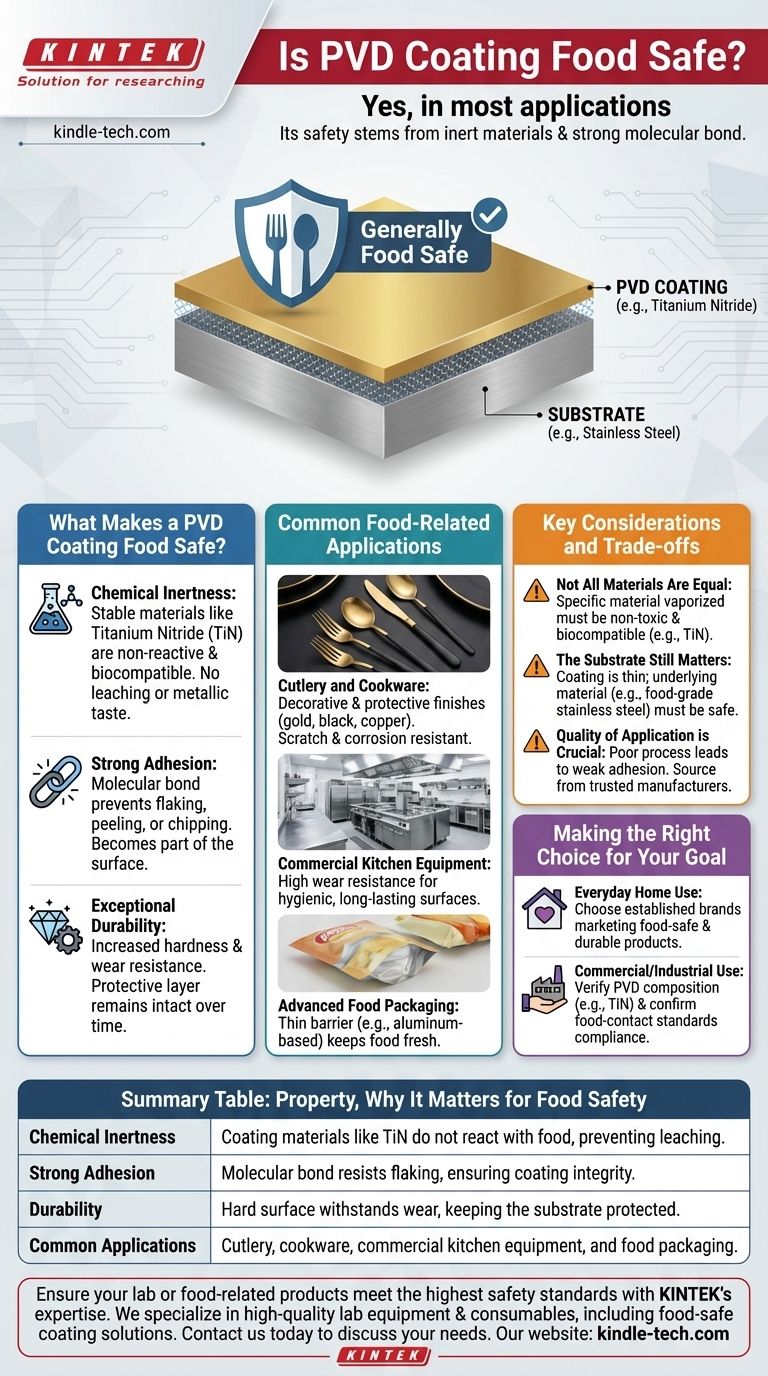
Yes, in most applications, PVD coating is considered food safe. Its safety stems from two key factors: the materials used for the coating are typically chemically and biologically inert, and the coating process creates an extremely strong bond with the underlying material, making it highly resistant to flaking or wearing off.
The food safety of a PVD-coated product depends less on the process itself and more on the specific materials used for the coating and the quality of its application. When food-grade materials like titanium nitride are used, the resulting surface is non-reactive, durable, and does not leach into food.

What Makes a PVD Coating Food Safe?
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a finishing technique that molecularly bonds a thin film to a surface. Several properties of this process contribute directly to its suitability for food-contact items.
The Principle of Chemical Inertness
The most common materials used for decorative and functional PVD coatings, such as titanium nitride (TiN), are chosen for their stability.
These materials are chemically inert and biocompatible, meaning they do not react with acids, alkalis, or other compounds found in food. This prevents any metallic taste or harmful substances from leaching out.
The Importance of Strong Adhesion
The PVD process creates a powerful, molecular-level bond between the thin coating and the substrate material (typically stainless steel).
This exceptional adhesion ensures the coating does not chip, peel, or flake off during normal use, even with cutting and scraping. The coating effectively becomes part of the surface.
Exceptional Durability and Wear Resistance
PVD coatings significantly increase the hardness and wear resistance of the surface.
This durability means the protective layer remains intact over time, preventing the underlying metal from being exposed and ensuring the inert surface is what consistently comes into contact with food.
Common Food-Related Applications
The unique combination of safety and durability has made PVD a trusted coating in both consumer and commercial food industries.
Cutlery and Cookware
PVD is widely used to apply decorative and protective finishes to cutlery, providing colors like gold, black, or copper. The coating protects against scratches and corrosion while remaining entirely food safe.
Commercial Kitchen Equipment
In high-use commercial kitchens, PVD-coated components are valued for their resistance to wear and tear. The coating extends the life of equipment and maintains a hygienic, easy-to-clean surface.
Advanced Food Packaging
PVD is also used in food packaging. A thin, aluminum-based PVD coating on plastic film, for example, creates a barrier that keeps snacks fresh without directly contacting the food in a way that poses a risk.
Key Considerations and Trade-offs
While generally safe, the final safety of a PVD-coated product is not automatic. It depends entirely on the materials and the quality of the manufacturing process.
Not All Coating Materials Are Equal
The term "PVD" describes the process, not a single material. For a product to be food safe, the specific material vaporized and deposited onto the surface must be non-toxic and biocompatible, like titanium nitride.
The Substrate Still Matters
PVD is a very thin coating, often just a few microns thick. The safety of the final product also relies on the underlying material, or substrate. Reputable manufacturers apply PVD coatings to high-quality, food-grade stainless steel.
Quality of Application is Crucial
A poorly executed PVD process can result in weak adhesion or an uneven coating. This could compromise the integrity of the surface, which is why it's critical to source PVD-coated products from trusted manufacturers who adhere to quality control standards.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When evaluating a PVD-coated product for food contact, your decision should be guided by its intended use and the reputation of its manufacturer.
- If your primary focus is everyday home use (e.g., cutlery): Choose products from established brands that explicitly market their items as food-safe and durable.
- If your primary focus is commercial or industrial applications: Verify the specific composition of the PVD coating (e.g., TiN) and confirm that it meets industry food-contact safety standards.
Ultimately, a well-made PVD coating using the right materials offers a safe, durable, and reliable surface for food applications.
Summary Table:
| Property | Why It Matters for Food Safety |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Coating materials like TiN do not react with food, preventing leaching. |
| Strong Adhesion | Molecular bond resists flaking, ensuring coating integrity. |
| Durability | Hard surface withstands wear, keeping the substrate protected. |
| Common Applications | Cutlery, cookware, commercial kitchen equipment, and food packaging. |
Ensure your lab or food-related products meet the highest safety standards with KINTEK's expertise. We specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including solutions that leverage durable, food-safe coatings for reliable performance. Whether you're in R&D or production, our team can help you select the right materials and equipment to ensure compliance and durability. Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory and food safety goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are diamond coated films? Enhance Materials with Super-Hard, Transparent Layers
- How are tools coated with diamond? Achieve Superior Hardness and Low Friction for Your Tools
- Is diamond coating permanent? The Truth About Its Long-Lasting Durability
- What is the process of CVD diamond coating? Grow a Superior, Chemically-Bonded Diamond Layer
- What is CVD diamond coating? Grow a Super-Hard, High-Performance Diamond Layer



















