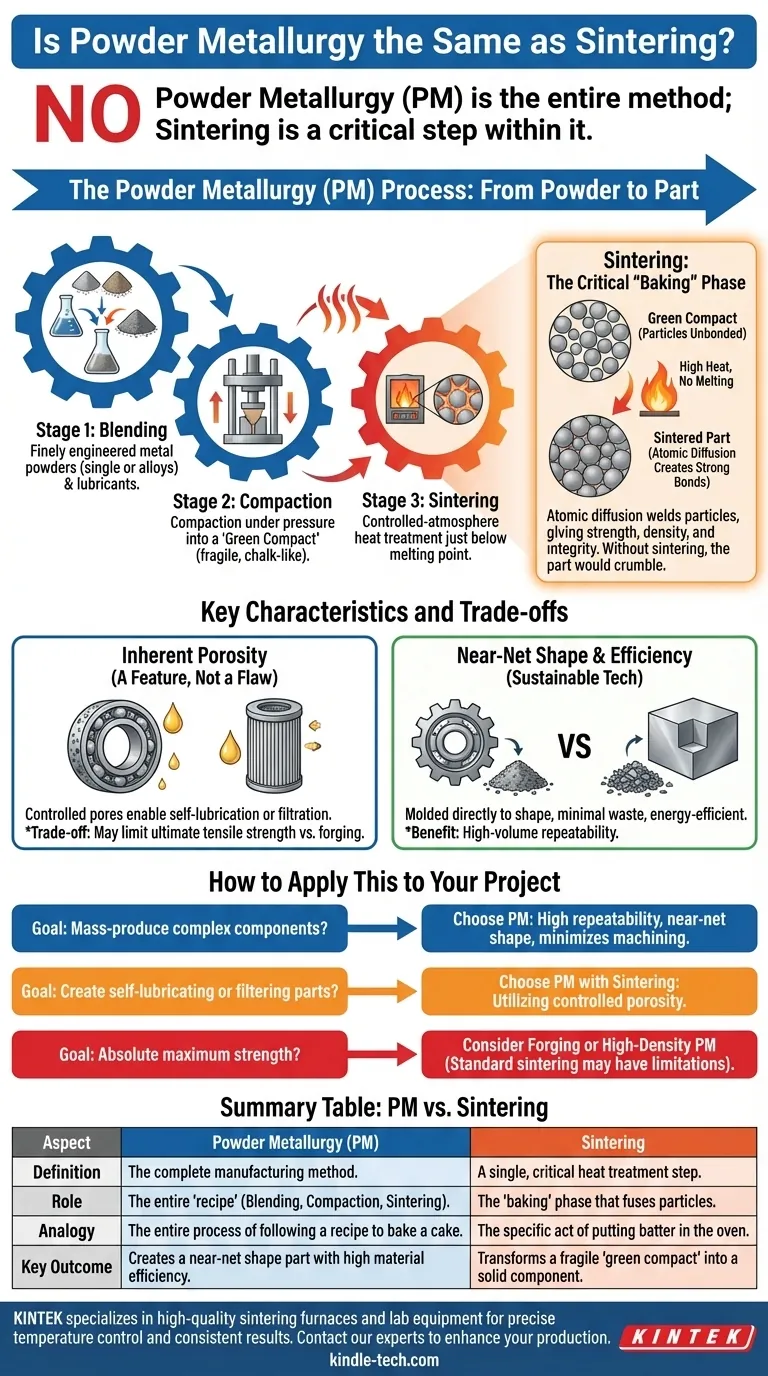
In short, no. Powder metallurgy is the name for the entire manufacturing method, while sintering is a single, critical heat treatment step within that method. To put it simply, powder metallurgy is the complete recipe for creating a metal part from powder, and sintering is the specific act of "baking" it to give it strength.
Sintering is not a process separate from powder metallurgy; it is the essential thermal stage that transforms a compacted powder into a solid, functional component. You cannot have modern powder metallurgy without sintering.
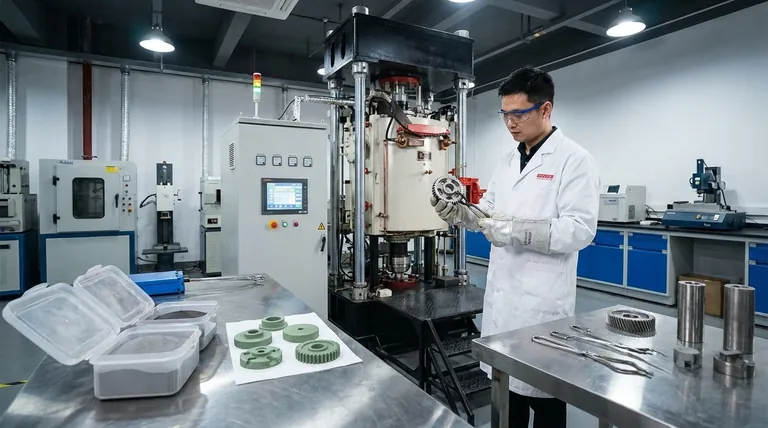

The Powder Metallurgy Process: From Powder to Part
To understand the relationship, it helps to see the entire powder metallurgy (PM) workflow. It is a precise, multi-stage process used to create "near-net shape" parts, which require little to no finish machining.
Stage 1: Blending
The process begins not with a solid block of metal, but with finely engineered metal powders. These powders can be a single metal or a blend of different alloys and lubricants designed to achieve specific final properties.
Stage 2: Compaction
Next, the blended powder is poured into a high-precision die. A powerful press then compacts the powder under immense pressure into the desired shape. The resulting piece is called a "green compact." It holds its shape but is fragile, similar in consistency to a piece of chalk.
Stage 3: Sintering
This is the decisive step. The green compact is moved into a controlled-atmosphere furnace and heated to a temperature just below the melting point of the primary metal. The heat causes the individual powder particles to bond and fuse together on an atomic level, a process called diffusion.
Why Sintering Is the Critical Bonding Phase
Sintering is where a fragile powder form gains the strength and integrity of a solid metal part. Without it, the green compact would simply crumble.
The Science of Fusing Without Melting
Sintering does not melt the metal. Instead, the high temperature provides the energy for atoms to move across the surfaces of the powder particles. This atomic diffusion creates strong metallurgical bonds, effectively welding the particles together and dramatically reducing the voids between them.
The Result: Strength and Integrity
This bonding process is what gives the final component its density, hardness, and mechanical strength. It transforms the part from a delicate green compact into a robust, work-ready component suitable for demanding applications like automotive gears, valve seats, and cutting tools.
Understanding the Key Characteristics and Trade-offs
Powder metallurgy, with sintering at its core, offers a unique set of advantages and considerations compared to other manufacturing methods like casting or forging.
Inherent Porosity: A Feature, Not a Flaw
The sintering process leaves behind microscopic pores. This controlled porosity is a major advantage for certain applications. It allows parts like bearings to be impregnated with oil for self-lubrication or used to create highly effective metal filters.
However, this same porosity means a standard PM part may not achieve the same ultimate tensile strength or impact resistance as a fully dense, forged component.
Near-Net Shape and Material Efficiency
Because parts are molded directly into complex shapes, PM is a "green" or sustainable technology. It produces very little waste material compared to subtractive methods like machining, which start with a large block and cut material away. This also reduces energy consumption, as the metal is never fully melted.
High-Volume Repeatability
Once the initial tooling (the die) is created, the PM process can produce millions of highly consistent parts with excellent dimensional accuracy. This makes it extremely cost-effective for large production runs common in the automotive industry.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Understanding the distinction between the overall PM process and the sintering step helps you choose the right manufacturing solution for your goal.
- If your primary focus is mass-producing complex components: Powder metallurgy is an exceptional choice for its high repeatability and ability to create near-net shapes, which minimizes costly secondary machining.
- If your primary focus is creating self-lubricating or filtering parts: The inherent and controllable porosity achieved through the sintering stage makes PM the ideal and often only viable technology.
- If your primary focus is absolute maximum strength and fatigue resistance: You may need to consider forging or specialized high-density PM techniques, as the residual porosity in standard sintered parts can be a limiting factor.
By recognizing that sintering is the metallurgical heart of the powder metallurgy process, you can better leverage its distinct capabilities to solve your engineering challenges.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Powder Metallurgy (PM) | Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The complete manufacturing method for creating parts from metal powder. | A single, critical heat treatment step within the PM process. |
| Role | The entire "recipe," including blending, compaction, and sintering. | The "baking" phase that fuses powder particles to give the part strength. |
| Analogy | The entire process of following a recipe to bake a cake. | The specific act of putting the batter in the oven to bake. |
| Key Outcome | Creates a near-net shape part with high material efficiency. | Transforms a fragile "green compact" into a solid metal component. |
Need a robust, cost-effective solution for your metal components?
Understanding the nuances of powder metallurgy and sintering is key to selecting the right manufacturing process for your application. Whether you're mass-producing complex parts, creating self-lubricating bearings, or exploring material-efficient solutions, the right equipment is crucial.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality sintering furnaces and lab equipment that provide the precise temperature control and consistent results your projects demand. Our expertise helps you leverage the full benefits of powder metallurgy, from material efficiency to high-volume repeatability.
Let's discuss how our solutions can enhance your production: Contact our experts today to find the perfect equipment for your laboratory or manufacturing needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Horizontal High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the necessity of using a laboratory drying oven for Mo-Ti-N catalysts? Protect Your Porous Architecture
- Why is it necessary to preheat silica particles? Master the Prep for Defect-Free Zinc Alloy Composites
- Can iron evaporate? Discover the Extreme Science Behind Gaseous Metals
- How do you convert pyrolysis oil to diesel? A Guide to Hydrodeoxygenation (HDO)
- Why is biochar production a carbon-neutral process? It's Actually a Powerful Carbon-Negative Tool
- Is pyrolysis good or bad? A Balanced Look at the Waste-to-Energy Solution
- Why are ultrasonic cleaners or homogenizers required for electrocatalyst inks? Ensure Uniform Dispersion Today
- What is an example of an alloy? Discover the Engineered Materials Shaping Our World



















