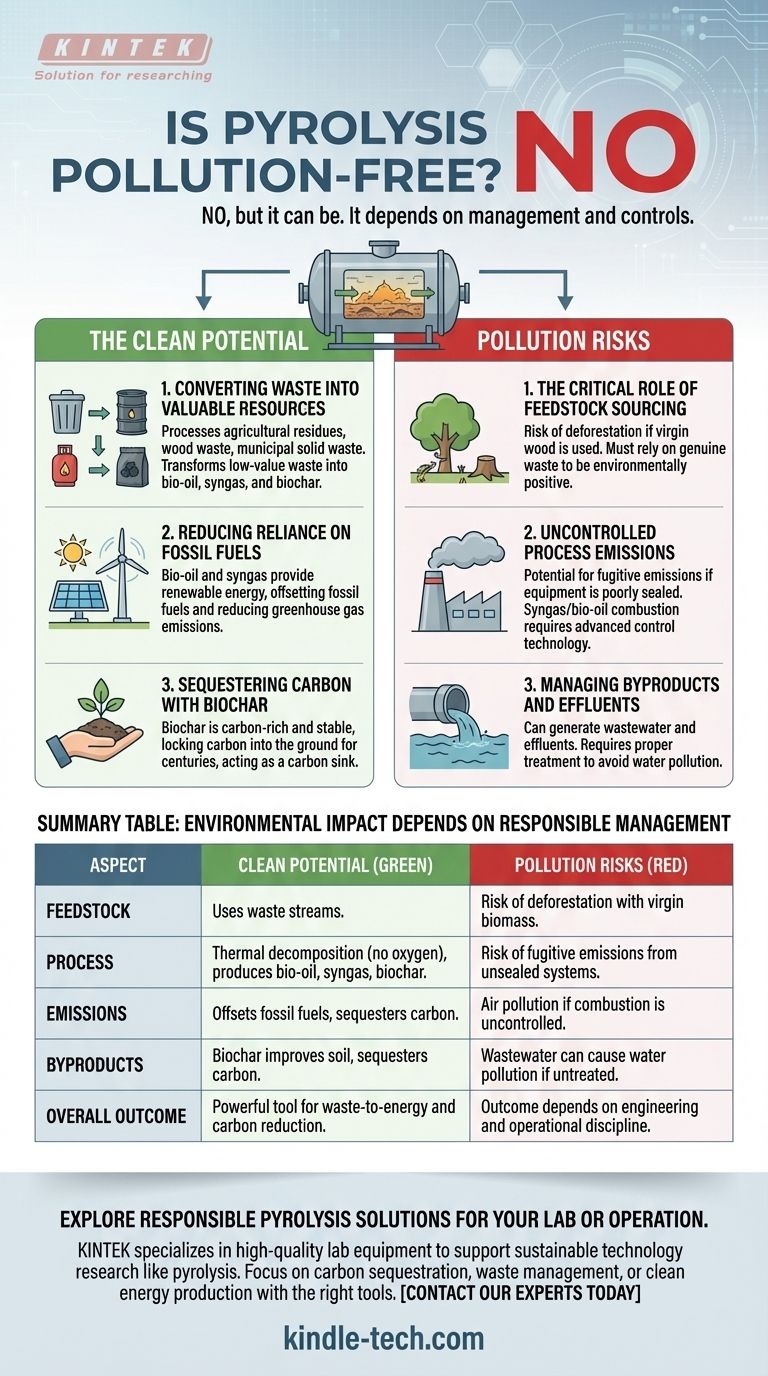
No, pyrolysis is not inherently pollution-free. While it represents a significant environmental improvement over processes like incineration and can produce clean energy from waste, its overall impact is highly dependent on the system's design, the source of its materials, and the strictness of its operational controls.
The core issue is one of management, not fundamental technology. Pyrolysis is a powerful tool that can convert waste into clean energy and sequester carbon, but like any industrial process, it can become a source of pollution if managed irresponsibly.

The "Clean" Potential of Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is fundamentally a process of thermal decomposition in the absence of oxygen. This distinction is what gives it significant environmental advantages over simply burning waste.
Converting Waste into Valuable Resources
Pyrolysis provides a method to process materials that would otherwise end up in a landfill, such as agricultural residues, wood waste, and even municipal solid waste.
This process transforms low-value waste into high-value products, including bio-oil, syngas, and biochar.
Reducing Reliance on Fossil Fuels
The bio-oil and syngas produced during pyrolysis can be used as fuel for heat and power generation. This creates a source of renewable energy from waste streams.
By offsetting the need for coal, oil, or natural gas, this process helps reduce the significant pollution and greenhouse gas emissions associated with burning fossil fuels.
Sequestering Carbon with Biochar
The solid, carbon-rich byproduct of pyrolysis is called biochar. When added to soil, biochar is extremely stable and resists decomposition for hundreds or thousands of years.
This effectively locks carbon into the ground, acting as a carbon sink and removing it from the atmosphere. This potential for carbon sequestration is a major environmental benefit.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pollution Risks
The potential for pyrolysis to be a "clean" technology is conditional. Poor practices at any stage can undermine its benefits and create new environmental problems.
The Critical Role of Feedstock Sourcing
The single greatest risk is the source of the biomass (feedstock). If pyrolysis plants drive demand for virgin wood, it can lead to deforestation and habitat destruction.
To be environmentally positive, the process must rely on genuine waste products like crop residues, forestry byproducts, or post-consumer waste.
Uncontrolled Process Emissions
While pyrolysis itself occurs in a sealed, oxygen-free environment, the system is not perfectly closed. There is a risk of fugitive emissions if the equipment is not properly sealed and maintained.
Furthermore, the handling and combustion of the resulting syngas and bio-oil must be managed with modern emissions control technology to prevent the release of pollutants into the atmosphere.
Managing Byproducts and Effluents
The process can also generate liquid effluents or require water for cooling and cleaning. This wastewater must be treated properly to avoid becoming a source of water pollution.
The responsible management of all outputs—not just the valuable ones—is essential to the system's overall environmental performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The environmental success of pyrolysis is not guaranteed by the technology itself but by the integrity of the entire operation, from sourcing to final output.
- If your primary focus is maximum carbon reduction: Prioritize systems that use sustainable waste feedstock and are optimized for high-quality biochar production for sequestration.
- If your primary focus is waste management: Focus on the efficiency of converting low-value municipal or agricultural waste streams into high-density fuels like bio-oil.
- If your primary focus is clean energy production: Ensure the system includes state-of-the-art gas cleanup and combustion technology to minimize air emissions.
Ultimately, the environmental outcome of a pyrolysis project depends entirely on responsible engineering, sustainable sourcing, and rigorous operational discipline.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Clean Potential | Pollution Risks |
|---|---|---|
| Feedstock | Uses agricultural residues, wood waste, and municipal solid waste. | Risk of deforestation if using virgin wood instead of waste. |
| Process | Thermal decomposition without oxygen; produces bio-oil, syngas, and biochar. | Risk of fugitive emissions from poorly sealed or maintained equipment. |
| Emissions | Syngas/bio-oil can offset fossil fuels, reducing greenhouse gases. Biochar sequesters carbon. | Air pollution if syngas/bio-oil combustion is not properly controlled. |
| Byproducts | Biochar can improve soil and sequester carbon long-term. | Wastewater and other effluents can cause water pollution if not treated. |
| Overall Outcome | A powerful tool for waste-to-energy and carbon reduction. | Outcome depends entirely on responsible management and engineering. |
Ready to explore responsible pyrolysis solutions for your laboratory or operation?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables to support research and development in sustainable technologies like pyrolysis. Whether you are focused on carbon sequestration, waste management, or clean energy production, having the right tools is the first step toward achieving your environmental goals.
Contact our experts today via our contact form to discuss how our equipment can help you design, monitor, and optimize your processes for maximum efficiency and minimal environmental impact.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy



















