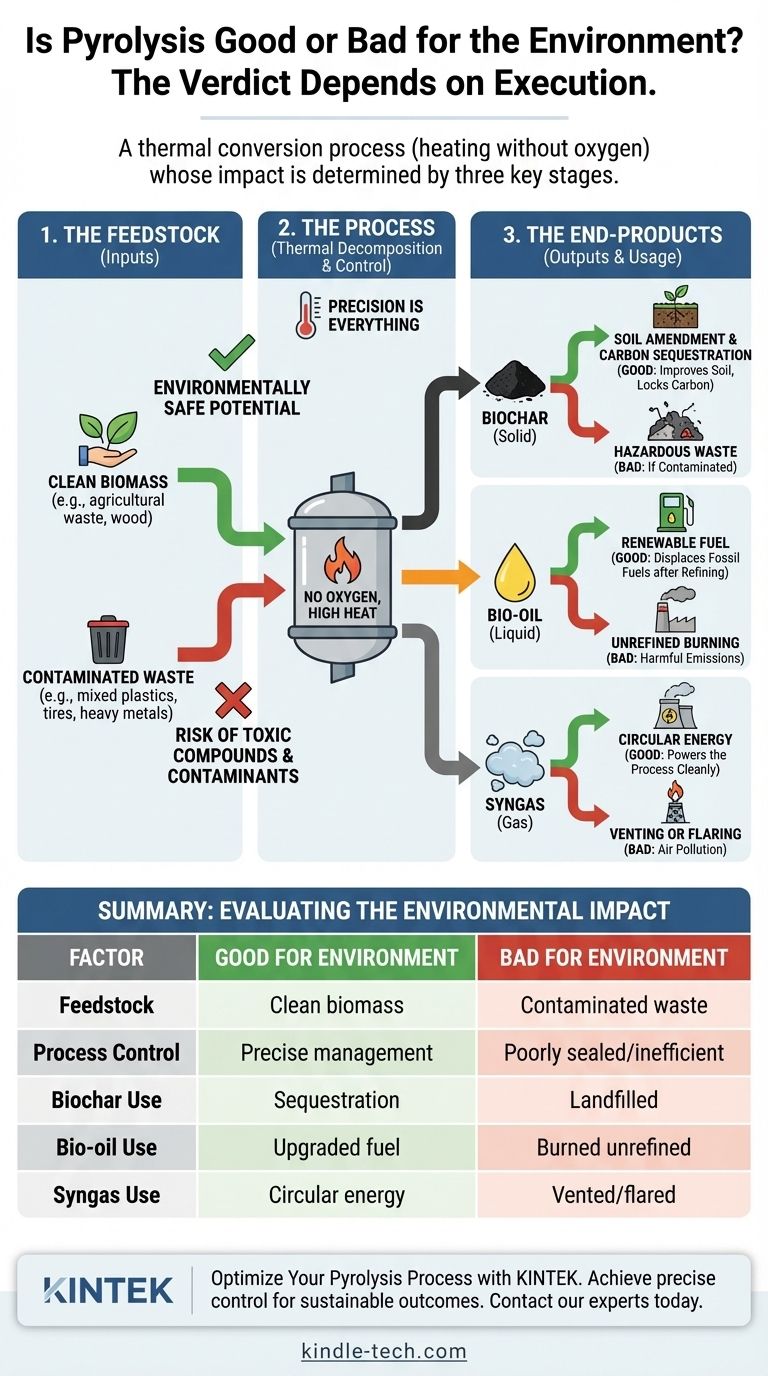
Ultimately, pyrolysis is neither inherently good nor bad for the environment. It is a sophisticated thermal conversion process, and its environmental impact depends entirely on the specific application. The key variables are the material being processed (feedstock), the precise control of the process conditions, and the final use or disposal of its products.
The environmental value of pyrolysis is not found in the process itself, but in how meticulously its inputs, operational parameters, and outputs are managed. Viewing it as a simple "good" or "bad" solution overlooks the critical details that determine its net benefit or harm.

How Pyrolysis Works
Not Burning, but Thermal Decomposition
Pyrolysis is the process of heating organic materials, like biomass, plastics, or tires, to high temperatures in an environment with little to no oxygen.
The absence of oxygen is critical. It prevents combustion (burning) and instead causes the complex molecules in the material to break down into simpler, smaller molecules.
A Spectrum of Outputs
The specific conditions of the pyrolysis process—primarily temperature and heating speed—determine the mix of products. The references show a clear relationship:
- Slow, low-temperature pyrolysis (<450°C) primarily yields a solid, carbon-rich material called biochar.
- Fast, moderate-temperature pyrolysis favors the production of a liquid known as bio-oil or pyrolysis oil.
- Very fast, high-temperature pyrolysis (>800°C) maximizes the output of non-condensable gases, collectively known as syngas.
The Factors Defining its Environmental Impact
The "good vs. bad" question can only be answered by examining three distinct stages of the process.
1. The Feedstock: What Goes In Matters
The "garbage in, garbage out" principle applies perfectly to pyrolysis. The composition of the starting material is the single most important factor.
Processing clean, homogenous feedstock like agricultural waste or untreated wood is relatively straightforward and environmentally safe.
Processing mixed municipal solid waste, plastics containing chlorine (like PVC), or tires can be problematic. Contaminants like heavy metals and chlorine do not disappear; they are concentrated in the biochar or can form highly toxic compounds like dioxins if the process is not managed with extreme precision.
2. The Process: Precision is Everything
A well-controlled pyrolysis unit is a sophisticated chemical reactor. A poorly controlled one can be a source of pollution.
The residence time (how long material stays in the hot zone) and temperature dictate the efficiency of the conversion. Inefficient conversion can leave behind partially pyrolyzed material and create a complex, difficult-to-handle mix of outputs.
Proper gas handling is also vital. The syngas produced must either be combusted cleanly to power the process or scrubbed of contaminants before any release.
3. The End-Products: Closing the Loop or Creating a New Problem
The final destination of the biochar, bio-oil, and syngas determines the net environmental benefit.
- Biochar: When used as a soil amendment, biochar can improve soil health and act as a highly stable form of carbon sequestration, effectively removing carbon from the atmosphere for centuries. This is a clear environmental good. If contaminated and landfilled, it's simply a new form of waste.
- Bio-oil: This liquid can be refined and upgraded into transportation fuels or used to generate heat and power, displacing fossil fuels. This is an environmental good. However, burning unrefined bio-oil can release harmful emissions, and it often requires significant energy to upgrade.
- Syngas: This mix of hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and other gases can be used as fuel to make the pyrolysis process self-sustaining. This circular use of energy is an environmental good. Venting or flaring it without proper controls is an environmental bad.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Pyrolysis is a powerful tool, but it is not without significant challenges that must be professionally managed.
Risk of Air Pollution
If the process is not completely sealed or the syngas is not managed correctly, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), carbon monoxide, and other pollutants can escape. Combustion of the outputs (syngas or bio-oil) without proper flue gas treatment can also release NOx, SOx, and particulate matter.
Concentration of Contaminants
Pyrolysis is excellent for reducing waste volume, but it also concentrates non-organic contaminants. Heavy metals (like lead and mercury) from electronics or painted wood will become concentrated in the solid biochar, which may then be classified as hazardous waste requiring specialized disposal.
Energy Balance
A pyrolysis plant can be a net energy consumer if not designed and operated efficiently. The energy required to dry the feedstock and heat the reactor can sometimes exceed the energy value of the bio-oil and syngas it produces, negating its benefit as a waste-to-energy solution.
How to Evaluate a Pyrolysis Solution
To determine if a specific pyrolysis project is environmentally beneficial, you must ask the right questions.
- If your primary focus is carbon sequestration: Your goal is to maximize stable biochar from clean, sustainable biomass through slow pyrolysis.
- If your primary focus is renewable fuel: You need a fast pyrolysis system optimized for bio-oil, coupled with a clear, energy-efficient plan for upgrading that oil into a usable product.
- If your primary focus is waste-to-energy: Your system must be optimized for syngas production and use that gas with maximum efficiency to generate heat or electricity on-site.
- If your primary focus is waste volume reduction: You must have a complete plan for the safe and beneficial use or disposal of all three outputs—biochar, bio-oil, and syngas—to ensure you are not just converting a solid waste problem into a liquid and air pollution problem.
Understanding and controlling these variables is the only way to ensure pyrolysis serves as an environmentally positive technology.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Good for Environment | Bad for Environment |
|---|---|---|
| Feedstock | Clean biomass, agricultural waste | Contaminated plastics, mixed waste |
| Process Control | Precise temperature & gas management | Poorly sealed, inefficient conversion |
| Biochar Use | Soil amendment, carbon sequestration | Landfilled as hazardous waste |
| Bio-oil Use | Upgraded to renewable fuel | Burned unrefined, releasing emissions |
| Syngas Use | Powers process, circular energy | Vented or flared without controls |
Optimize Your Pyrolysis Process with KINTEK
Harnessing pyrolysis for environmental benefit requires precision and expertise. KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables that enable precise control over pyrolysis conditions, from feedstock preparation to final product analysis. Whether your goal is carbon sequestration, renewable fuel production, or efficient waste-to-energy conversion, our solutions help you:
- Achieve precise thermal control for consistent, high-quality biochar, bio-oil, or syngas output.
- Analyze feedstock and outputs to ensure process efficiency and environmental safety.
- Scale your operations with reliable equipment designed for laboratory research and pilot projects.
Ready to develop a sustainable pyrolysis solution? Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's specialized lab equipment can support your environmental goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- What is the role of a quartz tube in the preparation of Mo2Ga2C powder precursors? Essential Synthesis Benefits
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing



















